Smart glass and electrochromic glass both offer dynamic control over light and privacy, but electrochromic glass specifically changes tint through a low-voltage electrical charge, providing energy-efficient solar heat and glare reduction. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize rapid switching capabilities or long-term energy savings and durability in window applications.
Table of Comparison
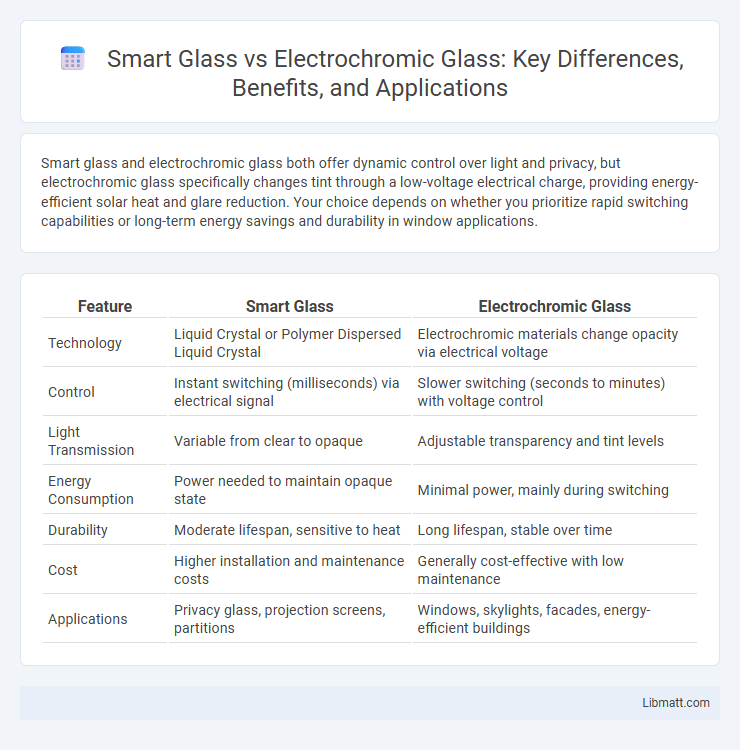
| Feature | Smart Glass | Electrochromic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Liquid Crystal or Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal | Electrochromic materials change opacity via electrical voltage |
| Control | Instant switching (milliseconds) via electrical signal | Slower switching (seconds to minutes) with voltage control |
| Light Transmission | Variable from clear to opaque | Adjustable transparency and tint levels |
| Energy Consumption | Power needed to maintain opaque state | Minimal power, mainly during switching |
| Durability | Moderate lifespan, sensitive to heat | Long lifespan, stable over time |
| Cost | Higher installation and maintenance costs | Generally cost-effective with low maintenance |
| Applications | Privacy glass, projection screens, partitions | Windows, skylights, facades, energy-efficient buildings |
Introduction to Smart Glass and Electrochromic Glass
Smart glass refers to advanced glazing technology that dynamically controls light transmission and heat based on external stimuli such as electric voltage, temperature, or light intensity. Electrochromic glass, a key type of smart glass, operates through a reversible electrochemical reaction that alters its tint when an electrical current passes through, enabling energy-efficient shading and privacy. This technology significantly reduces glare, UV rays, and cooling costs by adapting transparently or opaquely to environmental conditions.
How Smart Glass Works
Smart glass utilizes liquid crystal or polymer dispersed technology to control light transmission by adjusting the alignment of particles within the material when an electric current is applied, enabling instant opacity changes. Electrochromic glass, a subset of smart glass, operates by reversing voltage to trigger a chemical reaction that alters the glass's tint, modulating heat and glare with minimal energy consumption. Your choice of smart glass technology will depend on factors like desired response time, energy efficiency, and control precision.
How Electrochromic Glass Works
Electrochromic glass operates by applying a low voltage electrical current to change the opacity of the glass, allowing it to switch between transparent and tinted states. This technology involves multiple layers, including an electrochromic layer, ion conductor, and transparent electrodes, which work together to control light transmission and solar heat gain. The process enhances energy efficiency by reducing glare and heat without compromising natural daylight.
Key Differences Between Smart Glass and Electrochromic Glass
Smart glass encompasses a broad category of materials that can change their light transmission properties, including technologies such as electrochromic, photochromic, and thermochromic glass. Electrochromic glass specifically changes tint by applying a small electrical voltage, enabling gradual and reversible light modulation for energy efficiency and privacy control. Unlike other smart glass types, electrochromic glass offers precise, low-energy control of solar heat and glare without compromising visibility.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Buildings
Smart glass and electrochromic glass offer advanced solutions for energy-efficient residential and commercial building designs by controlling light and heat transmission. Electrochromic glass is commonly used in office buildings and high-end homes to reduce glare and enhance occupant comfort through dynamic tinting controlled by voltage changes. Smart glass technology finds applications in conference rooms, skylights, and privacy windows, enabling customizable transparency for aesthetic appeal and improved energy management.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Smart glass and electrochromic glass both enhance building energy efficiency by controlling solar heat gain and natural light. Electrochromic glass offers precise tint adjustment in response to electrical voltage, significantly reducing HVAC energy consumption by blocking up to 90% of solar infrared radiation. Smart glass technologies, including thermochromic and photochromic variations, improve energy savings by dynamically adapting to environmental conditions, with electrochromic glass generally providing superior long-term energy efficiency due to its customizable transparency levels.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Smart glass installation varies by technology but generally requires professional handling to ensure functionality and durability; electrochromic glass involves integrating thin layers of electrochromic material, conductive coatings, and control wiring, which can increase installation complexity and cost. Maintenance for smart glass is minimal but depends on the specific technology, with electrochromic glass requiring periodic system checks to ensure uniform tinting and electrical performance. Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for optimizing the lifespan and efficacy of both smart glass and electrochromic glass systems in commercial and residential applications.
Cost Analysis: Smart Glass vs Electrochromic Glass
Smart glass typically costs less upfront, with prices ranging between $50 to $100 per square foot, while electrochromic glass can reach $100 to $150 per square foot due to its advanced technology. Installation and maintenance expenses also vary, as electrochromic glass requires specialized wiring and control systems, increasing overall project costs. Your choice depends on balancing initial investment against long-term energy savings and customization features offered by each glass type.
Pros and Cons of Each Technology
Smart glass offers rapid transition between clear and opaque states, enhancing privacy and energy efficiency, but often requires continuous power to maintain its state and can be costly. Electrochromic glass changes tint gradually by applying voltage, providing excellent solar control and lower energy consumption, yet its slower response time and higher initial investment may limit some applications. Your choice depends on balancing instant functionality with energy-saving benefits tailored to your specific needs.
Future Trends in Glass Technology
Smart glass technology is rapidly advancing with innovations like electrochromic glass, which offers dynamic light and heat control through nanoparticles embedded in the glass. Future trends emphasize energy-efficient, self-cleaning, and even transparent solar glass, integrating IoT for enhanced building automation and sustainability. Electrochromic glass is expected to dominate due to its durability, low power consumption, and versatility in residential and commercial applications.
Smart glass vs electrochromic glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com