Co-extrusion combines multiple layers of materials in a single extrusion process, enhancing product durability and barrier properties by fusing layers seamlessly. Your choice between co-extrusion and lamination depends on desired material performance, production efficiency, and cost considerations.
Table of Comparison
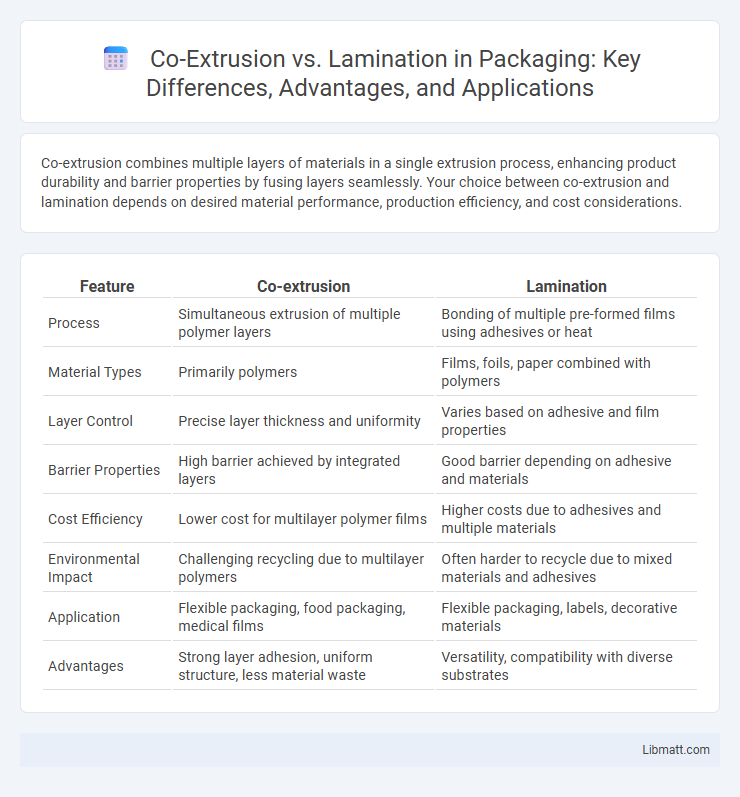
| Feature | Co-extrusion | Lamination |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Simultaneous extrusion of multiple polymer layers | Bonding of multiple pre-formed films using adhesives or heat |
| Material Types | Primarily polymers | Films, foils, paper combined with polymers |
| Layer Control | Precise layer thickness and uniformity | Varies based on adhesive and film properties |
| Barrier Properties | High barrier achieved by integrated layers | Good barrier depending on adhesive and materials |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost for multilayer polymer films | Higher costs due to adhesives and multiple materials |
| Environmental Impact | Challenging recycling due to multilayer polymers | Often harder to recycle due to mixed materials and adhesives |
| Application | Flexible packaging, food packaging, medical films | Flexible packaging, labels, decorative materials |
| Advantages | Strong layer adhesion, uniform structure, less material waste | Versatility, compatibility with diverse substrates |
Introduction to Co-extrusion and Lamination
Co-extrusion involves joining multiple layers of molten polymers through a single extrusion process to create a unified film with enhanced barrier and mechanical properties. Lamination combines separate pre-formed films or sheets using adhesives, heat, or pressure to achieve multi-layered structures for improved durability and functionality. You can choose co-extrusion for seamless multilayer integration or lamination for versatile material combinations tailored to specific packaging or industrial needs.
Understanding the Basics of Co-extrusion
Co-extrusion involves simultaneously extruding multiple polymer layers through a single die to create a unified film or sheet with distinct functional properties. This process enables precise control over the thickness and material composition of each layer, enhancing barrier performance, strength, and flexibility in packaging applications. Unlike lamination, which bonds separate films post-production, co-extrusion integrates layers during manufacturing, reducing material waste and improving production efficiency.
Overview of Lamination Processes
Lamination processes involve bonding multiple layers of materials together using adhesives, heat, or pressure to enhance strength, durability, and barrier properties. Common lamination techniques include thermal lamination, solvent lamination, and extrusion lamination, each offering different advantages for packaging, printing, and industrial applications. Your choice of lamination impacts product performance, moisture resistance, and overall aesthetic appeal.
Key Differences Between Co-extrusion and Lamination
Co-extrusion involves the simultaneous extrusion of multiple polymer layers through a single die, resulting in a unified multilayer film with enhanced barrier properties, whereas lamination joins pre-formed layers using adhesives or heat to combine different materials without melting them together. Co-extrusion offers superior bond strength, improved layer integration, and more precise control over layer thickness compared to lamination, which relies on surface adhesion and may suffer from delamination under stress. The choice between co-extrusion and lamination depends on factors such as material compatibility, desired mechanical performance, production speed, and cost-efficiency for applications like food packaging and flexible films.
Material Compatibility and Selection
Co-extrusion offers enhanced material compatibility by enabling the simultaneous extrusion of multiple polymers with distinct properties, creating a unified multi-layer structure without adhesives. Lamination relies on bonding pre-formed films or papers, which allows for combining incompatible materials but depends heavily on adhesive selection for durability and performance. Selecting materials in co-extrusion requires polymers with compatible melting points and chemical affinities, whereas lamination offers broader material choices but necessitates careful adhesive compatibility to sustain layer integrity.
Performance and Barrier Properties Comparison
Co-extrusion offers superior barrier properties by creating multiple layers of different polymers fused during the extrusion process, enhancing moisture, oxygen, and chemical resistance. Lamination, while effective in combining materials for improved durability and aesthetic appeal, typically relies on adhesives that may compromise overall barrier integrity. Your choice between co-extrusion and lamination should consider the specific performance requirements, with co-extrusion providing better seamless protection and lamination offering design flexibility.
Production Efficiency and Cost Considerations
Co-extrusion offers higher production efficiency by enabling multiple polymer layers to be combined in a single manufacturing step, reducing processing time and labor costs. Lamination involves bonding pre-formed films or sheets, which can increase material handling and energy expenses, leading to higher overall costs. Economies of scale in co-extrusion typically result in lower per-unit production costs compared to lamination, especially for large-volume applications.
Applications in Packaging and Industrial Uses
Co-extrusion is widely used in flexible packaging for food products, offering multi-layer barriers that enhance shelf life and protect against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants. Lamination is preferred in industrial applications requiring strong, durable bonding of different materials, such as automotive interiors and insulating panels. Both techniques optimize material performance, but co-extrusion excels in creating uniform multilayer films, while lamination provides versatility in combining diverse substrates.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Co-extrusion offers significant environmental benefits by reducing the need for adhesives and additives, which lowers chemical waste and simplifies recycling processes, enhancing Your product's sustainability profile. In contrast, lamination often involves multiple layers bonded with non-recyclable adhesives, leading to increased difficulty in material separation and higher environmental impact. Choosing co-extrusion can therefore contribute to a more circular economy by promoting easier recycling and reducing overall resource consumption.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Project
Choosing the right process for your project depends on factors such as material compatibility, cost-effectiveness, and desired product characteristics. Co-extrusion offers seamless bonding and enhanced barrier properties by simultaneously extruding multiple layers of polymers, ideal for flexible packaging and complex structures. Lamination provides versatility with various substrates and adhesives, allowing for improved strength and aesthetics, especially in applications requiring diverse material combinations.
Co-extrusion vs lamination Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com