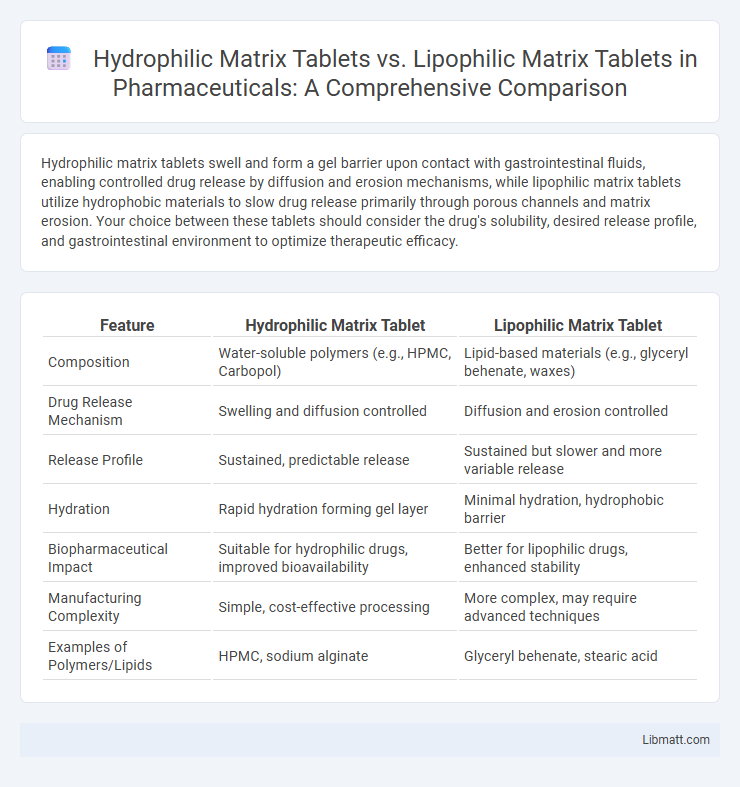
Hydrophilic matrix tablets swell and form a gel barrier upon contact with gastrointestinal fluids, enabling controlled drug release by diffusion and erosion mechanisms, while lipophilic matrix tablets utilize hydrophobic materials to slow drug release primarily through porous channels and matrix erosion. Your choice between these tablets should consider the drug's solubility, desired release profile, and gastrointestinal environment to optimize therapeutic efficacy.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydrophilic Matrix Tablet | Lipophilic Matrix Tablet |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Water-soluble polymers (e.g., HPMC, Carbopol) | Lipid-based materials (e.g., glyceryl behenate, waxes) |
| Drug Release Mechanism | Swelling and diffusion controlled | Diffusion and erosion controlled |
| Release Profile | Sustained, predictable release | Sustained but slower and more variable release |
| Hydration | Rapid hydration forming gel layer | Minimal hydration, hydrophobic barrier |
| Biopharmaceutical Impact | Suitable for hydrophilic drugs, improved bioavailability | Better for lipophilic drugs, enhanced stability |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Simple, cost-effective processing | More complex, may require advanced techniques |
| Examples of Polymers/Lipids | HPMC, sodium alginate | Glyceryl behenate, stearic acid |
Introduction to Matrix Tablets
Matrix tablets are solid dosage forms designed to control drug release through a polymeric matrix system. Hydrophilic matrix tablets utilize water-swelling polymers like hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) to form a gel barrier that modulates drug dissolution and diffusion rates. Lipophilic matrix tablets, typically composed of fatty materials such as hydrogenated vegetable oils, rely on their hydrophobic nature to slow drug release by reducing water penetration and controlling matrix erosion.
Overview of Hydrophilic Matrix Tablets
Hydrophilic matrix tablets utilize water-soluble polymers like hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) to control drug release through swelling and gel formation, enhancing sustained release properties. These tablets gradually absorb gastrointestinal fluids, forming a gel barrier that regulates drug diffusion and erosion, ensuring consistent plasma concentrations over time. Your choice of hydrophilic matrix tablets benefits drugs requiring prolonged release and improved bioavailability in oral dosage forms.
Overview of Lipophilic Matrix Tablets
Lipophilic matrix tablets utilize hydrophobic polymers or waxy substances to control drug release by forming a water-insoluble matrix that limits drug diffusion. These tablets provide sustained release profiles by creating a barrier to water penetration, resulting in slower drug dissolution compared to hydrophilic matrices. Common lipophilic materials include glyceryl behenate and hydrogenated castor oil, which enhance tablet stability and prolong the therapeutic effect.
Key Formulation Components
Hydrophilic matrix tablets primarily contain water-soluble polymers such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) that swell upon contact with gastrointestinal fluids, controlling drug release through gel formation. Lipophilic matrix tablets use insoluble lipids like glyceryl behenate or hydrogenated castor oil to create a hydrophobic matrix, which retards drug dissolution by limiting water penetration. Your choice between these matrices depends on the drug's solubility profile and desired release kinetics.
Mechanisms of Drug Release
Hydrophilic matrix tablets release drugs primarily through swelling and gel formation when exposed to gastrointestinal fluids, enabling controlled diffusion and erosion processes. In contrast, lipophilic matrix tablets rely on matrix integrity retention and gradual drug diffusion through a hydrophobic polymer network, leading to slower and more sustained drug release. The selection between hydrophilic and lipophilic matrices influences drug dissolution rates, bioavailability, and therapeutic efficacy depending on drug solubility and release profile requirements.
Comparative Advantages of Hydrophilic Matrices
Hydrophilic matrix tablets offer superior drug release control through swelling and gel layer formation, enhancing bioavailability for highly water-soluble drugs. These matrices provide consistent release rates and reduced risk of dose dumping compared to lipophilic matrices, which rely on slower diffusion and erosion mechanisms. The biocompatibility and ease of processing hydrophilic polymers, such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), further optimize formulation efficiency and patient compliance.
Comparative Advantages of Lipophilic Matrices
Lipophilic matrix tablets offer superior controlled-release properties by forming a stable, hydrophobic barrier that slows drug diffusion more effectively than hydrophilic matrices. Their enhanced chemical stability protects drug molecules from moisture-induced degradation, making them ideal for moisture-sensitive drugs. Lipophilic matrices also provide better compatibility with poorly water-soluble drugs, improving bioavailability through sustained release mechanisms.
Applications in Controlled Drug Delivery
Hydrophilic matrix tablets utilize water-soluble polymers like hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) to control drug release through swelling and gel formation, making them suitable for drugs requiring sustained release and improved bioavailability. Lipophilic matrix tablets employ hydrophobic substances such as waxes or fatty acids to slow drug dissolution, offering enhanced stability and prolonged release for poorly water-soluble drugs. Your choice between these matrix types depends on the drug's solubility, desired release profile, and formulation stability needs in controlled drug delivery systems.
Factors Influencing Matrix Selection
Matrix selection depends on drug solubility, desired release rate, and compatibility with active ingredients; hydrophilic matrices are ideal for water-soluble drugs requiring sustained release through swelling and gel formation. Lipophilic matrices suit poorly soluble drugs, providing controlled release via diffusion through a lipid barrier and enhanced stability against moisture. Your choice hinges on balancing release kinetics, manufacturing feasibility, and pharmacokinetic targets.
Future Trends in Matrix Tablet Development
Future trends in matrix tablet development emphasize enhanced control over drug release profiles through advanced hydrophilic and lipophilic polymers. Innovations in nanotechnology and biodegradable materials aim to optimize bioavailability and patient adherence by enabling targeted and sustained drug delivery. Integration of smart release mechanisms with matrix tablets is expected to revolutionize personalized medicine and improve therapeutic outcomes.
Hydrophilic Matrix Tablet vs Lipophilic Matrix Tablet Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com