Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing enhanced safety by holding shards together upon impact, while bulletproof glass is a specialized type of laminated glass designed with multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate to withstand high-velocity bullets. Your choice depends on the level of protection needed, with laminated glass suited for everyday safety and bulletproof glass essential for high-security applications.
Table of Comparison
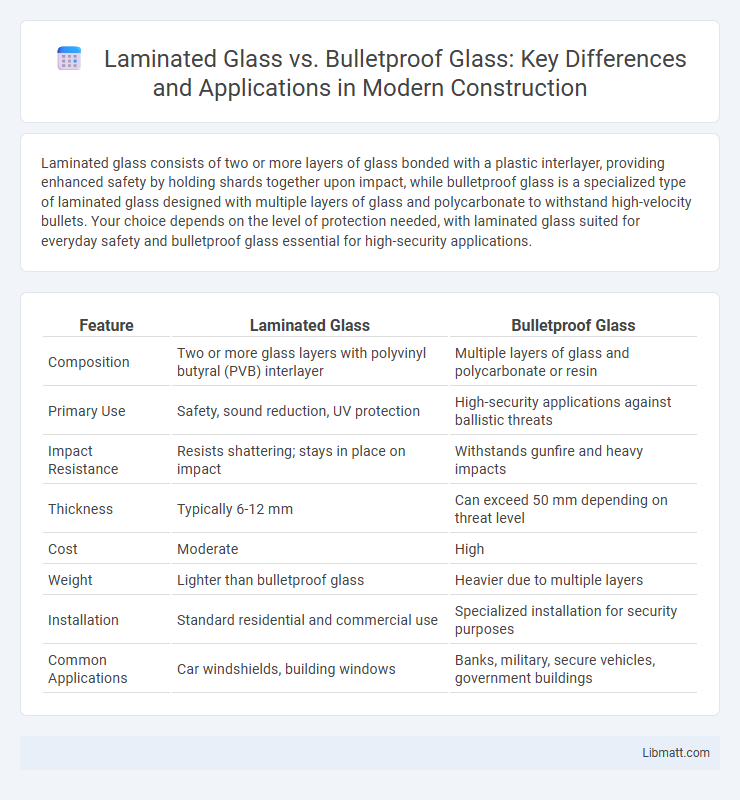
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Bulletproof Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer | Multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate or resin |
| Primary Use | Safety, sound reduction, UV protection | High-security applications against ballistic threats |
| Impact Resistance | Resists shattering; stays in place on impact | Withstands gunfire and heavy impacts |
| Thickness | Typically 6-12 mm | Can exceed 50 mm depending on threat level |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Weight | Lighter than bulletproof glass | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Installation | Standard residential and commercial use | Specialized installation for security purposes |
| Common Applications | Car windshields, building windows | Banks, military, secure vehicles, government buildings |
Introduction to Laminated and Bulletproof Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety by holding shards together upon impact. Bulletproof glass, often composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, offers superior ballistic resistance against high-velocity projectiles. The key distinction lies in bulletproof glass's ability to absorb and dissipate kinetic energy, making it ideal for security applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), produced through heat and pressure that fuses the layers to enhance impact resistance and safety. Bulletproof glass is a multi-layered composite combining laminated glass with polycarbonate or other transparent plastics, manufactured via advanced layering and curing processes that allow it to absorb and disperse high-velocity impacts from bullets. The complexity and thickness of bulletproof glass's composition significantly exceed laminated glass, providing superior ballistic protection by preventing penetration and minimizing spall.
Key Functional Differences
Laminated glass primarily offers enhanced safety by holding shards together upon impact, reducing injury risks during accidents or break-ins. Bulletproof glass comprises multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate, designed to absorb and disperse the energy of bullets, preventing penetration. Your choice depends on whether you need protection against everyday impacts or specific ballistic threats.
Levels of Protection Provided
Laminated glass typically offers protection against impact, shattering, and forced entry by holding the glass shards together through an interlayer, making it effective for safety and security in vehicles and buildings. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, provides a higher level of protection by stopping or slowing down bullets and other high-velocity projectiles. The ballistic resistance of bulletproof glass is categorized into levels based on standards such as NIJ (National Institute of Justice), with higher levels capable of withstanding more powerful firearms.
Applications in Various Industries
Laminated glass is widely used in automotive, architectural, and solar energy industries due to its safety features and ability to reduce noise and UV radiation. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, is essential in military, law enforcement, and security sectors for protection against ballistic threats. Both types of glass offer specialized solutions tailored to industry-specific safety and durability requirements.
Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing moderate strength and impact resistance suitable for everyday protection against shattering. Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass, combines multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, engineered to absorb and disperse high-velocity projectile energy, offering superior defense against gunfire. The multilayer composition and thickness of bulletproof glass result in significantly enhanced strength and impact resistance compared to standard laminated glass.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Laminated glass generally offers a more cost-effective solution with easier installation compared to bulletproof glass, which involves higher material expenses and complex mounting requirements due to its multi-layered construction. Bulletproof glass requires specialized frames and professional installation to ensure maximum security and structural integrity, often increasing overall project timelines and labor costs. Your choice should balance budget constraints with the desired level of protection and installation complexity.
Maintenance and Longevity
Laminated glass requires minimal maintenance, with occasional cleaning and inspection for delamination or cracks to ensure longevity, typically lasting up to 15 years depending on environmental conditions. Bulletproof glass demands more rigorous maintenance due to its multi-layer construction and vulnerability to impact damage, with lifespan varying from 10 to 25 years based on usage intensity and exposure to elements. Proper sealing and regular professional assessments extend the durability of both laminated and bulletproof glass installations, optimizing performance and safety over time.
Safety Standards and Certifications
Laminated glass typically meets safety standards such as ANSI Z97.1 and EN 356, ensuring impact resistance and fragmentation control, while bulletproof glass must comply with rigorous certifications like UL 752 and NIJ Standard 0108.01 that classify ballistic resistance levels. Bulletproof glass incorporates multiple polycarbonate layers and advanced interlayers to stop high-velocity projectiles, exceeding the minimal impact protection requirements of laminated glass. Safety certifications for bulletproof glass validate its durability under specific ballistic threats, making it essential for military, law enforcement, and secure facilities.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Laminated glass offers enhanced safety by holding shattered pieces together, making it ideal for everyday impact resistance and security applications like automotive windows and storefronts. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, provides superior protection against ballistic threats and is essential for high-risk environments such as military, government buildings, and armored vehicles. Selecting the appropriate glass depends on the balance between required security level, budget constraints, and the specific threat or impact resistance needed for your space.
laminated glass vs bulletproof glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com