Tempered glass packaging offers superior strength and shatter resistance, making it ideal for protecting fragile items during shipping, while annealed glass packaging is more prone to breakage and less durable under stress. Choosing tempered glass packaging enhances the safety of your products by reducing the risk of damage and ensuring a safer handling experience.
Table of Comparison
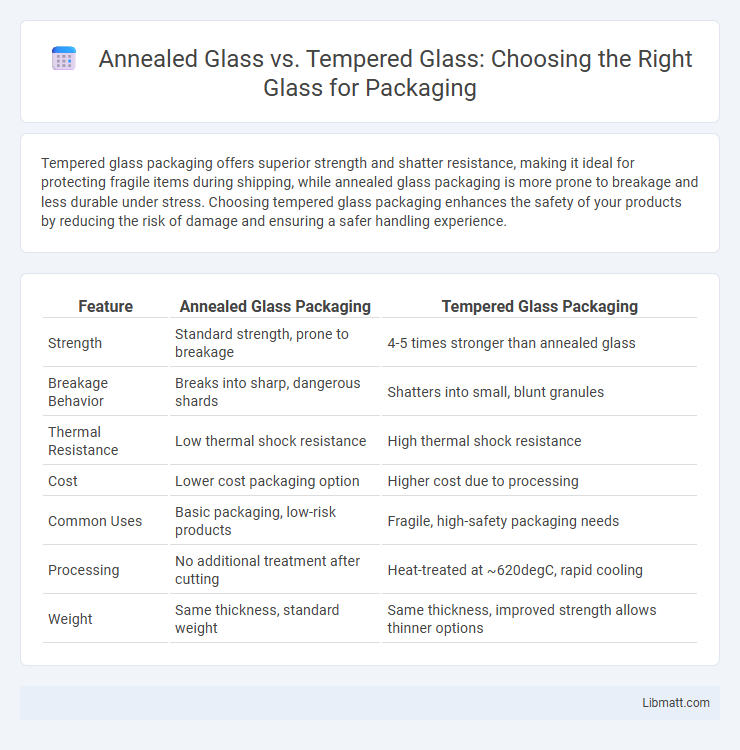
| Feature | Annealed Glass Packaging | Tempered Glass Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Standard strength, prone to breakage | 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass |
| Breakage Behavior | Breaks into sharp, dangerous shards | Shatters into small, blunt granules |
| Thermal Resistance | Low thermal shock resistance | High thermal shock resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost packaging option | Higher cost due to processing |
| Common Uses | Basic packaging, low-risk products | Fragile, high-safety packaging needs |
| Processing | No additional treatment after cutting | Heat-treated at ~620degC, rapid cooling |
| Weight | Same thickness, standard weight | Same thickness, improved strength allows thinner options |
Introduction to Glass Packaging Types
Annealed glass packaging offers cost-effective, easily cuttable, and flexible solutions but lacks the strength and safety features of tempered glass. Tempered glass packaging undergoes controlled thermal treatments to increase durability, impact resistance, and safety by shattering into small, less dangerous pieces upon breakage. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right glass type for packaging applications requiring specific strength and safety standards.
What is Annealed Glass?
Annealed glass is a type of glass that has been slowly cooled after being formed to relieve internal stresses, resulting in a softer and more flexible material compared to tempered glass. It is commonly used in packaging for its clarity and ease of cutting or shaping, though it is more prone to breakage under impact. Unlike tempered glass, annealed glass breaks into large, sharp shards rather than small, blunt fragments.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to annealed glass. It is designed to break into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing the risk of injury if shattered. Your packaging solutions can benefit from tempered glass's enhanced durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for protective and secure containment.
Key Differences: Annealed vs Tempered Glass
Annealed glass undergoes slow cooling to relieve internal stresses, resulting in a softer, more flexible material ideal for packaging that requires easy cutting and shaping. Tempered glass is heat-treated with rapid cooling, creating a strong, safety-oriented structure resistant to impact and thermal stress, making it suitable for protective packaging applications. You should choose annealed glass for custom design flexibility, while tempered glass offers enhanced durability and safety.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tempered glass offers significantly higher strength and durability compared to annealed glass, as it undergoes rapid cooling that increases its tensile strength up to four times. Annealed glass is more prone to breakage under impact or thermal stress due to its slower cooling process, making it less suitable for packaging requiring resilience. When choosing glass packaging, your priority for safety and longevity favors tempered glass to withstand rough handling and environmental pressures.
Safety Implications in Packaging
Annealed glass in packaging lacks the strength to resist impact and thermal stress, making it prone to shattering into sharp, dangerous shards upon breakage. Tempered glass enhances safety in packaging by undergoing heat treatment that increases its strength and causes it to break into small, blunt granules instead of sharp fragments, reducing injury risks. The superior impact resistance and controlled fracture pattern of tempered glass make it the preferred choice for safer packaging solutions in industries handling fragile or hazardous products.
Cost Considerations for Manufacturers
Annealed glass packaging offers lower manufacturing costs due to simpler production processes and less energy consumption compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass requires additional heating and rapid cooling stages, increasing labor and machinery expenses, which impact overall pricing for manufacturers. Cost efficiency in annealed glass makes it suitable for applications with minimal safety requirements, whereas tempered glass commands higher investment for enhanced durability and compliance with safety standards.
Applications in Food and Beverage Packaging
Tempered glass is widely used in food and beverage packaging due to its superior strength and resistance to thermal shock, ensuring durability during handling and transportation. Annealed glass, while more prone to breaking, offers better clarity and is often utilized for packaging where aesthetic appeal and visibility of the product are prioritized. Your choice between annealed and tempered glass impacts the safety, appearance, and longevity of packaged food and beverage items.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Annealed glass boasts a lower environmental impact due to its simpler manufacturing process that consumes less energy and produces fewer emissions compared to tempered glass. Its recyclability is high, as it can be easily crushed and melted down without special treatment, reducing waste and facilitating closed-loop recycling systems. Tempered glass, while stronger and safer, requires controlled crushing methods to recycle, often necessitating specialized facilities, which can limit its recyclability and increase environmental costs.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Packaging Needs
Annealed glass offers greater flexibility for custom cuts and shapes, making it ideal for packaging that requires precise dimensions and design variety. Tempered glass provides significantly enhanced strength and safety, with heat treatment that increases resistance to impact and thermal stress, ensuring durable and secure packaging solutions. Selecting between annealed and tempered glass depends on whether the priority is design customization or maximum durability and safety in packaging applications.
Annealed glass vs tempered glass packaging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com