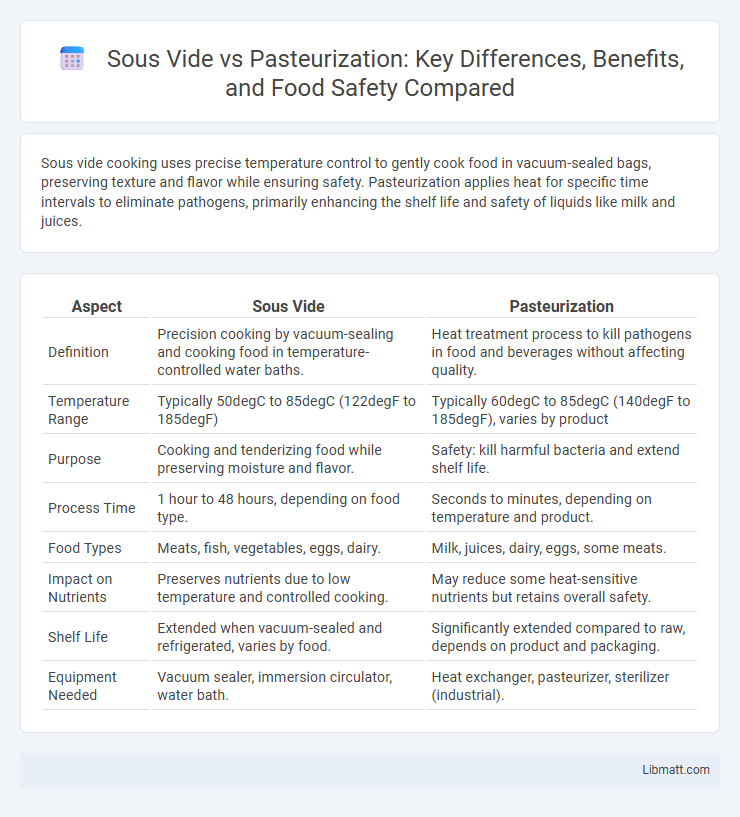
Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control to gently cook food in vacuum-sealed bags, preserving texture and flavor while ensuring safety. Pasteurization applies heat for specific time intervals to eliminate pathogens, primarily enhancing the shelf life and safety of liquids like milk and juices.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Pasteurization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Precision cooking by vacuum-sealing and cooking food in temperature-controlled water baths. | Heat treatment process to kill pathogens in food and beverages without affecting quality. |
| Temperature Range | Typically 50degC to 85degC (122degF to 185degF) | Typically 60degC to 85degC (140degF to 185degF), varies by product |
| Purpose | Cooking and tenderizing food while preserving moisture and flavor. | Safety: kill harmful bacteria and extend shelf life. |
| Process Time | 1 hour to 48 hours, depending on food type. | Seconds to minutes, depending on temperature and product. |
| Food Types | Meats, fish, vegetables, eggs, dairy. | Milk, juices, dairy, eggs, some meats. |
| Impact on Nutrients | Preserves nutrients due to low temperature and controlled cooking. | May reduce some heat-sensitive nutrients but retains overall safety. |
| Shelf Life | Extended when vacuum-sealed and refrigerated, varies by food. | Significantly extended compared to raw, depends on product and packaging. |
| Equipment Needed | Vacuum sealer, immersion circulator, water bath. | Heat exchanger, pasteurizer, sterilizer (industrial). |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Pasteurization
Sous vide is a precision cooking technique that involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a water bath at a consistent, low temperature to ensure even doneness and retain moisture. Pasteurization, developed by Louis Pasteur, is a heat treatment process that kills harmful bacteria in liquids like milk and juices by heating them to specific temperatures for set times. Both methods rely on controlled heat application but serve distinct purposes: sous vide for culinary perfection and pasteurization for food safety.
How Sous Vide Works
Sous Vide works by vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath at low temperatures for extended periods, ensuring even heat distribution and preventing overcooking. This method maintains optimal texture and flavor while safely eliminating harmful bacteria through consistent temperature control. Your meals benefit from enhanced tenderness and juiciness without the nutrient loss often caused by traditional pasteurization.
Understanding Pasteurization
Pasteurization is a heat treatment process that kills harmful microorganisms in food and beverages by exposing them to precise temperatures for a specified duration, ensuring safety and extending shelf life. This method typically involves heating liquids like milk or juice to around 72degC (161degF) for 15 seconds in high-temperature short-time (HTST) pasteurization. Unlike sous vide, pasteurization aims primarily for microbial safety rather than cooking food to a desired texture or flavor.
Key Differences Between Sous Vide and Pasteurization
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it at precise, low temperatures for extended periods to retain flavor and texture, while pasteurization refers to heat treatment aimed at killing pathogens by using higher temperatures for shorter times. Sous vide maintains food quality through controlled heating, often between 50degC and 65degC, whereas pasteurization typically requires temperatures above 72degC for rapid microbial inactivation. The key differences lie in their purpose--culinary enhancement versus safety assurance--and the temperature-time combinations used for processing.
Temperature and Time Comparison
Sous vide cooking typically uses precise temperatures between 125degF to 195degF (52degC to 90degC) for extended periods ranging from 1 to 48 hours, targeting texture and flavor enhancement while ensuring food safety. Pasteurization involves higher temperatures, usually above 140degF (60degC), for shorter durations like 15 to 30 minutes to eliminate pathogens rapidly and increase shelf life. Understanding your cooking goals helps determine whether the controlled low-temperature, long-time approach of sous vide or the shorter high-temperature process of pasteurization is more suitable.
Effects on Food Safety
Sous vide cooking maintains precise temperature control, effectively killing pathogens by holding food at pasteurization temperatures for extended periods, enhancing food safety without overcooking. Pasteurization, commonly used in dairy and liquid products, relies on short high-temperature treatments to eliminate harmful microorganisms quickly. Both methods prioritize reducing microbial contamination, but sous vide provides additional advantages by combining heat with vacuum sealing, limiting oxygen exposure and preventing spoilage.
Impact on Flavor and Texture
Sous vide cooking gently heats food to precise temperatures, preserving natural juices and enhancing flavor complexity while maintaining tender, even texture. Pasteurization, primarily designed for safety, uses higher heat that can alter taste profiles and firm textures by denaturing proteins more extensively. Your choice between these methods affects whether the food retains subtle flavors and delicate textures or prioritizes microbial safety with a firmer bite.
Nutrient Retention: Sous Vide vs Pasteurization
Sous vide cooking preserves nutrients more effectively than traditional pasteurization by using lower, controlled temperatures and vacuum-sealed environments that minimize nutrient loss. Pasteurization, which typically involves higher heat for short periods, can degrade sensitive vitamins such as vitamin C and B-complex vitamins more extensively. Studies indicate sous vide maintains up to 90% of water-soluble vitamins, whereas pasteurization may retain only about 70-80%, impacting overall nutritional value.
Best Uses for Each Method
Sous vide excels in precise temperature control for cooking delicate foods such as fish, eggs, and tender meats, ensuring optimal texture and flavor retention. Pasteurization is best suited for liquid products like milk, juice, and eggs, effectively eliminating harmful pathogens while preserving nutritional quality. Each method serves unique purposes: sous vide for culinary applications requiring gentle cooking, and pasteurization for food safety and extended shelf life of consumables.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Sous vide offers precise temperature control ideal for tenderizing meats and preserving nutrients, while pasteurization ensures food safety by eliminating harmful pathogens through higher heat exposure. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize flavor and texture enhancement or strict microbial safety. Understanding the specific requirements of your food preparation goals will help determine the most effective method.
Sous Vide vs Pasteurization Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com