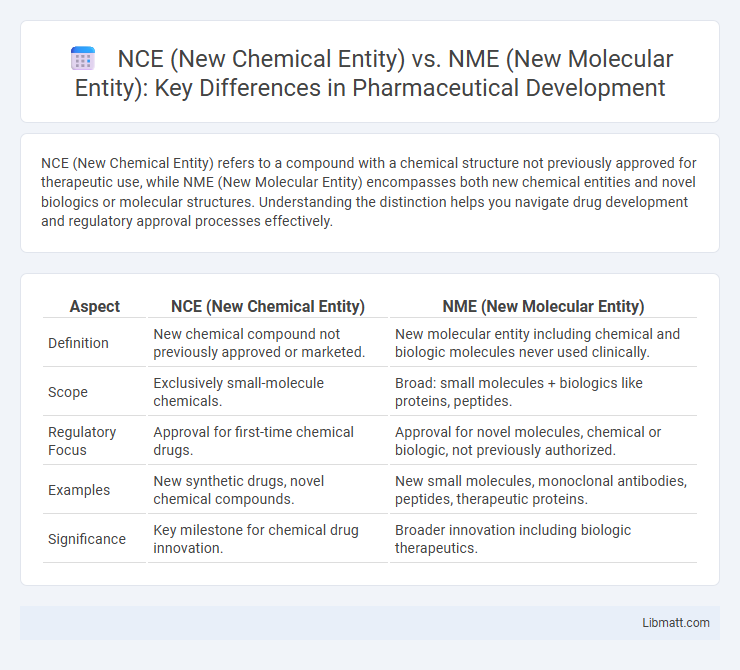
NCE (New Chemical Entity) refers to a compound with a chemical structure not previously approved for therapeutic use, while NME (New Molecular Entity) encompasses both new chemical entities and novel biologics or molecular structures. Understanding the distinction helps you navigate drug development and regulatory approval processes effectively.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | NCE (New Chemical Entity) | NME (New Molecular Entity) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | New chemical compound not previously approved or marketed. | New molecular entity including chemical and biologic molecules never used clinically. |
| Scope | Exclusively small-molecule chemicals. | Broad: small molecules + biologics like proteins, peptides. |
| Regulatory Focus | Approval for first-time chemical drugs. | Approval for novel molecules, chemical or biologic, not previously authorized. |
| Examples | New synthetic drugs, novel chemical compounds. | New small molecules, monoclonal antibodies, peptides, therapeutic proteins. |
| Significance | Key milestone for chemical drug innovation. | Broader innovation including biologic therapeutics. |
Introduction to NCE and NME
New Chemical Entity (NCE) and New Molecular Entity (NME) both refer to novel compounds under drug development, yet NCE specifically highlights chemically synthesized molecules, while NME encompasses all new molecular structures including biologics. Drug regulatory agencies use these terms to classify innovative treatments that contain no previously approved active ingredients, supporting the advancement of unique therapeutic options. Understanding the distinction helps you navigate pharmaceutical innovation and regulatory processes effectively.
Defining New Chemical Entity (NCE)
A New Chemical Entity (NCE) refers to a compound with a novel chemical structure that has not been previously approved or marketed as a drug. NCEs represent unique molecules with potential therapeutic effects, distinct from existing drugs, and are crucial in the pharmaceutical industry for innovation and patent protection. Your understanding of NCEs is essential for recognizing their role in drug development and regulatory approval processes, differentiating them from New Molecular Entities (NMEs), which might include biologics or other non-chemical substances.
Defining New Molecular Entity (NME)
New Molecular Entity (NME) refers to a drug that contains an active ingredient never previously approved by regulatory authorities, marking a novel molecular structure or compound. NMEs represent innovative therapeutic options by introducing unique mechanisms of action, distinct from existing medications. Regulatory agencies evaluate NMEs rigorously to assess safety, efficacy, and potential benefits in treating specific medical conditions.
Regulatory Perspectives on NCE vs NME
Regulatory authorities such as the FDA and EMA often use the terms NCE (New Chemical Entity) and NME (New Molecular Entity) interchangeably to classify drugs that contain active substances not previously approved. The distinction lies in the NCE specifically referring to new chemical compounds, whereas NME may encompass biologics or other novel molecular structures beyond traditional chemicals. Regulatory evaluation for both focuses on demonstrating safety, efficacy, and manufacturing quality, with specific guidelines tailored to the chemical or molecular nature of the entity.
Key Differences Between NCE and NME
NCE (New Chemical Entity) refers specifically to a compound with a novel chemical structure that has not been previously approved for therapeutic use. NME (New Molecular Entity) encompasses NCEs but also includes biologics, peptides, and other molecular structures as new drug candidates. Understanding the distinction between NCE and NME is crucial for regulatory submissions and drug development strategies, as your choice impacts the approval pathway and patent considerations.
Importance in Drug Development
NCE (New Chemical Entity) and NME (New Molecular Entity) are critical concepts in drug development, representing compounds with novel chemical structures not previously approved for therapeutic use. Their importance lies in their potential to address unmet medical needs by offering new mechanisms of action and improved efficacy or safety profiles compared to existing drugs. Approval of NCEs and NMEs signifies innovation, driving pharmaceutical pipelines and expanding treatment options across diverse disease areas.
Examples of NCEs and NMEs
NCEs (New Chemical Entities) include innovative small molecule drugs like aspirin or sildenafil, representing entirely novel chemical compounds not previously approved. NMEs (New Molecular Entities) encompass both small molecules and biologics, such as monoclonal antibodies like pembrolizumab, that introduce new active ingredients to the market. Both terms highlight groundbreaking therapeutic substances, with NME serving as a broader category including NCEs and newly approved biologics.
Impact on Patenting and Exclusivity
NCE (New Chemical Entity) and NME (New Molecular Entity) both represent novel compounds eligible for patent protection, granting exclusive commercial rights that can last up to 20 years from the filing date. Patenting NCEs often results in stronger intellectual property barriers due to their unique chemical structures, which translate into prolonged market exclusivity periods and delayed generic competition. Regulatory agencies commonly use these designations to determine exclusivity terms, impacting drug development strategies and investment returns in the pharmaceutical industry.
Challenges in Classification
Classifying New Chemical Entities (NCEs) and New Molecular Entities (NMEs) presents challenges due to overlapping definitions and regulatory ambiguities. Both terms refer to novel compounds, but NCEs emphasize chemical novelty while NMEs include broader molecular innovations, making precise categorization complex. Your understanding of these distinctions is crucial for accurate regulatory submissions and patent protections.
Future Trends in NCE and NME Development
Future trends in NCE and NME development focus on leveraging advanced technologies like AI-driven drug design and high-throughput screening to accelerate discovery phases. Personalized medicine and precision therapies increasingly shape the pipeline, emphasizing molecular innovation tailored to specific genetic profiles. Your investment in integrating bioinformatics and novel biomarker identification will enhance the efficiency and success rates of developing groundbreaking chemical and molecular entities.
NCE (New Chemical Entity) vs NME (New Molecular Entity) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com