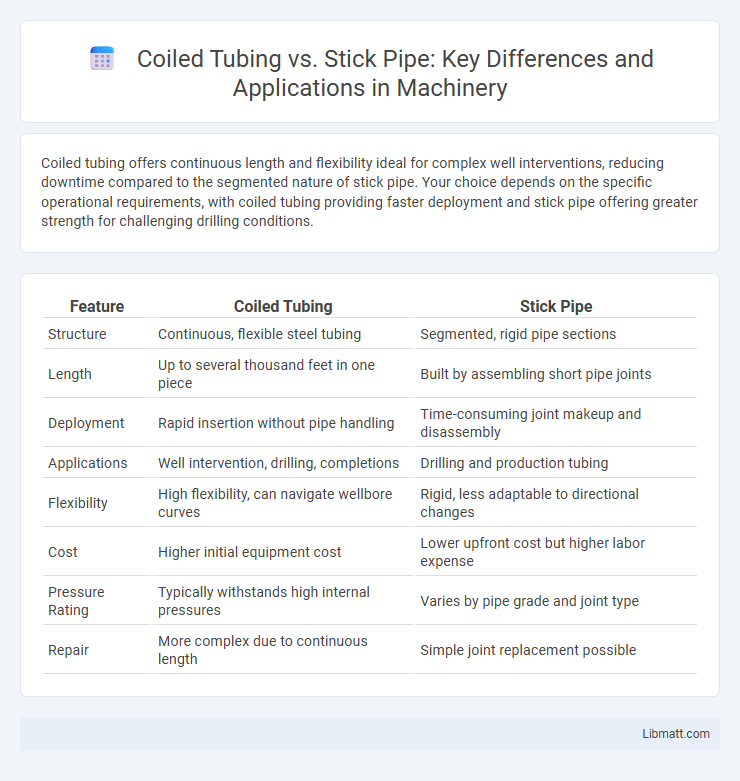
Coiled tubing offers continuous length and flexibility ideal for complex well interventions, reducing downtime compared to the segmented nature of stick pipe. Your choice depends on the specific operational requirements, with coiled tubing providing faster deployment and stick pipe offering greater strength for challenging drilling conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Coiled Tubing | Stick Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Continuous, flexible steel tubing | Segmented, rigid pipe sections |
| Length | Up to several thousand feet in one piece | Built by assembling short pipe joints |
| Deployment | Rapid insertion without pipe handling | Time-consuming joint makeup and disassembly |
| Applications | Well intervention, drilling, completions | Drilling and production tubing |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, can navigate wellbore curves | Rigid, less adaptable to directional changes |
| Cost | Higher initial equipment cost | Lower upfront cost but higher labor expense |
| Pressure Rating | Typically withstands high internal pressures | Varies by pipe grade and joint type |
| Repair | More complex due to continuous length | Simple joint replacement possible |
Introduction to Coiled Tubing and Stick Pipe
Coiled tubing consists of a continuous, flexible steel tube wound on a spool, allowing for rapid deployment and real-time operations in wellbores without the need to disconnect joints. Stick pipe refers to traditional, rigid steel pipe segments that are threaded and connected individually, offering a modular approach for deep and complex well drilling or intervention. Understanding the distinct advantages of coiled tubing's continuous length and stick pipe's jointed design helps optimize your well servicing strategy.
Key Differences Between Coiled Tubing and Stick Pipe
Coiled tubing offers continuous length without joints, enabling faster, more efficient operations in well interventions and drilling compared to stick pipe, which consists of individual segments connected by threaded joints. The flexibility of coiled tubing allows for superior maneuverability in deviated or horizontal wells, whereas stick pipe provides higher tensile strength and is preferred for deeper, more complex drilling projects. Your choice between coiled tubing and stick pipe depends on factors such as well design, operational efficiency, and cost considerations.
Applications in Oil and Gas Operations
Coiled tubing is primarily used for continuous, underbalanced drilling, well cleanouts, and acidizing in oil and gas operations due to its flexibility and ability to perform interventions without tripping out of the hole. Stick pipe, consisting of rigid joints, is preferred for conventional rotary drilling, allowing for higher torque and weight on bit, making it suitable for deeper or high-pressure wells. Both tools are essential, with coiled tubing excelling in quick, cost-efficient well servicing, while stick pipe offers robust drilling capabilities in complex formations.
Deployment and Operational Efficiency
Coiled tubing offers superior deployment speed and operational efficiency compared to stick pipe due to its continuous length, eliminating the need for frequent connections and disconnections. Its ability to be deployed on-site with minimal rig-up time reduces downtime and enhances workover productivity in well interventions. You benefit from faster deployment, reduced labor costs, and improved safety in complex well environments when choosing coiled tubing over stick pipe.
Cost Comparison: Coiled Tubing vs Stick Pipe
Coiled tubing generally incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized equipment and reel systems, while stick pipe tends to have lower initial expenses but higher operational and labor costs. The continuous nature of coiled tubing reduces downtime and improves efficiency, often resulting in lower overall project costs despite the investment. Stick pipe's segmented handling can increase rig time and associated costs, making coiled tubing more cost-effective for complex or extended operations.
Safety Considerations for Each Method
Coiled tubing offers enhanced safety by reducing the need for manual connections, lowering the risk of pinch points and operator exposure during continuous deployment. Stick pipe requires frequent manual connections, increasing potential hazards such as dropped objects, pinches, and mechanical failures under high-stress conditions. Safety protocols for coiled tubing emphasize fatigue monitoring and pressure control, while stick pipe operations demand stringent rig floor safety measures and thorough inspection of threaded joints.
Technical Limitations and Challenges
Coiled tubing faces technical limitations such as reduced tensile strength and fatigue resistance compared to stick pipe, making it less suitable for highly deviated or extended reach wells. Stick pipe offers superior strength and ability to withstand higher torque and compression forces but involves longer connection times and increased downtime. Challenges for coiled tubing include managing buckling and maintaining pressure integrity, while stick pipe struggles with operational complexity and increased risk of connection failures.
Maintenance and Lifespan Factors
Coiled tubing requires less maintenance due to its continuous construction, reducing the risk of leaks and failures common in stick pipe connections. The lifespan of coiled tubing is generally longer as it withstands cyclic bending and stress better, while stick pipe sections are prone to fatigue at threaded joints. Your choice between coiled tubing and stick pipe should consider these maintenance demands and durability for cost-effective, reliable well intervention.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Coiled tubing offers a smaller environmental footprint compared to stick pipe due to reduced rigging time, less waste generation, and minimal soil disturbance during operations. Its ability to enhance well interventions with fewer emissions supports sustainability goals in oil and gas extraction. Choosing coiled tubing can improve Your operational efficiency while aligning with environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Coiled tubing offers continuous, flexible delivery ideal for underbalanced drilling and well interventions, reducing trip time and minimizing formation damage. Stick pipe provides superior strength and rigidity, making it suitable for deep wells and heavy-duty drilling operations requiring high torque and tension resistance. Selecting the right solution depends on project depth, well conditions, and operational requirements, ensuring optimal efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Coiled tubing vs stick pipe Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com