Active ingredients are the chemical substances responsible for the therapeutic effects of a medication, while excipients serve as inactive components that aid in the drug's stability, absorption, and administration. Understanding the role of excipients versus active ingredients helps you better comprehend how medications work and their overall formulation.
Table of Comparison
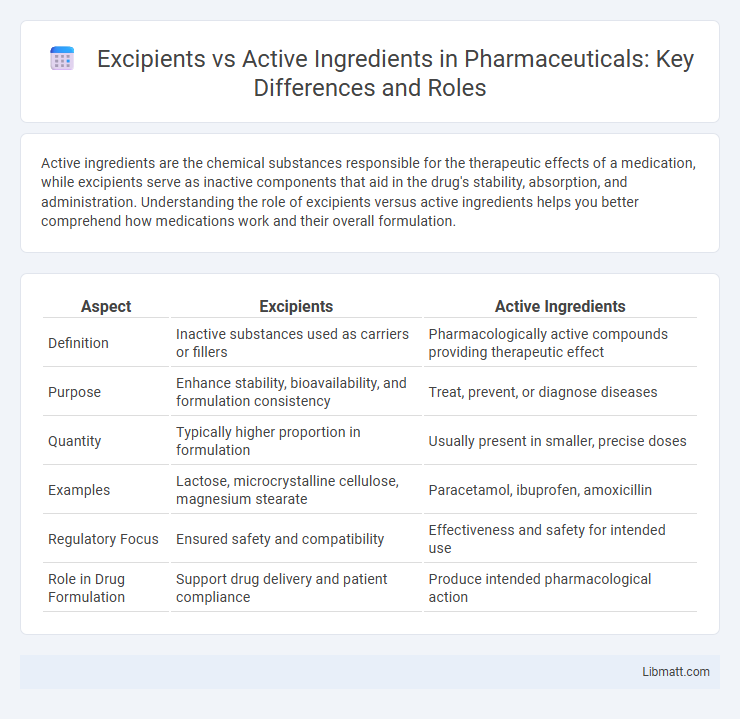
| Aspect | Excipients | Active Ingredients |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inactive substances used as carriers or fillers | Pharmacologically active compounds providing therapeutic effect |
| Purpose | Enhance stability, bioavailability, and formulation consistency | Treat, prevent, or diagnose diseases |
| Quantity | Typically higher proportion in formulation | Usually present in smaller, precise doses |
| Examples | Lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate | Paracetamol, ibuprofen, amoxicillin |
| Regulatory Focus | Ensured safety and compatibility | Effectiveness and safety for intended use |
| Role in Drug Formulation | Support drug delivery and patient compliance | Produce intended pharmacological action |
Introduction to Excipients and Active Ingredients
Active ingredients are the essential compounds in medications responsible for the therapeutic effect, targeting specific medical conditions or symptoms. Excipients serve as inactive substances that support the formulation, stability, and delivery of the active ingredients without impacting the drug's efficacy. Understanding the role of excipients alongside active ingredients is crucial for ensuring your medication's safety, effectiveness, and overall quality.
Defining Excipients: Roles and Functions
Excipients are inactive substances formulated alongside the active ingredient in medications, serving crucial roles such as enhancing drug stability, bioavailability, and patient acceptability. They function as fillers, binders, preservatives, or disintegrants to ensure the active ingredient is delivered effectively and safely. Understanding the distinction between excipients and active ingredients highlights the importance of excipients in optimizing drug performance and formulation quality.
Understanding Active Ingredients: Core Benefits
Active ingredients are the essential compounds responsible for the therapeutic effects in medications, directly targeting specific health conditions. They determine the drug's efficacy, dosage, and safety profile within pharmaceutical formulations. Understanding these core benefits enables precise treatment outcomes and informs drug development processes.
Key Differences Between Excipients and Active Ingredients
Excipients are inactive substances in pharmaceuticals that serve as carriers, stabilizers, or fillers for the active ingredients, which are the compounds responsible for the therapeutic effect. Active ingredients provide the intended medicinal action by targeting specific biological pathways or disease processes, while excipients ensure the formulation's stability, bioavailability, and patient acceptability. The primary difference lies in their function: active ingredients deliver the desired pharmacological response, whereas excipients facilitate the drug's manufacturing, delivery, and overall effectiveness without therapeutic effects themselves.
Common Types of Excipients in Pharmaceuticals
Common types of excipients in pharmaceuticals include binders, which help hold the ingredients together; fillers, which add bulk to the formulation; and disintegrants, which assist in breaking down the tablet for absorption. Other frequently used excipients include lubricants to prevent sticking during manufacturing, preservatives to extend shelf life, and flavoring agents to improve taste. Understanding these excipients can help you recognize how they support the effectiveness and stability of active ingredients in your medications.
Importance of Active Ingredients in Drug Formulation
Active ingredients are the essential components in drug formulation responsible for the therapeutic effect and pharmacological action. While excipients serve as carriers or stabilizers, the efficacy and safety of a medication depend primarily on the quality, concentration, and bioavailability of its active ingredients. Ensuring consistent dosage and purity of active ingredients is crucial for achieving the desired treatment outcomes and maintaining patient trust in your medication.
Safety, Regulations, and Quality Control
Active ingredients must comply with stringent regulatory standards to ensure therapeutic efficacy and patient safety, while excipients undergo rigorous evaluation for toxicity, allergenicity, and interaction potential. Safety assessments focus on excipient biocompatibility and absence of harmful contaminants, supported by guidelines from agencies like FDA, EMA, and ICH. Quality control protocols include identity, purity, and potency testing of active ingredients alongside excipient characterization to maintain formulation stability and performance.
Impact on Drug Efficacy and Stability
Active ingredients determine the drug's therapeutic effect by interacting with biological targets, while excipients influence drug efficacy indirectly through their role in drug formulation, affecting absorption and bioavailability. Excipients contribute significantly to the stability of the active ingredient by protecting it from degradation caused by environmental factors such as moisture, light, and temperature. The careful selection of excipients enhances drug stability and ensures consistent efficacy throughout the product's shelf life.
Challenges in Formulation: Balancing Excipients and Actives
Formulation challenges arise from the need to balance excipients and active ingredients to ensure stability, efficacy, and patient safety. Excipients must support the active ingredient's bioavailability without causing adverse reactions or compromising the drug's therapeutic effect. Optimizing this balance requires extensive compatibility testing and careful selection of excipient types, concentrations, and physicochemical properties.
Conclusion: Why Both Components Matter in Medication
Excipients and active ingredients both play crucial roles in medication effectiveness and safety, with active ingredients delivering therapeutic effects while excipients aid in stability, absorption, and patient compliance. Neglecting excipient quality can compromise drug delivery and cause adverse reactions, emphasizing their importance alongside active components. Optimal drug formulation requires balanced integration of both to ensure maximum efficacy and safety in pharmaceutical treatments.
Excipients vs Active Ingredients Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com