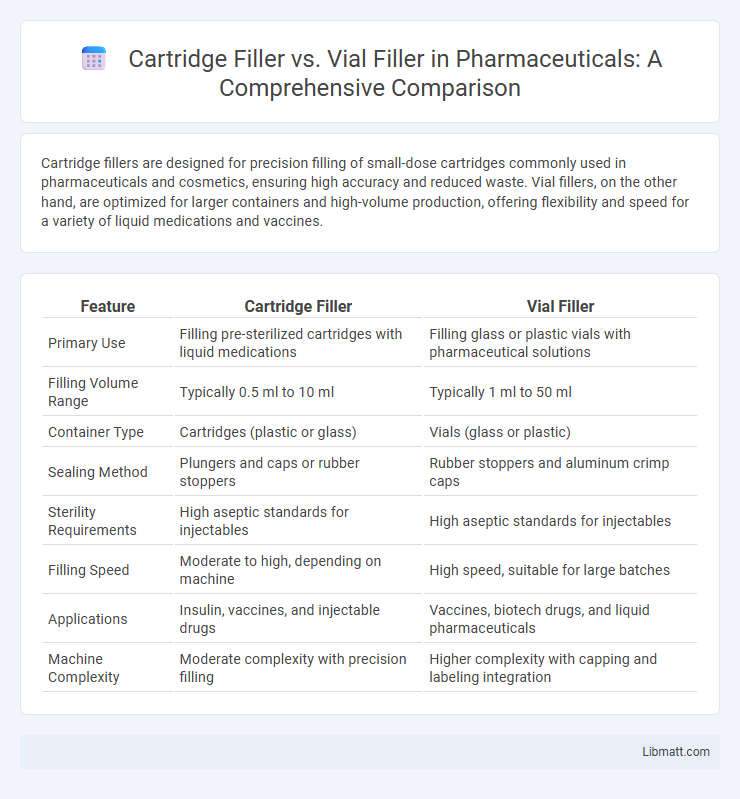
Cartridge fillers are designed for precision filling of small-dose cartridges commonly used in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, ensuring high accuracy and reduced waste. Vial fillers, on the other hand, are optimized for larger containers and high-volume production, offering flexibility and speed for a variety of liquid medications and vaccines.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cartridge Filler | Vial Filler |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Filling pre-sterilized cartridges with liquid medications | Filling glass or plastic vials with pharmaceutical solutions |
| Filling Volume Range | Typically 0.5 ml to 10 ml | Typically 1 ml to 50 ml |
| Container Type | Cartridges (plastic or glass) | Vials (glass or plastic) |
| Sealing Method | Plungers and caps or rubber stoppers | Rubber stoppers and aluminum crimp caps |
| Sterility Requirements | High aseptic standards for injectables | High aseptic standards for injectables |
| Filling Speed | Moderate to high, depending on machine | High speed, suitable for large batches |
| Applications | Insulin, vaccines, and injectable drugs | Vaccines, biotech drugs, and liquid pharmaceuticals |
| Machine Complexity | Moderate complexity with precision filling | Higher complexity with capping and labeling integration |
Introduction to Cartridge Filler and Vial Filler
Cartridge fillers are designed for precise, efficient filling of pre-formed cartridges commonly used in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, ensuring accurate dosage and minimal waste. Vial fillers specialize in filling glass or plastic vials, crucial for sterile liquid medications, vaccines, and injectable drugs, maintaining stringent contamination control. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right equipment for your packaging needs and production requirements.
Understanding Cartridge Fillers: Features and Uses
Cartridge fillers are precision machines designed to accurately dispense liquid medications and oils into cartridges, featuring essential components like dosing pumps, filling needles, and sealing systems to ensure contamination-free packaging. Commonly used in pharmaceutical and cannabis industries, cartridge fillers support various viscosities and accommodate different cartridge sizes, enhancing production efficiency and maintaining product integrity. Compared to vial fillers, cartridge fillers offer specialized handling for pre-filled cartridges, optimizing processes for vape cartridges, insulin pens, and cosmetic dispensers.
Exploring Vial Fillers: Key Functions and Applications
Vial fillers are specialized machines designed to accurately fill liquid medications into glass or plastic vials with precision and speed, ensuring sterile conditions essential for pharmaceutical production. They support various vial sizes and are integral to high-throughput environments, offering features like automatic capping, labeling, and quality inspection to maintain product integrity. Your choice of a vial filler enhances efficiency and compliance with strict industry standards in vaccine, injectable, and biotech manufacturing.
Efficiency Comparison: Cartridge Filler vs Vial Filler
Cartridge fillers generally offer higher efficiency with faster fill speeds and less downtime due to simpler design and fewer parts compared to vial fillers. Vial fillers provide more precise dosing and are better suited for products requiring aseptic conditions, though they typically have slower throughput and more complex maintenance. Choosing between the two depends on production volume, formulation sensitivity, and packaging requirements.
Precision and Accuracy: Which Filler Performs Better?
Cartridge fillers generally offer higher precision and accuracy due to their specialized design tailored for uniform dosing in small volumes, making them ideal for pharmaceutical applications. Vial fillers, while versatile and suitable for larger batches, often experience slight variances in fill volume because of differing vial sizes and shapes. The choice depends on production requirements, but cartridge fillers typically outperform vial fillers in delivering consistent, exact fills.
Ease of Operation and Maintenance
Cartridge fillers typically offer simpler operation with fewer moving parts, reducing downtime and facilitating quick changeovers between batches. Vial fillers, while capable of higher precision and throughput, often require more complex calibration and cleaning procedures, increasing maintenance efforts. Choosing between cartridge and vial fillers depends on balancing ease of operation with production requirements and cleaning protocols.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Operational Expenses
Cartridge fillers generally require lower upfront investment compared to vial fillers, making them cost-effective for small to medium-scale production. Operational expenses for cartridge fillers tend to be less due to simpler mechanics and faster changeover times, reducing labor costs. Your choice will depend on production volume and product specifications, as vial fillers, while more expensive initially, may offer greater precision and flexibility for larger batches.
Suitability for Different Industries and Products
Cartridge fillers are ideal for industries requiring precise filling of viscous or semi-solid products such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food items, ensuring minimal product waste and contamination. Vial fillers excel in pharmaceutical and biotech sectors where sterile liquid medications and vaccines demand high-speed, aseptic filling with strict compliance to regulatory standards. Both systems adapt to different container sizes and filling volumes, but cartridge fillers offer more flexibility for small-batch production, while vial fillers support large-scale, automated pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Safety and Compliance Considerations
Cartridge fillers and vial fillers differ significantly in safety and compliance considerations due to their design and application. Cartridge fillers often incorporate advanced contamination control features such as closed-system transfers and nitrogen purging to ensure sterile filling, aligning with stringent pharmaceutical FDA and EMA regulations. Vial fillers require robust aseptic processing environments and frequent sterilization protocols to meet GMP standards, minimizing particulate contamination risk and ensuring compliance with USP <797> and <800> guidelines.
Choosing the Right Filler for Your Application
Selecting the right filler depends on your specific packaging needs, with cartridge fillers excelling in precision dosing for small volumes and medicinal cartridges. Vial fillers are ideal for large-scale pharmaceutical production due to their high-speed, automated processes. Understanding your product viscosity and container type ensures your filling operation achieves optimal efficiency and accuracy.
Cartridge Filler vs Vial Filler Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com