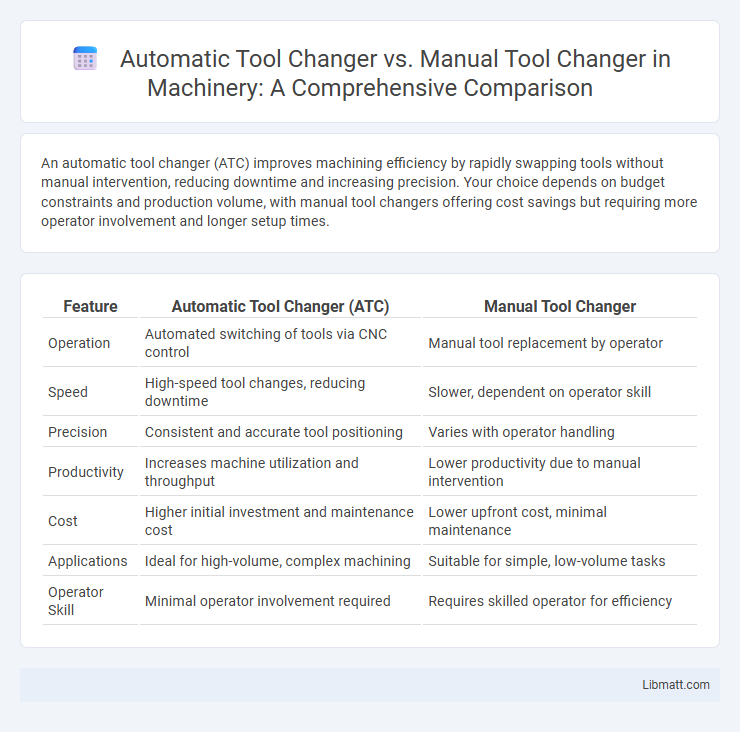
An automatic tool changer (ATC) improves machining efficiency by rapidly swapping tools without manual intervention, reducing downtime and increasing precision. Your choice depends on budget constraints and production volume, with manual tool changers offering cost savings but requiring more operator involvement and longer setup times.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Automatic Tool Changer (ATC) | Manual Tool Changer |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Automated switching of tools via CNC control | Manual tool replacement by operator |
| Speed | High-speed tool changes, reducing downtime | Slower, dependent on operator skill |
| Precision | Consistent and accurate tool positioning | Varies with operator handling |
| Productivity | Increases machine utilization and throughput | Lower productivity due to manual intervention |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and maintenance cost | Lower upfront cost, minimal maintenance |
| Applications | Ideal for high-volume, complex machining | Suitable for simple, low-volume tasks |
| Operator Skill | Minimal operator involvement required | Requires skilled operator for efficiency |
Introduction to Tool Changers
Automatic tool changers (ATCs) revolutionize machining efficiency by swiftly swapping tools without human intervention, drastically reducing downtime in CNC operations. Manual tool changers require an operator to stop the machine and physically change tools, which increases production time and limits precision during tool transitions. By understanding the differences, you can optimize your manufacturing process for speed, accuracy, and overall productivity.
Overview of Automatic Tool Changers
Automatic tool changers (ATCs) enhance CNC machine efficiency by swiftly swapping tools without manual intervention, reducing downtime and improving precision. These systems are equipped with robotic arms or motorized carousels that hold multiple tools, enabling automated transitions during machining processes. Your manufacturing workflow benefits from consistent tool alignment and faster operation cycles, setting ATCs apart from manual tool changers.
Overview of Manual Tool Changers
Manual tool changers require operators to physically remove and replace cutting tools on machinery, relying on human intervention for tool swapping. These systems are cost-effective and simpler but reduce operational efficiency and increase downtime compared to automatic tool changers. Your productivity may be impacted by the slower tool change process and potential for human error in manual setups.
Key Differences Between Automatic and Manual Tool Changers
Automatic tool changers (ATCs) significantly increase machining efficiency by swiftly swapping tools without operator intervention, minimizing downtime and human error. Manual tool changers require your direct involvement, slowing production and increasing the risk of inconsistencies and tool misalignment. The key differences lie in automation level, speed, precision, and suitability for high-volume manufacturing versus smaller, customized jobs.
Efficiency and Productivity Comparison
Automatic tool changers (ATCs) significantly enhance efficiency and productivity by minimizing machine downtime during tool swaps, enabling faster transitions and continuous operation in CNC machining processes. Manual tool changers require operator intervention, increasing production time and the risk of human error, which can delay workflows and reduce overall throughput. Integration of ATCs supports high-volume manufacturing environments by optimizing cycle times and ensuring consistent precision, outperforming manual systems in both speed and reliability.
Cost Implications and ROI Analysis
Automatic tool changers typically involve higher upfront costs due to complex machinery and integration expenses, but they significantly reduce labor costs and downtime, enhancing overall productivity. Manual tool changers have lower initial investments but increase labor requirements and machine idle time, which can limit your long-term return on investment. Evaluating the balance between initial expenditure and operational efficiency is crucial for optimizing cost implications and achieving maximum ROI.
Maintenance Requirements and Downtime
Automatic tool changers require less frequent maintenance compared to manual tool changers due to their precision engineering and automated processes, reducing the risk of human error and tool misalignment. Your production efficiency benefits from minimized downtime, as automatic systems enable rapid tool swaps without halting machine operations. In contrast, manual tool changers demand more regular inspections and adjustments, leading to longer maintenance periods and increased downtime that can disrupt workflows.
Safety Considerations in Tool Changing
Automatic tool changers significantly enhance safety by minimizing human intervention during the tool switching process, reducing risks of injuries from sharp or heavy tools. Manual tool changers require operators to handle tools directly, increasing exposure to potential hazards such as cuts, crush injuries, or repetitive strain. Your workshop benefits from automatic systems by ensuring consistent safety protocols and lowering accident rates related to tool changes.
Best Applications for Each Tool Changer Type
Automatic tool changers excel in high-volume manufacturing environments where rapid tool swaps increase productivity and minimize downtime, making them ideal for CNC machining centers in automotive and aerospace industries. Manual tool changers are better suited for low-volume, custom, or prototype production where tool change frequency is low and cost efficiency is prioritized. Your choice depends on production scale, complexity, and required machining flexibility.
Choosing the Right Tool Changer for Your Needs
Automatic tool changers provide faster, more efficient tool swaps, reducing downtime and increasing production rates in CNC machining. Manual tool changers offer cost-effective simplicity and greater control, ideal for low-volume or custom projects. Your choice depends on balancing budget, workflow speed, and the complexity of your machining tasks.
Automatic tool changer vs manual tool changer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com