Tapered roller bearings feature conical rollers that handle both radial and axial loads, making them ideal for applications requiring combined load support and precise alignment. Cylindrical roller bearings, with their straight rollers, excel at supporting heavy radial loads and allow for higher speed capabilities but offer limited axial load capacity.
Table of Comparison
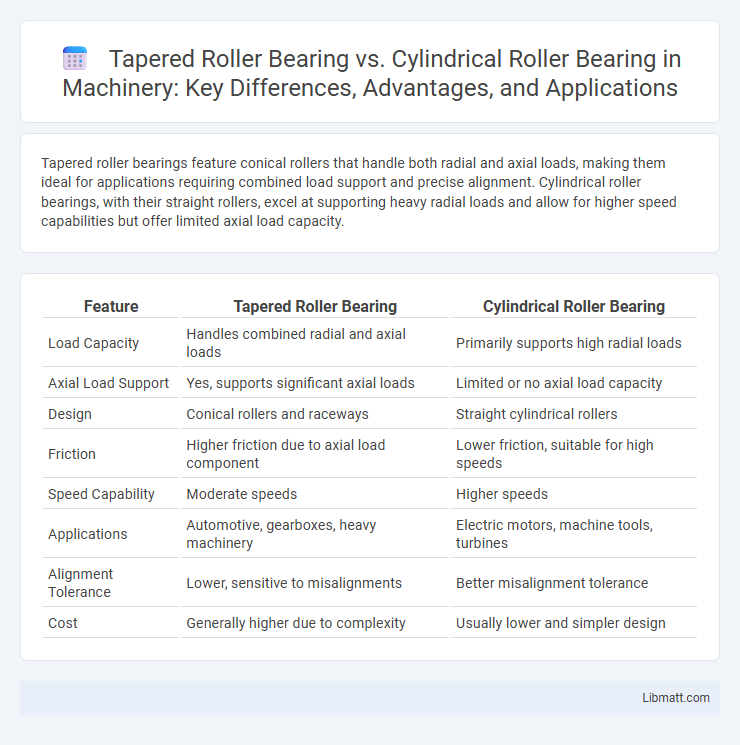
| Feature | Tapered Roller Bearing | Cylindrical Roller Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Handles combined radial and axial loads | Primarily supports high radial loads |
| Axial Load Support | Yes, supports significant axial loads | Limited or no axial load capacity |
| Design | Conical rollers and raceways | Straight cylindrical rollers |
| Friction | Higher friction due to axial load component | Lower friction, suitable for high speeds |
| Speed Capability | Moderate speeds | Higher speeds |
| Applications | Automotive, gearboxes, heavy machinery | Electric motors, machine tools, turbines |
| Alignment Tolerance | Lower, sensitive to misalignments | Better misalignment tolerance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to complexity | Usually lower and simpler design |
Introduction to Tapered and Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings feature conical rollers designed to handle combined radial and axial loads, offering high load capacity and precise alignment in applications such as automotive wheels and gearboxes. Cylindrical roller bearings utilize straight rollers ideal for accommodating heavy radial loads with low friction and high-speed performance, commonly used in electric motors and industrial machinery. Your choice between the two depends on the specific load direction and operating conditions of your mechanical system.
Structural Differences Between Tapered and Cylindrical Bearings
Tapered roller bearings feature conically shaped rollers and raceways designed to handle both radial and axial loads, while cylindrical roller bearings consist of straight rollers that primarily support radial loads. The tapered design allows angled contact between rollers and raceways, providing better alignment and load distribution in tapered bearings. Understanding these structural differences helps you select the appropriate bearing type for your specific load and application requirements.
Load Handling Capabilities
Tapered roller bearings excel in handling combined radial and axial loads due to their conical geometry, which distributes forces evenly along the rollers and raceways. Cylindrical roller bearings are optimized primarily for high radial load capacity but offer limited axial load support because their rollers are parallel to the bearing axis. Choosing between these bearings depends on specific application demands for axial load absorption alongside radial load capacity.
Axial vs. Radial Load Support
Tapered roller bearings excel in supporting both axial and radial loads due to their conical roller shape and angled raceways, making them ideal for applications with combined load conditions. Cylindrical roller bearings primarily support high radial loads with limited axial load capacity, as their rollers are parallel to the bearing axis and do not effectively handle thrust forces. Selecting between these bearings depends on the specific load requirements, with tapered roller bearings preferred for axial load components and cylindrical roller bearings favored for pure radial load situations.
Applications of Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings excel in applications involving combined radial and axial loads, such as automotive wheel hubs and gearboxes, due to their ability to handle thrust loads efficiently. Their design allows for high load-bearing capacity and durability in heavy-duty machinery, including construction and mining equipment. You will find these bearings ideal for maintaining precision and stability in systems subject to both axial and radial forces.
Applications of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings are widely used in applications requiring high radial load capacity and moderate speed, such as electric motors, gearboxes, and machine tool spindles. Their design allows for axial displacement, making them ideal for accommodating thermal expansion in engines and turbines. You will find these bearings crucial in heavy machinery and automotive transmissions where durability and precision are essential.
Performance in High-Speed Operations
Tapered roller bearings provide excellent axial and radial load support but are generally less suited for very high-speed applications due to higher friction and heat generation. Cylindrical roller bearings excel in high-speed operations, offering lower friction and better heat dissipation, which enhances performance and bearing life. Selecting the appropriate bearing depends on the specific balance of load capacity and speed requirements in the application.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Tapered roller bearings require precise axial and radial alignment during installation to ensure correct cup and cone positioning, reducing premature wear and optimizing load distribution. Cylindrical roller bearings allow easier mounting due to separable inner and outer rings, simplifying inspection and replacement without full disassembly. Maintenance of tapered roller bearings often involves meticulous lubrication checks to prevent brinelling, while cylindrical roller bearings benefit from less frequent adjustments but require monitoring for cage integrity under high-speed operations.
Cost Comparison and Lifespan
Tapered roller bearings generally have a higher initial cost compared to cylindrical roller bearings due to their complex design and higher load-carrying capacity. Your choice impacts lifespan since tapered roller bearings typically offer longer durability under combined radial and axial loads, while cylindrical roller bearings excel in pure radial loading with moderate wear. Evaluating operating conditions and maintenance practices helps optimize investment by balancing upfront cost against expected bearing lifespan.
Choosing the Right Bearing for Your Application
Tapered roller bearings excel in handling combined radial and axial loads, making them ideal for applications with significant thrust forces, such as automotive wheel hubs and heavy equipment. Cylindrical roller bearings offer high radial load capacity and reduced friction for high-speed operations, commonly used in electric motors and gearboxes. Selecting the right bearing depends on load direction, rotational speed, and application-specific demands to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Tapered roller bearing vs cylindrical roller bearing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com