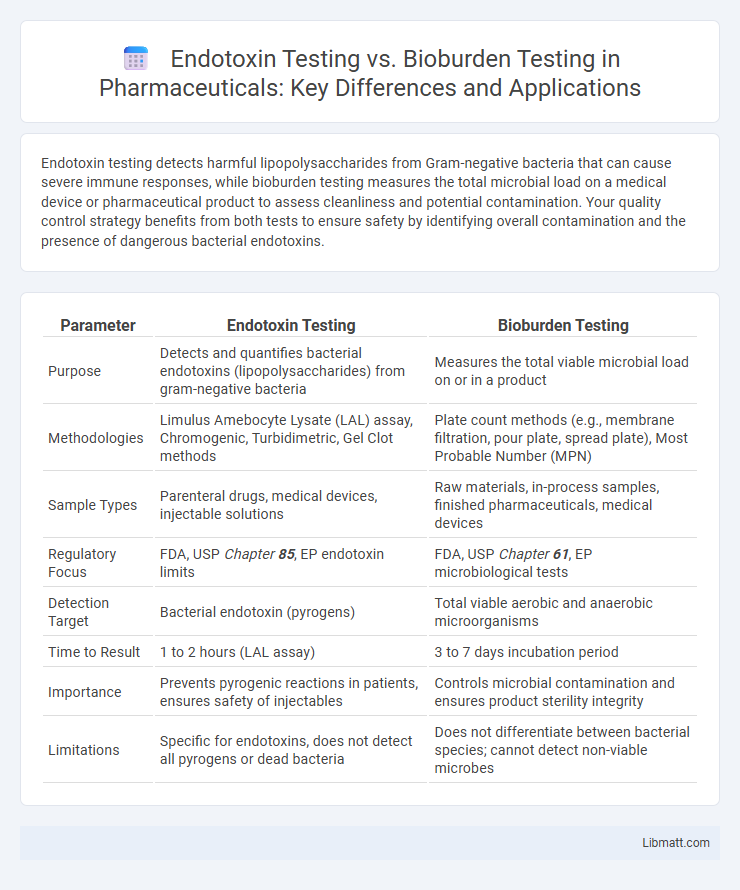
Endotoxin testing detects harmful lipopolysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria that can cause severe immune responses, while bioburden testing measures the total microbial load on a medical device or pharmaceutical product to assess cleanliness and potential contamination. Your quality control strategy benefits from both tests to ensure safety by identifying overall contamination and the presence of dangerous bacterial endotoxins.
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | Endotoxin Testing | Bioburden Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects and quantifies bacterial endotoxins (lipopolysaccharides) from gram-negative bacteria | Measures the total viable microbial load on or in a product |
| Methodologies | Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) assay, Chromogenic, Turbidimetric, Gel Clot methods | Plate count methods (e.g., membrane filtration, pour plate, spread plate), Most Probable Number (MPN) |
| Sample Types | Parenteral drugs, medical devices, injectable solutions | Raw materials, in-process samples, finished pharmaceuticals, medical devices |
| Regulatory Focus | FDA, USP Chapter 85, EP endotoxin limits | FDA, USP Chapter 61, EP microbiological tests |
| Detection Target | Bacterial endotoxin (pyrogens) | Total viable aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms |
| Time to Result | 1 to 2 hours (LAL assay) | 3 to 7 days incubation period |
| Importance | Prevents pyrogenic reactions in patients, ensures safety of injectables | Controls microbial contamination and ensures product sterility integrity |
| Limitations | Specific for endotoxins, does not detect all pyrogens or dead bacteria | Does not differentiate between bacterial species; cannot detect non-viable microbes |
Introduction to Endotoxin and Bioburden Testing
Endotoxin testing detects bacterial endotoxins, toxic substances released from Gram-negative bacteria, critical for ensuring the safety of pharmaceutical and medical devices. Bioburden testing measures the total microbial load present on a product before sterilization, providing essential data for assessing contamination risk. Your understanding of both tests ensures compliance with regulatory standards and supports effective quality control in manufacturing processes.
Defining Endotoxin Testing: Purpose and Process
Endotoxin testing measures the presence of bacterial endotoxins, primarily lipopolysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria, to ensure the safety of pharmaceuticals and medical devices by preventing febrile reactions in patients. This testing involves techniques such as the Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) assay, which detects endotoxins with high sensitivity. Your product passes endotoxin testing when endotoxin levels are below established regulatory limits, confirming it is safe for clinical use.
Understanding Bioburden Testing: Scope and Significance
Bioburden testing quantifies the total number of viable microorganisms present on medical devices or pharmaceutical products before sterilization, ensuring contamination levels comply with regulatory standards. This testing scope includes bacteria, fungi, and yeast to assess product safety and sterility assurance. Unlike endotoxin testing, which targets specific bacterial toxins, bioburden testing evaluates the overall microbial load critical for effective sterilization process validation.
Key Differences Between Endotoxin and Bioburden Testing
Endotoxin testing specifically measures the presence of bacterial endotoxins, primarily from Gram-negative bacteria, which can cause severe inflammatory responses in humans. Bioburden testing quantifies the total viable microbial population, including bacteria, fungi, and yeasts, on a product or surface to assess contamination levels before sterilization. Your choice between these tests depends on regulatory requirements and the nature of the product, as endotoxin limits are critical in injectable drugs while bioburden is essential for ensuring overall microbial cleanliness.
Regulatory Guidelines for Endotoxin and Bioburden Tests
Regulatory guidelines for endotoxin testing primarily follow standards set by the United States Pharmacopeia (USP)
Methods and Technologies Used in Endotoxin Testing
Endotoxin testing primarily utilizes the Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) assay, which detects bacterial endotoxins through a clotting reaction triggered by lipopolysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria. Alternative methods include recombinant Factor C assays and turbidimetric or chromogenic techniques that quantify endotoxin presence with high sensitivity and specificity. These technologies ensure accurate monitoring of endotoxin levels in pharmaceutical products to prevent pyrogenic responses in patients.
Techniques and Tools for Bioburden Analysis
Bioburden analysis employs techniques such as membrane filtration, plate count methods, and most probable number (MPN) assays to quantify microbial contamination on medical devices or pharmaceutical products. Key tools include incubators for culturing microorganisms, colony counters for quantification, and specialized growth media tailored to detect bacteria, yeast, and mold. These methods ensure compliance with regulatory standards by accurately assessing microbial load before endotoxin testing, which specifically detects lipopolysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria.
Applications in Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Industries
Endotoxin testing is critical in pharmaceutical and medical device industries for ensuring products are free from harmful pyrogens that can cause severe inflammatory responses in patients. Bioburden testing quantifies the total viable microbial load on raw materials, components, and finished products, serving as a key control step before sterilization processes. Both tests support compliance with regulatory standards such as USP <85> for endotoxins and USP <61> for bioburden, safeguarding patient safety and product quality.
Interpreting Test Results: Safety and Quality Implications
Interpreting endotoxin testing results requires assessing the levels of bacterial endotoxins to ensure products meet safety thresholds, preventing harmful inflammatory responses in patients. Bioburden testing quantifies the total microbial load, guiding sterilization processes to maintain product quality and reduce contamination risks. Your ability to analyze these results accurately impacts compliance with regulatory standards and safeguards patient health.
Choosing the Right Test: Factors and Recommendations
Selecting the appropriate test between endotoxin testing and bioburden testing depends on your product's regulatory requirements, intended use, and contamination risk. Endotoxin testing targets gram-negative bacterial toxins critical in injectable and implantable devices, while bioburden testing assesses total viable microbial load, essential for sterilization validation. Your decision should consider factors such as endotoxin sensitivity, microbial limits, and product sterility specifications to ensure compliance and patient safety.
Endotoxin testing vs Bioburden testing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com