Heat mirror glass enhances insulation by using multiple layers of glass with sealed air spaces to trap heat, making it ideal for energy-efficient windows. Low-e glass features a microscopically thin metal oxide coating that reflects infrared heat while allowing natural light, helping you reduce energy costs and improve indoor comfort.
Table of Comparison
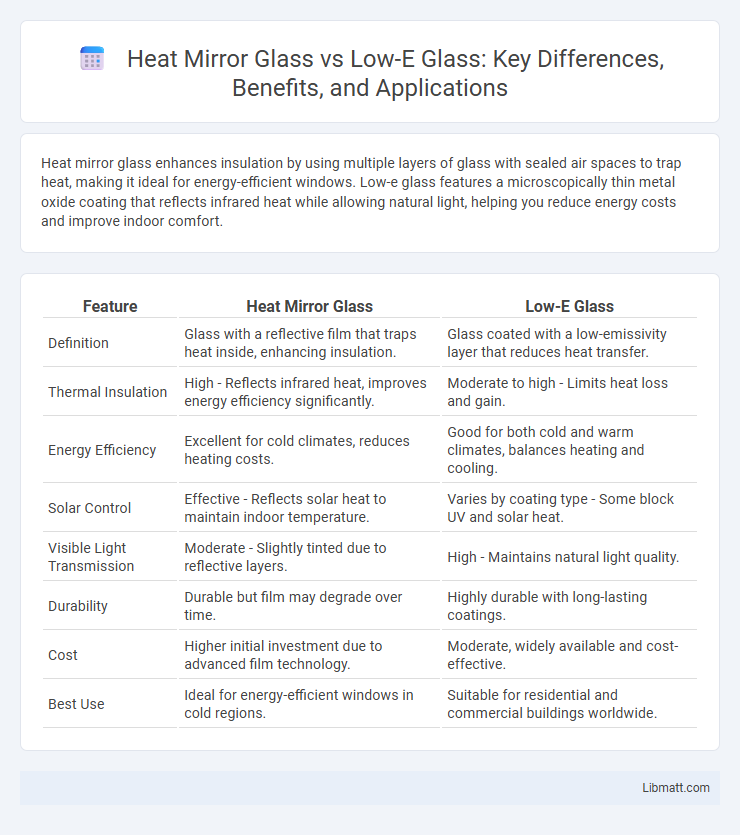
| Feature | Heat Mirror Glass | Low-E Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass with a reflective film that traps heat inside, enhancing insulation. | Glass coated with a low-emissivity layer that reduces heat transfer. |
| Thermal Insulation | High - Reflects infrared heat, improves energy efficiency significantly. | Moderate to high - Limits heat loss and gain. |
| Energy Efficiency | Excellent for cold climates, reduces heating costs. | Good for both cold and warm climates, balances heating and cooling. |
| Solar Control | Effective - Reflects solar heat to maintain indoor temperature. | Varies by coating type - Some block UV and solar heat. |
| Visible Light Transmission | Moderate - Slightly tinted due to reflective layers. | High - Maintains natural light quality. |
| Durability | Durable but film may degrade over time. | Highly durable with long-lasting coatings. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to advanced film technology. | Moderate, widely available and cost-effective. |
| Best Use | Ideal for energy-efficient windows in cold regions. | Suitable for residential and commercial buildings worldwide. |
Introduction to Heat Mirror Glass and Low-E Glass
Heat mirror glass features a transparent insulating layer that enhances energy efficiency by trapping heat, making it ideal for reducing heating and cooling costs. Low-E (low emissivity) glass has a microscopically thin metal oxide coating that reflects infrared energy while allowing visible light to pass through, improving thermal performance and reducing UV damage. Your choice between heat mirror glass and low-E glass depends on specific insulation needs and window applications for optimal energy savings.
How Heat Mirror Glass Works
Heat mirror glass features a sealed cavity filled with a transparent film coated with a low-emissivity (low-e) material, creating an insulating barrier that reduces heat transfer by reflecting infrared energy back into the room. This multi-layer construction enhances thermal performance by trapping air and blocking radiant heat, making it more effective in maintaining indoor temperatures compared to standard low-e glass. Your choice of heat mirror glass can significantly lower energy costs by improving insulation without sacrificing natural light.
How Low-E Glass Works
Low-E glass features a microscopically thin, transparent coating that reflects infrared energy while allowing visible light to pass through, enhancing energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer. Its coating minimizes heat loss in winter by reflecting interior heat back inside and reduces heat gain in summer by reflecting exterior heat away. This selective reflection helps maintain indoor temperature stability, lowering heating and cooling costs compared to standard glass.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Heat mirror glass features a multi-layer, gas-filled cavity design that enhances thermal insulation by significantly reducing heat transfer. Low-E glass utilizes a microscopically thin, transparent coating that reflects infrared energy, effectively limiting heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. When comparing thermal performance, heat mirror glass generally offers superior insulation values (lower U-factors) due to its multi-pane structure, while Low-E glass excels in optimizing solar heat control with selective emissivity properties.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
Heat mirror glass provides superior energy efficiency by incorporating multiple transparent layers with insulating air gaps, significantly reducing heat transfer and improving thermal insulation. Low-e glass features a microscopically thin metallic coating that reflects infrared energy, helping retain indoor heat during winter and reject solar heat in summer, thereby lowering heating and cooling costs. Both technologies enhance building energy performance but heat mirror glass generally offers higher R-values and better overall insulation compared to standard low-e glass.
Cost Differences and ROI
Heat mirror glass typically costs 20-30% more than standard low-E glass due to its multiple layers that provide superior insulation and energy savings. Despite the higher upfront investment, the improved thermal performance of heat mirror glass can result in a return on investment (ROI) within 5 to 7 years through reduced heating and cooling expenses. Low-E glass offers a lower initial cost and decent energy efficiency, but heat mirror glass delivers greater long-term savings for homeowners seeking maximum energy conservation.
UV Protection and Fading Prevention
Heat mirror glass offers superior UV protection by reflecting and absorbing harmful ultraviolet rays, significantly reducing fading of interior furnishings and artwork. Low-e glass also provides effective UV filtering through its thin metal oxide coating, minimizing heat transfer and preventing color deterioration. Choosing the right glass for your windows enhances durability and preserves the vibrancy of your home's interior over time.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Heat mirror glass requires careful installation due to its multilayer structure, necessitating precise handling to maintain its insulating properties and avoid damage. Maintenance involves cleaning with non-abrasive materials to preserve the reflective coatings, and inspecting seals to prevent moisture intrusion. Low-e glass is generally easier to install as a single pane or double-pane with durable coatings, demanding routine cleaning and periodic checks for coating integrity to sustain energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Heat mirror glass significantly enhances energy efficiency by trapping radiant heat within insulated window units, reducing heating and cooling demands and lowering carbon emissions. Low-e glass features a microscopically thin metallic coating that reflects infrared energy, minimizing heat transfer and contributing to a building's thermal insulation with a smaller environmental footprint. Both technologies support sustainability by decreasing reliance on fossil fuels, but heat mirror glass's superior insulation performance often results in greater long-term energy savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Heat mirror glass offers superior insulation by trapping air or inert gas between multiple layers, making it ideal for projects focused on energy efficiency and noise reduction. Low-e glass features a microscopically thin coating that reflects infrared heat while allowing visible light, perfect for controlling solar heat gain and enhancing indoor comfort. Selecting between heat mirror and low-e glass depends on project-specific needs such as climate, energy goals, and budget constraints.
heat mirror glass vs low-e glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com