Foil packaging offers superior barrier protection against light, moisture, and oxygen, preserving product freshness and extending shelf life compared to plastic packaging. Your choice depends on priorities like environmental impact, cost, and the specific preservation needs of the product.
Table of Comparison
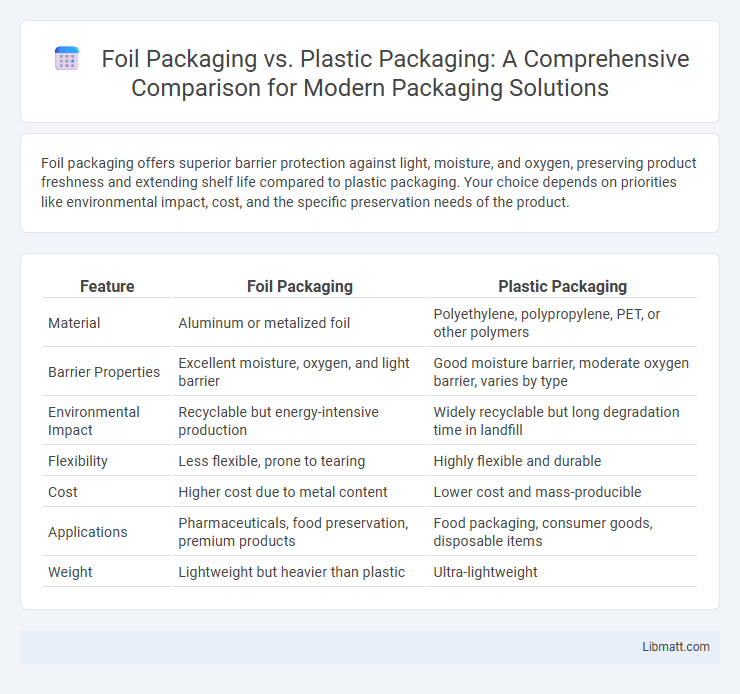
| Feature | Foil Packaging | Plastic Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum or metalized foil | Polyethylene, polypropylene, PET, or other polymers |
| Barrier Properties | Excellent moisture, oxygen, and light barrier | Good moisture barrier, moderate oxygen barrier, varies by type |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but energy-intensive production | Widely recyclable but long degradation time in landfill |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, prone to tearing | Highly flexible and durable |
| Cost | Higher cost due to metal content | Lower cost and mass-producible |
| Applications | Pharmaceuticals, food preservation, premium products | Food packaging, consumer goods, disposable items |
| Weight | Lightweight but heavier than plastic | Ultra-lightweight |
Introduction to Foil and Plastic Packaging
Foil packaging uses thin sheets of aluminum or metalized film to provide an excellent barrier against moisture, light, and oxygen, preserving the freshness and extending the shelf life of products. Plastic packaging, made from various polymers like polyethylene or polypropylene, offers versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness but may lack the same level of protection against external elements. Your choice between foil and plastic packaging depends on product requirements such as protection needs, environmental impact, and cost considerations.
Material Composition and Properties
Foil packaging consists primarily of aluminum, offering excellent barrier properties against moisture, light, and oxygen, which preserves product freshness and extends shelf life. Plastic packaging, made from polymers such as polyethylene or polypropylene, provides flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness but typically has lower barrier resistance compared to foil. Combining both materials in laminates can optimize strength, protection, and product preservation by leveraging the unique properties of each.
Environmental Impact: Foil vs Plastic
Foil packaging offers superior recyclability and faster decomposition compared to traditional plastic packaging, which often persists in landfills for centuries due to its non-biodegradable nature. Your choice of foil packaging reduces environmental pollution by minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving natural resources through efficient recycling processes. Plastic packaging, especially single-use varieties, significantly contributes to ocean pollution and microplastic contamination, posing greater ecological risks than foil alternatives.
Barrier Protection and Shelf Life
Foil packaging offers superior barrier protection against moisture, oxygen, and light compared to plastic packaging, significantly extending the shelf life of perishable products. The multi-layer structure of foil prevents contamination and preserves freshness by minimizing exposure to environmental factors. Your products benefit from longer durability and reduced spoilage when using foil packaging for sensitive goods.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Foil packaging generally incurs higher initial costs than plastic packaging due to the expense of aluminum production and energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Plastic packaging offers lower material and production costs, making it more economically viable for high-volume, low-margin products. Long-term economic considerations include foil's superior barrier properties, which can reduce product waste and extend shelf life, potentially offsetting higher upfront expenses.
Sustainability and Recycling Challenges
Foil packaging offers superior barrier properties that extend product shelf life, contributing to reduced food waste, yet its aluminum content complicates recycling processes compared to widely recyclable plastic packaging. Plastic packaging, while easier to recycle through established municipal programs, often suffers from downcycling and limited circular economy integration, leading to increased environmental pollution. Both materials present distinct sustainability challenges, requiring advanced sorting technologies and consumer participation to improve recycling efficiency and reduce landfill burden.
Applications in Food and Beverage Industry
Foil packaging offers superior barrier properties against light, oxygen, and moisture, making it ideal for preserving the freshness and extending the shelf life of perishable food and beverage products such as dairy, coffee, and snacks. Plastic packaging remains widely used due to its flexibility, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness, commonly applied in bottled beverages, fresh produce, and ready-to-eat meals. Combining foil with plastic layers in laminated packaging enhances durability and protection, optimizing food safety and maintaining product quality across the supply chain.
Consumer Perceptions and Preferences
Consumers often perceive foil packaging as premium and environmentally friendly due to its recyclability and superior barrier properties, which help maintain product freshness and quality. Plastic packaging, while favored for its flexibility and cost-effectiveness, faces criticism for environmental concerns related to single-use waste and limited recyclability. Market trends indicate a growing preference for sustainable packaging options, with many consumers willing to pay a premium for products packaged in foil that align with eco-conscious values.
Innovations in Packaging Technology
Innovations in packaging technology have propelled foil packaging ahead with its enhanced barrier properties, effectively preserving product freshness by blocking moisture, oxygen, and light better than traditional plastic packaging. Advanced metallized films and laminated foil structures offer superior mechanical strength and thermal insulation, extending shelf life significantly. Your choice of foil packaging supports sustainability efforts through increased recyclability and reduced environmental footprint compared to conventional single-use plastic options.
Choosing the Right Packaging Solution
Foil packaging offers superior barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and light, making it ideal for preserving food freshness and extending shelf life compared to plastic packaging. Plastic packaging provides flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and recyclability options, suitable for a wide range of products with less stringent preservation needs. Assessing product sensitivity, environmental impact, and budget considerations is crucial in choosing the right packaging solution between foil and plastic.
Foil packaging vs plastic packaging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com