Nylon 6/12 offers a unique balance of flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and dimensional stability. Your choice between Nylon 6/12 and Nylon 12 depends on the specific mechanical properties and environmental conditions needed for optimal performance.
Table of Comparison
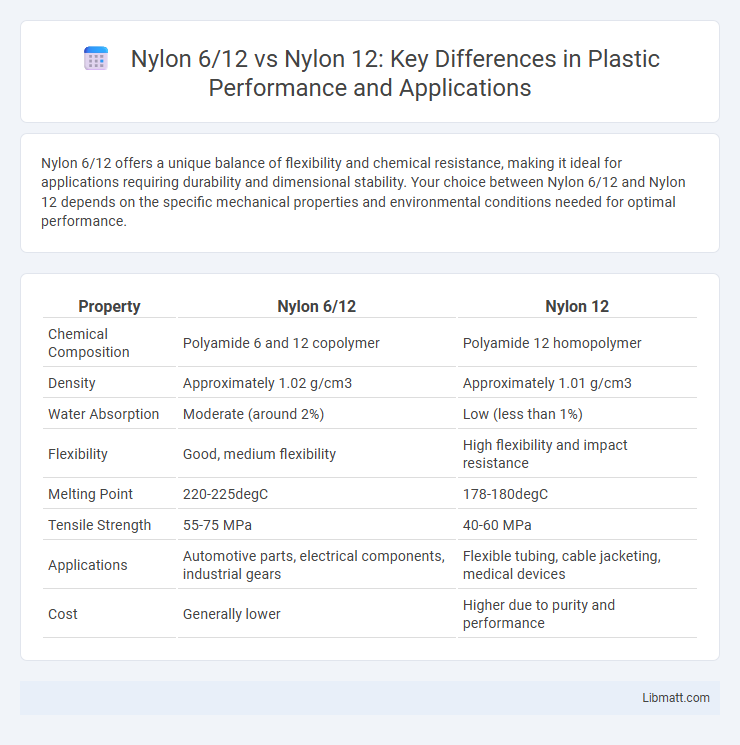
| Property | Nylon 6/12 | Nylon 12 |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Polyamide 6 and 12 copolymer | Polyamide 12 homopolymer |
| Density | Approximately 1.02 g/cm3 | Approximately 1.01 g/cm3 |
| Water Absorption | Moderate (around 2%) | Low (less than 1%) |
| Flexibility | Good, medium flexibility | High flexibility and impact resistance |
| Melting Point | 220-225degC | 178-180degC |
| Tensile Strength | 55-75 MPa | 40-60 MPa |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electrical components, industrial gears | Flexible tubing, cable jacketing, medical devices |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to purity and performance |
Introduction to Nylon 6/12 and Nylon 12
Nylon 6/12 is a copolymer composed of six and twelve carbon atoms in its monomers, offering a balance of flexibility, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption. Nylon 12, a homopolymer with twelve carbon atoms, features superior abrasion resistance, excellent dimensional stability, and very low water absorption. Both materials are widely used in automotive, electrical, and consumer goods industries due to their durability and versatile mechanical properties.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Nylon 6/12 features a copolymer structure combining hexamethylene diamine with both adipic acid and laurolactam, resulting in alternating amide linkages that provide a balance of flexibility and chemical resistance. Nylon 12 consists solely of laurolactam-derived repeating units, giving it a more linear and less crystalline structure, which enhances its toughness and low moisture absorption. The chemical differences influence their thermal properties and mechanical behavior, with Nylon 6/12 offering improved dimensional stability compared to the more elastomeric nature of Nylon 12.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Nylon 6/12 offers superior chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption compared to Nylon 12, making it ideal for applications requiring dimensional stability in humid environments. Its tensile strength and impact resistance are generally higher, providing enhanced durability under mechanical stress, whereas Nylon 12 excels with greater flexibility and elongation at break. Your choice between these materials should consider the balance between strength and flexibility required for optimal performance in specific engineering or industrial applications.
Moisture Absorption Differences
Nylon 6/12 absorbs more moisture than Nylon 12 due to its higher amide group content, which attracts water molecules. This increased moisture absorption in Nylon 6/12 can lead to dimensional changes and reduced mechanical properties under humid conditions. Choosing Nylon 12 for your applications ensures better moisture resistance and improved stability in damp environments.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Nylon 6/12 offers enhanced thermal stability compared to Nylon 12 due to its higher melting point, making it suitable for applications requiring resistance to elevated temperatures. Nylon 12 provides superior flexibility and impact resistance but tends to have a lower thermal endurance, limiting its use in high-heat environments. Your choice between these materials should consider the specific thermal performance needs of your project to ensure optimal durability and functionality.
Processing and Molding Characteristics
Nylon 6/12 offers improved dimensional stability and lower moisture absorption compared to Nylon 12, enhancing its processing and molding performance in demanding applications. It features a higher melting point, which provides better thermal resistance during molding, resulting in more precise and consistent part formation. Nylon 12 processes faster due to its lower melting temperature but may suffer from greater shrinkage and warpage, making Nylon 6/12 preferable for complex, high-precision components.
Applications and Industry Uses
Nylon 6/12 offers a balance of chemical resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for automotive fuel lines, electrical connectors, and industrial tubing. Nylon 12 excels in flexibility, low moisture absorption, and abrasion resistance, widely used in medical devices, sporting goods, and flexible tubing. Your choice between Nylon 6/12 and Nylon 12 depends on specific application requirements like durability, chemical exposure, and environmental conditions.
Cost and Availability
Nylon 6/12 generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to Nylon 12, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects without significantly compromising performance. Nylon 12, known for its superior flexibility and chemical resistance, tends to be less readily available and commands higher prices due to its specialized applications and manufacturing complexities. Your choice between these materials will depend on balancing cost considerations with the specific availability and performance requirements of your application.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nylon 6/12 and Nylon 12 differ significantly in environmental impact, with Nylon 12 often favored for its lower carbon footprint and reduced greenhouse gas emissions during production. Nylon 6/12 typically requires more energy and resources, resulting in higher environmental costs, whereas Nylon 12's synthesis from renewable monomers enhances its sustainability profile. Choosing Nylon 12 for your applications supports eco-conscious manufacturing by minimizing waste and promoting recyclable, biodegradable materials.
Choosing Between Nylon 6/12 and Nylon 12
Choosing between Nylon 6/12 and Nylon 12 depends on your specific application requirements such as mechanical strength, flexibility, and moisture absorption. Nylon 6/12 offers a balance of toughness and chemical resistance, making it suitable for automotive and industrial parts, while Nylon 12 provides superior flexibility and lower water uptake, ideal for applications requiring dimensional stability and fatigue resistance. Evaluating these material properties ensures you select the optimal nylon type for performance and durability in your project.
Nylon 6/12 vs Nylon 12 Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com