Biodegradable plastics break down naturally through microbial activity but may take longer and leave residues, while compostable plastics decompose fully into non-toxic components within a specific timeframe under industrial composting conditions. Choosing compostable options supports Your efforts to reduce environmental impact by ensuring complete material breakdown without harmful byproducts.
Table of Comparison
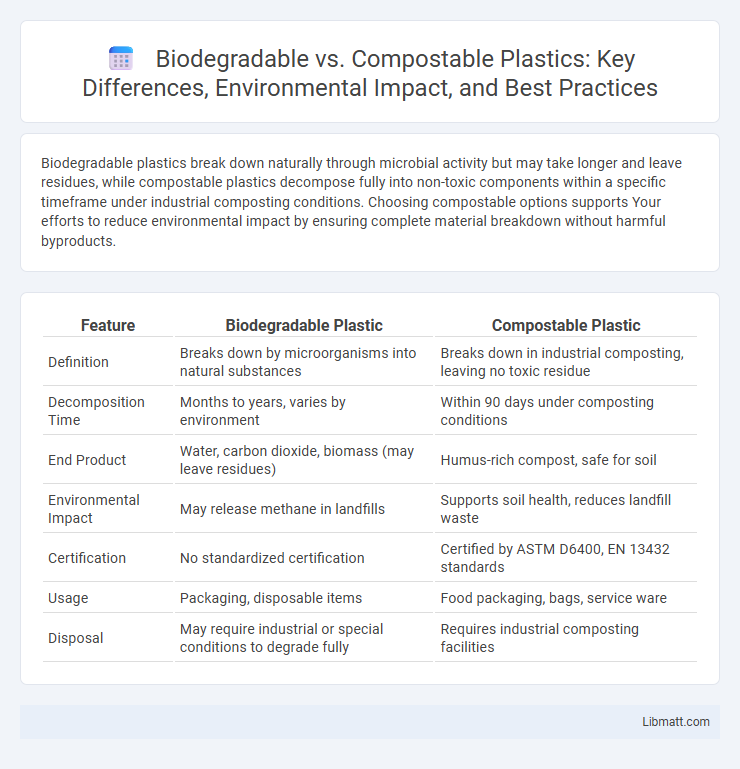
| Feature | Biodegradable Plastic | Compostable Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Breaks down by microorganisms into natural substances | Breaks down in industrial composting, leaving no toxic residue |
| Decomposition Time | Months to years, varies by environment | Within 90 days under composting conditions |
| End Product | Water, carbon dioxide, biomass (may leave residues) | Humus-rich compost, safe for soil |
| Environmental Impact | May release methane in landfills | Supports soil health, reduces landfill waste |
| Certification | No standardized certification | Certified by ASTM D6400, EN 13432 standards |
| Usage | Packaging, disposable items | Food packaging, bags, service ware |
| Disposal | May require industrial or special conditions to degrade fully | Requires industrial composting facilities |
Understanding Biodegradable and Compostable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics break down into natural elements through microbial activity over time but may leave behind microplastics or residues. Compostable plastics, by contrast, decompose fully into non-toxic components under specific composting conditions, typically within 180 days, ensuring zero harmful residues. Understanding these differences helps you choose materials that align with environmental goals and waste management systems effectively.
Key Differences Between Biodegradable and Compostable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics break down through microbial activity over time but may leave behind microplastics or residues, while compostable plastics disintegrate completely into non-toxic components within a specific timeframe in industrial composting facilities. The key difference lies in compostable plastics meeting strict standards like ASTM D6400, ensuring safe decomposition, unlike biodegradable variants that lack consistent criteria. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose environmentally friendly products that align with proper disposal methods and reduce ecological impact.
How Biodegradable Plastics Break Down
Biodegradable plastics break down through the action of naturally occurring microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and algae, which metabolize the plastic into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. This process depends heavily on environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, and oxygen availability, with some biodegradable plastics requiring industrial composting facilities for complete degradation. Understanding how your biodegradable plastic disposes is crucial for minimizing environmental impact and ensuring it breaks down effectively.
Compostable Plastics: Definition and Requirements
Compostable plastics are designed to break down into non-toxic components such as carbon dioxide, water, and biomass within a specific timeframe under industrial composting conditions. These plastics must meet strict standards like ASTM D6400 or EN 13432, ensuring they disintegrate completely without leaving harmful residues. Your choice of compostable plastics supports sustainable waste management by facilitating nutrient recycling in composting facilities.
Environmental Impact of Biodegradable vs Compostable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics break down through microbial activity but can leave harmful residues or microplastics, posing long-term environmental risks. Compostable plastics, certified to degrade within specific timeframes under industrial composting conditions, minimize pollution by converting into non-toxic organic matter. Understanding the environmental impact of these materials helps ensure Your choice supports sustainable waste management and reduces landfill burden.
Certifications and Industry Standards
Biodegradable plastics certified by standards such as ASTM D6400 or EN 13432 ensure the material breaks down under specific conditions without leaving toxic residues. Compostable plastics meet stricter certifications, guaranteeing complete decomposition into non-toxic components within industrial composting facilities, aligning with standards like the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) certification. Understanding these certifications helps you choose plastics that comply with environmental regulations and support sustainable waste management practices.
Common Applications and Product Examples
Biodegradable plastics are commonly used in single-use items like grocery bags, food packaging, and disposable cutlery, as they break down under natural conditions but may leave residues. Compostable plastics are designed for commercial or home composting environments, often found in food service items such as coffee pods, plates, and mulch films, fully degrading into non-toxic components. Understanding your product's disposal method ensures it aligns with appropriate waste management systems, reducing environmental impact.
Challenges in Waste Management and Recycling
Biodegradable and compostable plastics present significant challenges in waste management due to their varying degradation rates and conditions, which complicate sorting and processing in recycling facilities. Contamination from mixing these plastics with conventional plastics often leads to reduced efficiency and increased costs in recycling streams. Effective infrastructure upgrades and clear labeling standards are essential to mitigate the impact on recycling systems and ensure proper disposal.
Consumer Awareness and Labeling Issues
Consumer awareness of biodegradable versus compostable plastics remains limited due to confusing labeling and inconsistent standards, which often leads to improper disposal. Clear, standardized labels indicating environmental impact and disposal methods are essential to help you make informed choices and reduce contamination in recycling and composting facilities. Improving transparency in product certification can enhance trust and promote responsible consumption of eco-friendly plastics.
Future Trends and Innovations in Sustainable Plastics
Future trends in sustainable plastics emphasize the development of advanced biodegradable and compostable materials derived from renewable resources like plant-based polymers and algae, enhancing degradation rates without toxic residues. Innovations include enzyme-engineered plastics that accelerate breakdown in various environments and smart packaging integrating sensors to optimize compost conditions. Your adoption of these cutting-edge sustainable plastics can significantly reduce environmental impact and support circular economy initiatives in the packaging industry.
Biodegradable vs compostable plastic Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com