PE extrusion coating involves applying a molten layer of polyethylene directly onto a substrate, creating a strong, uniform bond that enhances moisture resistance and durability; lamination, on the other hand, combines multiple layers of materials using adhesives or heat to form a composite structure with improved barrier properties and flexibility. When choosing between PE extrusion coating and lamination, consider your product's requirements for strength, barrier performance, and cost-effectiveness to determine the best method.
Table of Comparison
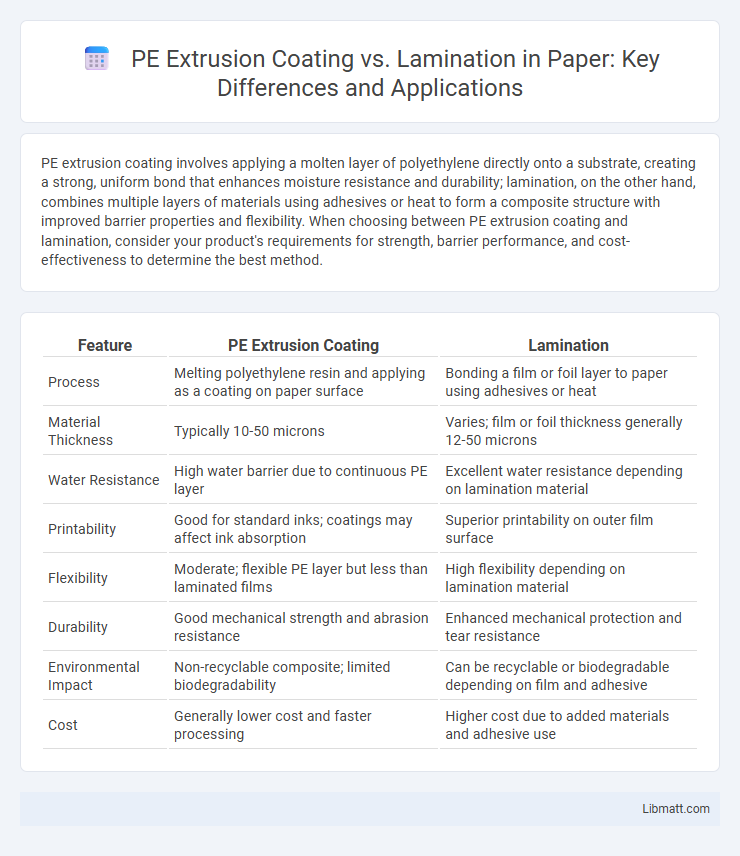
| Feature | PE Extrusion Coating | Lamination |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Melting polyethylene resin and applying as a coating on paper surface | Bonding a film or foil layer to paper using adhesives or heat |
| Material Thickness | Typically 10-50 microns | Varies; film or foil thickness generally 12-50 microns |
| Water Resistance | High water barrier due to continuous PE layer | Excellent water resistance depending on lamination material |
| Printability | Good for standard inks; coatings may affect ink absorption | Superior printability on outer film surface |
| Flexibility | Moderate; flexible PE layer but less than laminated films | High flexibility depending on lamination material |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength and abrasion resistance | Enhanced mechanical protection and tear resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Non-recyclable composite; limited biodegradability | Can be recyclable or biodegradable depending on film and adhesive |
| Cost | Generally lower cost and faster processing | Higher cost due to added materials and adhesive use |
Introduction to PE Extrusion Coating and Lamination
PE extrusion coating involves applying a molten polyethylene layer directly onto substrates like paper, foil, or fabric to enhance barrier properties and durability, while lamination bonds two or more layers using adhesives or heat to create a composite material with combined strength and functionality. Both techniques serve to improve packaging performance, but extrusion coating offers a seamless, moisture-resistant coating ideal for food packaging, whereas lamination provides versatility in material combinations for customized applications. Your choice depends on the desired barrier efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness in the final product.
Overview of PE Extrusion Coating Process
PE extrusion coating involves melting polyethylene resin and applying it directly onto substrates such as paper, foil, or film to create a protective, moisture-resistant layer. The process includes feeding polyethylene pellets into an extruder where they are heated and melted before being forced through a die onto the moving substrate, forming a uniform coating as it cools and solidifies. This method offers strong adhesion, excellent barrier properties, and improved surface durability compared to lamination, which bonds layers via adhesives.
Overview of Lamination Process
Lamination involves bonding multiple layers of materials, such as films, foils, or papers, using adhesives, heat, or pressure to create a composite structure with enhanced barrier properties and durability. This process improves moisture resistance, mechanical strength, and aesthetic appeal for packaging applications. Unlike PE extrusion coating, lamination offers greater flexibility in combining diverse substrates to achieve specific functional requirements.
Key Material Differences
PE extrusion coating uses molten polyethylene to form a direct, uniform layer on substrates, enhancing moisture resistance and sealing properties. Lamination bonds multiple layers of different materials, often combining polyethylene films with adhesives to improve barrier performance and mechanical strength. Your choice depends on required durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, as extrusion coating offers seamless protection, while lamination provides tailored multi-layer functionality.
Performance Comparison: Barrier Properties
PE extrusion coating provides superior moisture resistance and a strong seal due to its uniform polyethylene layer, making it ideal for products requiring effective water vapor barriers. Lamination combines multiple materials, enhancing overall stiffness and mechanical strength but may offer less consistent barrier performance compared to PE extrusion coatings. Your choice should consider that extrusion coating excels in moisture barrier properties, while lamination is better suited for applications needing a balance of barrier and structural benefits.
Cost Implications and Efficiency
PE extrusion coating generally offers lower initial investment costs and faster production speeds compared to lamination, making it more cost-effective for high-volume runs. Lamination provides superior barrier properties and aesthetic finishes but involves higher material costs and longer processing times, reducing overall production efficiency. Businesses prioritize extrusion coating when aiming for economical scalability, whereas lamination suits applications demanding premium quality despite increased expenditure.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
PE extrusion coating offers improved recyclability compared to traditional lamination by using a single material, often polyethylene, which facilitates easier sorting and processing in recycling facilities. Lamination typically combines multiple layers of different materials, complicating recycling efforts and increasing environmental impact due to higher waste and energy consumption. Choosing PE extrusion coating reduces landfill waste and lowers the carbon footprint by enabling more efficient material recovery and promoting circular economy practices in packaging production.
Applications in Packaging Industries
PE extrusion coating enhances packaging durability and moisture resistance by applying a protective polyethylene layer on substrates like paperboard or aluminum foil, making it ideal for food and beverage packaging. Lamination involves bonding multiple layers of materials such as plastic films, paper, and metal foils, providing superior barrier properties, increased strength, and improved printability for flexible packaging and pouches. Both methods are widely used to ensure product protection, extend shelf life, and improve the visual appeal of consumer goods packaging.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
PE extrusion coating offers superior adhesion and moisture resistance, making it ideal for flexible packaging and food-grade applications, but it can be less versatile with substrate compatibility compared to lamination. Lamination provides enhanced barrier properties, improved printability, and better mechanical strength, yet it involves higher costs and more complex processing steps. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize cost efficiency and moisture protection (extrusion coating) or mechanical durability and advanced barrier performance (lamination).
Choosing Between PE Extrusion Coating and Lamination
Selecting between PE extrusion coating and lamination depends on the desired barrier properties and application requirements. PE extrusion coating offers superior moisture resistance and a strong bond to substrates like paper or foil, making it ideal for packaging requiring heat-sealable, airtight seals. Lamination provides enhanced mechanical strength and printability by combining multiple layers, suited for products needing durability and complex graphic designs.
PE extrusion coating vs lamination Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com