Vegan gelatin, derived from plant-based sources like agar-agar or carrageenan, offers a cruelty-free and environmentally sustainable alternative to traditional animal gelatin made from collagen in animal bones and skin. Choosing vegan gelatin supports ethical consumption and is suitable for those with dietary restrictions or allergies associated with animal products.
Table of Comparison
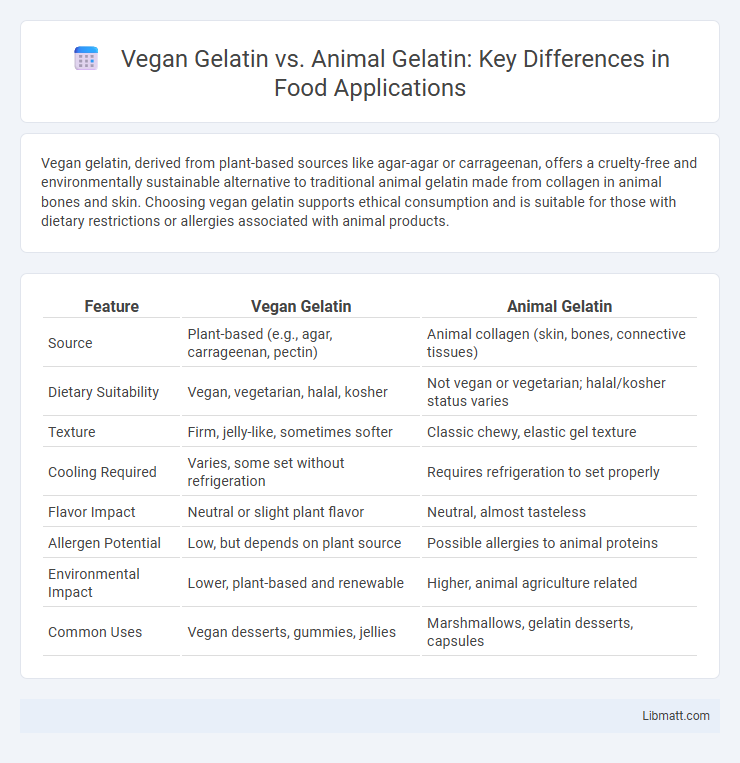
| Feature | Vegan Gelatin | Animal Gelatin |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant-based (e.g., agar, carrageenan, pectin) | Animal collagen (skin, bones, connective tissues) |
| Dietary Suitability | Vegan, vegetarian, halal, kosher | Not vegan or vegetarian; halal/kosher status varies |
| Texture | Firm, jelly-like, sometimes softer | Classic chewy, elastic gel texture |
| Cooling Required | Varies, some set without refrigeration | Requires refrigeration to set properly |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral or slight plant flavor | Neutral, almost tasteless |
| Allergen Potential | Low, but depends on plant source | Possible allergies to animal proteins |
| Environmental Impact | Lower, plant-based and renewable | Higher, animal agriculture related |
| Common Uses | Vegan desserts, gummies, jellies | Marshmallows, gelatin desserts, capsules |
Understanding Gelatin: Vegan vs Animal Sources
Gelatin derived from animal sources is a protein obtained by boiling the skin, bones, and connective tissues of animals like pigs and cows, commonly used for its gelling properties in food products. Vegan gelatin alternatives, such as agar-agar, carrageenan, and pectin, come from plant-based sources like seaweed and fruits, providing similar texture without animal-derived ingredients. Understanding these distinctions helps you make informed choices aligned with dietary preferences and ethical considerations.
Key Differences Between Vegan and Animal Gelatin
Vegan gelatin is derived from plant-based sources such as agar-agar, carrageenan, or pectin, while animal gelatin is made from collagen extracted from the bones, skin, and connective tissues of animals. The key differences between vegan and animal gelatin include their source, dietary restrictions, and environmental impact, with vegan gelatin being suitable for vegetarians and vegans and offering a more sustainable alternative. Your choice between the two can affect the texture and gelling properties in recipes, as animal gelatin typically provides a firmer set compared to most plant-based options.
Common Ingredients in Vegan Gelatin
Common ingredients in vegan gelatin typically include agar-agar, derived from red seaweed, carrageenan extracted from Irish moss, and pectin found in fruit skins. These plant-based compounds provide similar gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties as animal gelatin without the use of animal products. Your recipes can achieve a comparable texture and consistency while remaining suitable for vegan and vegetarian diets.
Health Benefits of Vegan Gelatin
Vegan gelatin, derived from plant-based sources like agar-agar or carrageenan, offers significant health benefits compared to animal gelatin, including lower cholesterol and saturated fat content. It is rich in dietary fiber and promotes digestive health while reducing the risk of allergic reactions associated with animal-derived gelatin. Furthermore, vegan gelatin supports a cruelty-free lifestyle and is free from hormones or antibiotics often present in animal gelatin.
Nutritional Comparison: Vegan vs Animal Gelatin
Vegan gelatin, typically derived from sources like agar-agar, carrageenan, or pectin, offers a fiber-rich, cholesterol-free alternative to animal gelatin, which is protein-dense and contains collagen peptides essential for skin, joint, and bone health. While animal gelatin provides amino acids such as glycine and proline that support connective tissue repair, vegan gelatin lacks these proteins but compensates with antioxidants and plant-based nutrients beneficial for digestion. Nutritionally, animal gelatin is superior in promoting bone and joint benefits, whereas vegan gelatin aligns with heart health goals due to its absence of saturated fats and cholesterol.
Allergen and Dietary Considerations
Vegan gelatin, derived from plant-based sources such as agar-agar, carrageenan, or pectin, offers a hypoallergenic alternative to animal gelatin, which is often sourced from bovine or porcine collagen and can trigger allergies in sensitive individuals. Vegan gelatin supports dietary preferences including vegan, vegetarian, halal, and kosher diets since it contains no animal products, while animal gelatin is unsuitable for these dietary restrictions. The absence of animal-derived proteins in vegan gelatin also eliminates concerns related to transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), making it a safer choice for those with specific health considerations.
Environmental Impact of Gelatin Production
Vegan gelatin, derived from plant sources such as agar-agar, carrageenan, or pectin, significantly reduces environmental impact compared to animal gelatin produced from collagen in livestock by-products. Animal gelatin production contributes to high greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and deforestation linked to livestock farming, whereas vegan alternatives rely on renewable, low-impact crops and generate minimal waste. Choosing vegan gelatin supports sustainability efforts by lowering carbon footprints and preserving biodiversity through reduced reliance on animal agriculture.
Culinary Uses of Vegan vs Animal Gelatin
Vegan gelatin, often derived from agar-agar, carrageenan, or pectin, excels in plant-based desserts, jellies, and vegan marshmallows where a firm yet clear gel is desired. Animal gelatin, sourced from collagen in animal bones and skin, is prized for its rich mouthfeel and is commonly used in traditional recipes like marshmallows, gummy candies, and panna cotta. Your choice between vegan and animal gelatin depends on culinary needs, with vegan options better suited for clean labeling and dietary restrictions, while animal gelatin offers superior texture in classic preparations.
Taste, Texture, and Performance in Recipes
Vegan gelatin, derived from sources like agar-agar or pectin, offers a subtle, neutral taste that blends seamlessly into your recipes without the slight animal-derived aftertaste found in traditional animal gelatin. Texturally, vegan gelatin provides a firmer, more consistent gel that holds up well at room temperature, while animal gelatin typically yields a softer, more elastic texture that melts quickly on the palate. In terms of performance, vegan gelatin excels in stability and can withstand higher cooking temperatures, making it ideal for plant-based desserts, whereas animal gelatin is prized for its melt-in-the-mouth quality and smooth finish in classic gelatin-based dishes.
Choosing the Right Gelatin for Your Lifestyle
Vegan gelatin, derived from plant-based sources like agar-agar, carrageenan, or pectin, offers a cruelty-free and environmentally sustainable alternative to traditional animal gelatin made from collagen in animal bones and skin. Selecting the right gelatin depends on your dietary preferences, allergies, and environmental values, with vegan options supporting a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle and providing similar gelling properties in recipes. Your choice affects texture and nutrition, so consider the source and intended use to align your gelatin with your overall wellness goals.
Vegan Gelatin vs Animal Gelatin Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com