Induction sealing uses electromagnetic fields to heat a foil liner on a container, providing a hermetic seal without direct contact, while conduction sealing applies direct heat and pressure through contact to bond materials. Your choice depends on factors like container type, sealing speed, and product sensitivity, with induction offering faster, non-contact sealing ideal for tamper-evident packaging.
Table of Comparison
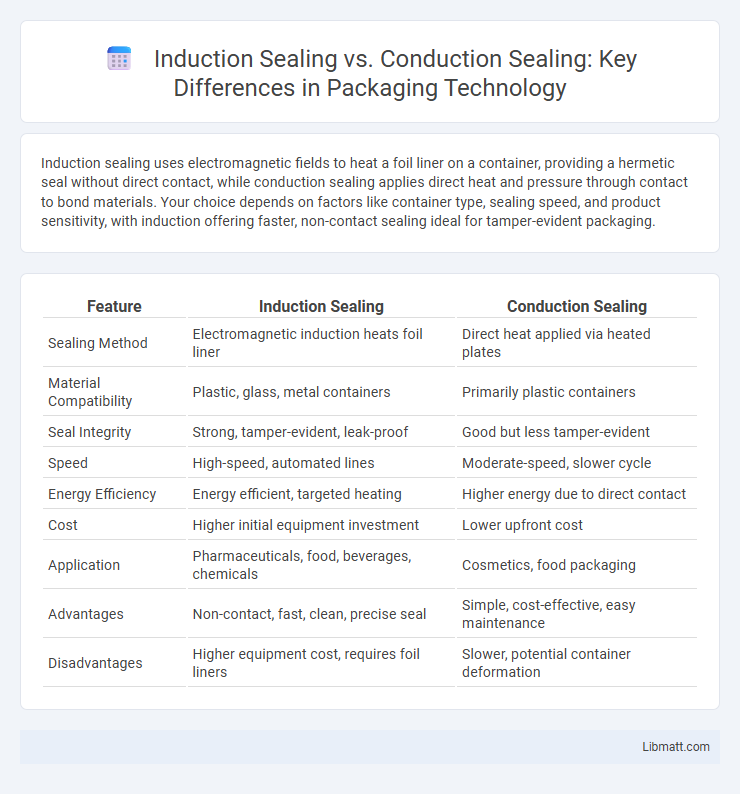
| Feature | Induction Sealing | Conduction Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Method | Electromagnetic induction heats foil liner | Direct heat applied via heated plates |
| Material Compatibility | Plastic, glass, metal containers | Primarily plastic containers |
| Seal Integrity | Strong, tamper-evident, leak-proof | Good but less tamper-evident |
| Speed | High-speed, automated lines | Moderate-speed, slower cycle |
| Energy Efficiency | Energy efficient, targeted heating | Higher energy due to direct contact |
| Cost | Higher initial equipment investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Application | Pharmaceuticals, food, beverages, chemicals | Cosmetics, food packaging |
| Advantages | Non-contact, fast, clean, precise seal | Simple, cost-effective, easy maintenance |
| Disadvantages | Higher equipment cost, requires foil liners | Slower, potential container deformation |
Overview of Induction Sealing and Conduction Sealing
Induction sealing uses electromagnetic fields to heat a foil liner inside a container cap, creating a hermetic seal without direct contact, ideal for tamper evidence and freshness preservation. Conduction sealing involves direct contact heat transfer applied to packaging materials, commonly used for sealing plastic films or laminates in food and pharmaceutical applications. Understanding these methods allows you to select the most efficient sealing technique based on your packaging requirements and production environment.
How Induction Sealing Works
Induction sealing works by generating an electromagnetic field through a coil, which heats a foil liner inside the bottle cap to create a hermetic seal. This non-contact process uses high-frequency magnetic energy that induces eddy currents, rapidly heating the foil without direct heat application, ensuring an airtight barrier. Your products benefit from increased shelf life and tamper evidence due to the precision and reliability of this method compared to conduction sealing.
How Conduction Sealing Works
Conduction sealing works by directly applying heat through a heated platen or sealing head that contacts the lid or foil liner, causing the material to melt and bond to the container rim. This method depends on contact pressure and precise temperature control to ensure a secure and consistent seal. For your packaging needs, conduction sealing offers reliable sealing for small to medium-sized production runs where direct heat application is practical.
Key Differences Between Induction and Conduction Sealing
Induction sealing uses electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly in the foil liner, creating a secure seal without contact, while conduction sealing relies on direct heat transfer through a heated element pressed against the container cap or foil. Induction sealing offers faster sealing speeds and is ideal for tamper-evident, leak-proof packaging, whereas conduction sealing provides consistent heat application suitable for thicker materials but is slower and less adaptable. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the most efficient sealing method for your product packaging needs.
Applications of Induction Sealing
Induction sealing is widely used in the pharmaceutical, food, and beverage industries to provide tamper-evident and leak-proof seals on containers, preserving product freshness and preventing contamination. This method efficiently seals plastic or glass containers with aluminum foil liners, making it ideal for packaging liquids, powders, and sensitive products that require airtight protection. Your choice of induction sealing enhances product safety and extends shelf life in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Applications of Conduction Sealing
Conduction sealing is widely used in packaging industries for sealing materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and aluminum foils in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, ensuring product freshness and tamper evidence. This sealing method is ideal for rigid containers like jars and bottles, offering precise heat control and consistent seals for your packaging needs. Its applications extend to dairy products, beverages, and medical supplies, where reliable and durable seals are critical.
Advantages of Induction Sealing
Induction sealing offers several advantages including non-contact, rapid, and reliable sealing that prevents leaks and contamination, ensuring product freshness and tamper evidence. This method is energy-efficient and compatible with various container materials and shapes, making it highly versatile for different industries. You benefit from improved production speed and reduced maintenance costs compared to conduction sealing, which relies on direct heat transfer.
Advantages of Conduction Sealing
Conduction sealing offers superior heat control by directly transmitting heat to the lid material, ensuring consistent and reliable seals that prevent leaks and contamination. This method reduces energy consumption compared to induction sealing, as it targets only the sealing area without heating the entire container. You benefit from faster sealing cycles and enhanced process efficiency, making conduction sealing ideal for a wide range of packaging applications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Sealing Method
Choosing between induction sealing and conduction sealing involves evaluating factors such as product type, packaging material, and sealing speed requirements. Induction sealing excels with metal foils and fast, non-contact sealing, making it ideal for non-contact hygiene-sensitive applications, while conduction sealing works well with heat-conductive plastics requiring direct heat transfer. Your decision should consider energy efficiency, equipment cost, and the desired seal integrity to ensure optimal packaging performance.
Cost Comparison: Induction vs Conduction Sealing
Induction sealing typically involves higher initial equipment costs compared to conduction sealing due to the sophisticated electromagnetic technology required. However, induction sealing offers lower energy consumption and faster sealing speeds, resulting in reduced operational costs over time. Your choice between induction and conduction sealing should weigh upfront investment against long-term efficiency and maintenance expenses.
Induction sealing vs conduction sealing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com