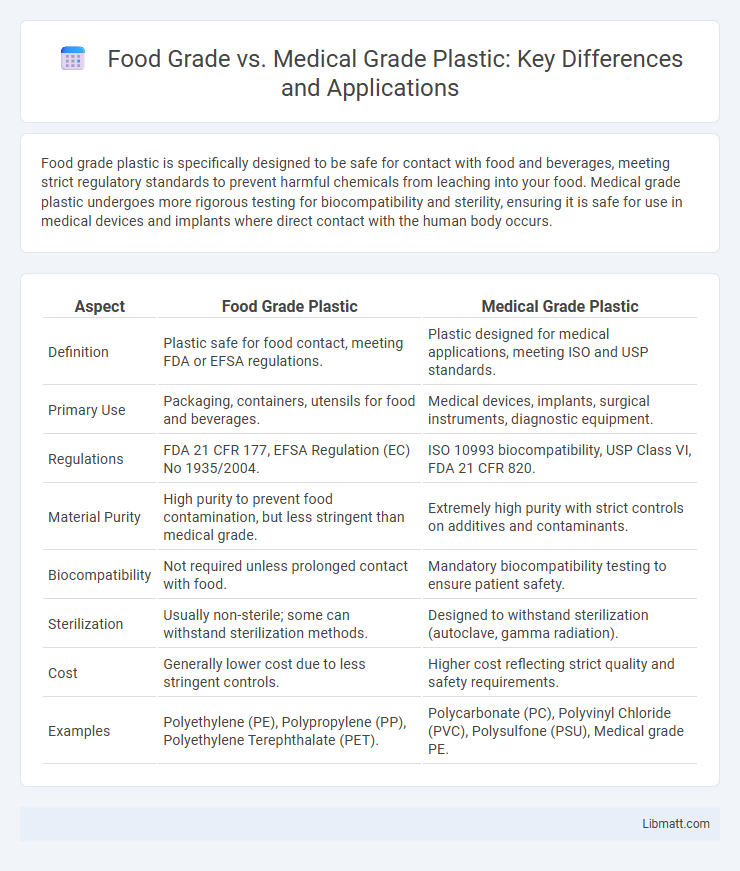
Food grade plastic is specifically designed to be safe for contact with food and beverages, meeting strict regulatory standards to prevent harmful chemicals from leaching into your food. Medical grade plastic undergoes more rigorous testing for biocompatibility and sterility, ensuring it is safe for use in medical devices and implants where direct contact with the human body occurs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Food Grade Plastic | Medical Grade Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plastic safe for food contact, meeting FDA or EFSA regulations. | Plastic designed for medical applications, meeting ISO and USP standards. |
| Primary Use | Packaging, containers, utensils for food and beverages. | Medical devices, implants, surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment. |
| Regulations | FDA 21 CFR 177, EFSA Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. | ISO 10993 biocompatibility, USP Class VI, FDA 21 CFR 820. |
| Material Purity | High purity to prevent food contamination, but less stringent than medical grade. | Extremely high purity with strict controls on additives and contaminants. |
| Biocompatibility | Not required unless prolonged contact with food. | Mandatory biocompatibility testing to ensure patient safety. |
| Sterilization | Usually non-sterile; some can withstand sterilization methods. | Designed to withstand sterilization (autoclave, gamma radiation). |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to less stringent controls. | Higher cost reflecting strict quality and safety requirements. |
| Examples | Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). | Polycarbonate (PC), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Polysulfone (PSU), Medical grade PE. |
Introduction to Food Grade and Medical Grade Plastics
Food grade plastic is designed to safely store and handle consumables without contaminating food, meeting strict regulatory standards like FDA or EFSA approvals. Medical grade plastic is engineered to endure sterilization processes and maintain biocompatibility, essential for use in medical devices and implants. Both types of plastic differ significantly in chemical composition, durability, and compliance requirements tailored to their specific applications.
Defining Food Grade Plastic
Food grade plastic is defined by its compliance with safety standards set by regulatory agencies like the FDA, ensuring it is free from harmful chemicals that could leach into food. It is specifically engineered to maintain food safety by resisting contamination and withstanding different temperatures encountered during food storage and processing. Materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and PET are commonly used for food grade plastics due to their inert properties and durability in direct contact with edible products.
What Qualifies as Medical Grade Plastic?
Medical grade plastic qualifies based on strict biocompatibility standards, ensuring safety for direct and prolonged contact with the human body. It undergoes rigorous testing for toxicity, sterilization compatibility, and chemical resistance, distinguishing it from food grade plastic designed primarily for safe food storage. Your medical applications require such materials certified to meet FDA or ISO 10993 standards to prevent adverse reactions and maintain sterility.
Key Differences Between Food Grade and Medical Grade Plastics
Food grade plastics are designed to meet strict safety standards for contact with consumables, ensuring non-toxicity, resistance to chemicals, and prevention of contamination. Medical grade plastics must adhere to even more rigorous regulations, including biocompatibility, sterilization capability, and stringent purity requirements to ensure safety in direct contact with body tissues or fluids. The primary differences lie in their regulatory certifications, performance under sterilization processes, and suitability for use in medical devices versus food packaging.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Food grade plastic complies with FDA and EFSA regulations ensuring it is safe for direct contact with consumables, while medical grade plastic adheres to stricter standards such as ISO 10993 and USP Class VI for biocompatibility and sterility. Your choice depends on whether the application involves ingestion or invasive medical use, as medical grade plastics undergo extensive testing to meet health and safety certifications required for implants or medical devices. Understanding these regulatory standards is crucial for selecting the appropriate plastic to ensure safety and compliance in your specific industry.
Common Applications in Food and Medical Industries
Food grade plastic is widely used in containers, packaging, and utensils due to its non-toxic, BPA-free composition that ensures food safety and prevents contamination. Medical grade plastic, characterized by its sterility and biocompatibility, is essential for manufacturing surgical instruments, implantable devices, and diagnostic equipment components. Both plastics meet stringent regulatory standards, with food grade plastics adhering to FDA and EU food contact regulations, while medical grade plastics comply with ISO 10993 and USP Class VI certifications.
Types of Plastics Used in Food and Medical Contexts
Food grade plastics commonly include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET), chosen for their non-toxic properties and resistance to chemicals, making them ideal for packaging and storage. Medical grade plastics such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polycarbonate (PC), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) are specially engineered to meet stringent sterilization and biocompatibility standards used in devices and implants. These plastics differ significantly in material composition, with medical grade plastics undergoing rigorous testing to ensure safety in clinical environments, contrasting the food grade plastics' focus on food-contact safety and durability.
Safety, Toxicity, and Performance Considerations
Food grade plastic is engineered to meet strict safety standards set by regulatory bodies like the FDA, ensuring low toxicity and safe contact with consumables, while medical grade plastic adheres to even higher purity and biocompatibility requirements necessary for patient safety and sterilization. Food grade plastics prioritize resistance to food acids, fats, and temperature variations to maintain safety and taste, whereas medical grade plastics are optimized for performance in surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic devices, emphasizing durability, sterilization compatibility, and minimal leaching of harmful substances. Both classifications undergo rigorous testing, but medical grade plastics demand superior mechanical properties and stringent chemical inertness to reduce infection risks and ensure long-term biocompatibility.
Choosing the Right Plastic: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right plastic involves prioritizing safety standards and intended use, where food grade plastics comply with FDA regulations to prevent harmful chemical leaching into food, while medical grade plastics meet stricter biocompatibility and sterilization requirements for medical applications. Key factors include chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and regulatory certifications such as FDA, USP Class VI, or ISO 10993 to ensure material suitability. Durability, potential exposure to bodily fluids or food items, and environmental conditions also influence whether food grade or medical grade plastic is appropriate for a specific application.
Future Trends in Food and Medical Grade Plastics
Future trends in food and medical grade plastics emphasize sustainability, with increasing development of biodegradable and compostable materials designed to reduce environmental impact while maintaining safety standards. Innovations in antimicrobial and nanocomposite plastics enhance hygiene and durability, crucial for applications in sterile medical environments and food packaging. Regulatory bodies are pushing for stricter compliance and transparency, driving advancements in bio-based polymers and recyclable materials that align with circular economy principles.
Food grade vs medical grade plastic Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com