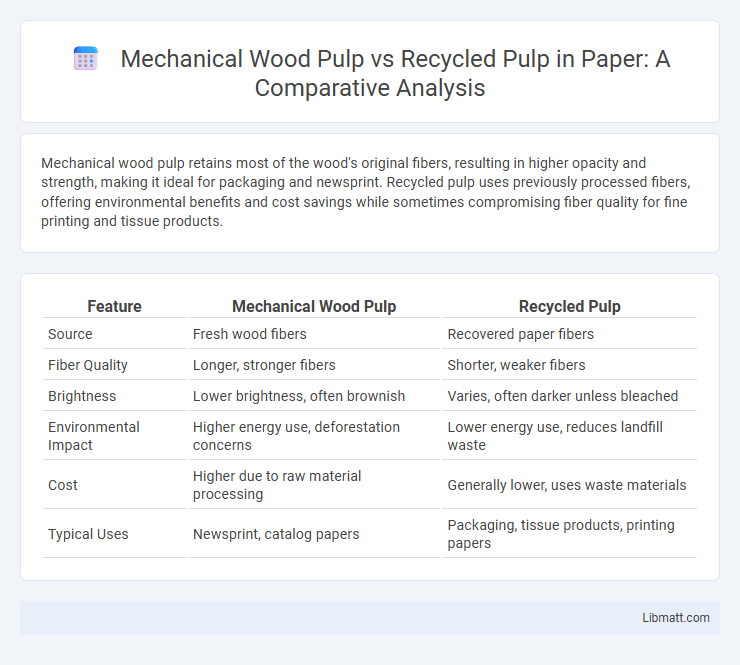
Mechanical wood pulp retains most of the wood's original fibers, resulting in higher opacity and strength, making it ideal for packaging and newsprint. Recycled pulp uses previously processed fibers, offering environmental benefits and cost savings while sometimes compromising fiber quality for fine printing and tissue products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mechanical Wood Pulp | Recycled Pulp |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fresh wood fibers | Recovered paper fibers |
| Fiber Quality | Longer, stronger fibers | Shorter, weaker fibers |
| Brightness | Lower brightness, often brownish | Varies, often darker unless bleached |
| Environmental Impact | Higher energy use, deforestation concerns | Lower energy use, reduces landfill waste |
| Cost | Higher due to raw material processing | Generally lower, uses waste materials |
| Typical Uses | Newsprint, catalog papers | Packaging, tissue products, printing papers |
Introduction to Mechanical Wood Pulp and Recycled Pulp
Mechanical wood pulp is produced by physically grinding wood logs to separate fibers, resulting in high-yield pulp with long fibers ideal for strength in paper products. Recycled pulp comes from reprocessing used paper materials, significantly reducing environmental impact by conserving trees and energy while maintaining adequate fiber quality for various applications. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right pulp type for sustainable and efficient paper manufacturing.
Raw Materials and Sourcing
Mechanical wood pulp is produced directly from freshly harvested logs, typically softwood or hardwood species like pine or birch, providing high fiber yield and strength due to retained lignin content. Recycled pulp is sourced from post-consumer paper waste, such as old newspapers, cardboard, and office paper, reducing reliance on virgin wood and supporting circular resource use. The choice between these raw materials impacts environmental sustainability, fiber characteristics, and overall pulp quality in papermaking processes.
Pulping Processes: Mechanical vs. Recycled
Mechanical wood pulp is produced by physically grinding wood logs or chips to separate fibers, preserving most of the lignin and resulting in higher yield but lower brightness and strength. Recycled pulp, on the other hand, originates from reclaimed paper products that undergo deinking and cleaning processes to remove inks, fillers, and contaminants before fiber recovery. Mechanical pulping maintains fiber length but limits durability, whereas recycled pulping depends on fiber quality and cleaning efficiency, influencing the final paper's performance and environmental impact.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Mechanical wood pulp production consumes less energy compared to recycled pulp, but it results in higher water usage and increased release of organic pollutants. Recycled pulp significantly reduces deforestation and landfill waste, lowering the carbon footprint and conserving natural resources. Despite higher energy demands, recycled pulp supports a circular economy by minimizing environmental degradation and promoting sustainable material reuse.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Mechanical wood pulp requires significantly higher energy consumption, often up to 20 times more than recycled pulp due to the intensive grinding process needed to separate fibers. Recycled pulp, derived from processed paper waste, demands less energy, enhancing overall production efficiency and reducing operational costs. This energy efficiency in recycled pulp production contributes to lower environmental impact and supports sustainable paper manufacturing practices.
Paper Quality and Performance Differences
Mechanical wood pulp produces paper with higher brightness and bulk but lower strength and durability compared to recycled pulp, which often contains shorter fibers resulting in weaker, less opaque sheets. Your choice impacts print quality; mechanical pulp offers better ink absorption for printing, while recycled pulp may cause uneven texture and reduced print sharpness. Paper made from recycled pulp tends to be more environmentally sustainable but may require additives to improve performance for specific applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Mechanical wood pulp generally incurs lower production costs due to less intensive processing compared to recycled pulp, which requires additional cleaning and deinking steps. However, recycled pulp offers cost savings in raw material acquisition since it utilizes waste paper, reducing dependence on virgin timber. Economic feasibility depends on market prices for raw materials and energy, as well as demand for environmentally sustainable products.
Applications in the Paper Industry
Mechanical wood pulp is widely used in the production of newsprint, catalogs, and paperboards due to its high bulk and opacity, enhancing print quality and durability. Recycled pulp, on the other hand, is primarily employed in printing and writing papers, packaging materials, and tissue products, offering environmental benefits and cost efficiency. Your choice between mechanical wood pulp and recycled pulp impacts product performance, sustainability goals, and manufacturing costs in the paper industry.
Sustainability and Circular Economy Perspectives
Mechanical wood pulp offers sustainability advantages by maximizing fiber yield from raw timber, reducing the need for chemical treatments and conserving natural resources. Recycled pulp supports circular economy principles by diverting paper waste from landfills, lowering energy consumption, and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions during production. Both pulps contribute to sustainable forestry management and resource efficiency, though recycled pulp emphasizes waste reduction and material reuse more directly.
Future Trends in Pulp Production
Future trends in pulp production emphasize sustainability, with mechanical wood pulp and recycled pulp playing pivotal roles. Mechanical wood pulp offers high yields and energy efficiency, while recycled pulp reduces environmental impact by minimizing deforestation. Your choice of pulp can align with evolving industry standards focused on reducing carbon footprints and enhancing circular economy practices.
mechanical wood pulp vs recycled pulp Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com