Polystyrene offers rigidity and clarity, making it ideal for packaging and disposable cutlery, while polypropylene provides superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, suited for automotive parts and reusable containers. Understanding the differences between these plastics can help you select the right material for durability and specific application needs.
Table of Comparison
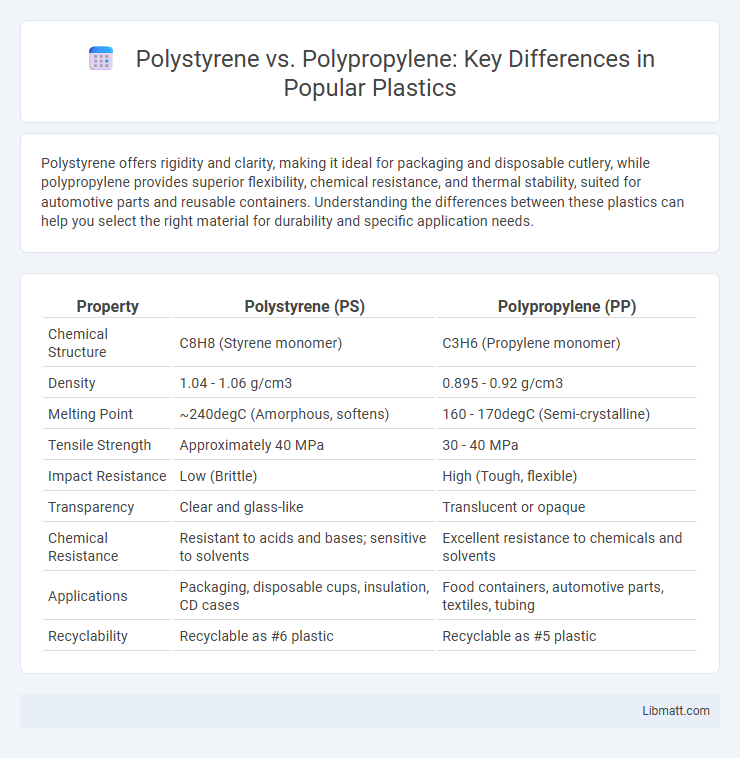
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | C8H8 (Styrene monomer) | C3H6 (Propylene monomer) |
| Density | 1.04 - 1.06 g/cm3 | 0.895 - 0.92 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | ~240degC (Amorphous, softens) | 160 - 170degC (Semi-crystalline) |
| Tensile Strength | Approximately 40 MPa | 30 - 40 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Low (Brittle) | High (Tough, flexible) |
| Transparency | Clear and glass-like | Translucent or opaque |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and bases; sensitive to solvents | Excellent resistance to chemicals and solvents |
| Applications | Packaging, disposable cups, insulation, CD cases | Food containers, automotive parts, textiles, tubing |
| Recyclability | Recyclable as #6 plastic | Recyclable as #5 plastic |
Introduction to Polystyrene and Polypropylene
Polystyrene is a versatile thermoplastic known for its rigidity, clarity, and ease of molding, commonly used in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation. Polypropylene, a durable and flexible polymer, is prized for its resistance to chemicals, fatigue, and high temperatures, making it ideal for automotive parts, textiles, and container lids. Understanding the properties of polystyrene and polypropylene helps you select the right material for your specific application needs.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Polystyrene consists of a phenyl group attached to every other carbon atom in its hydrocarbon backbone, resulting in rigidity and clarity, while polypropylene features a methyl group on every other carbon, providing flexibility and higher chemical resistance. Polystyrene's brittle nature and low melting point contrast with polypropylene's toughness, fatigue resistance, and melting point around 160degC. Understanding these chemical structures helps you select the ideal polymer for applications requiring specific mechanical strength, thermal stability, or chemical durability.
Manufacturing Processes
Polystyrene is produced through the polymerization of styrene monomers using suspension or bulk polymerization techniques, which enable the formation of rigid or foam products with precise control over density and texture. Polypropylene is manufactured via chain-growth polymerization of propylene monomers, predominantly employing gas-phase, slurry, or solution polymerization methods that yield materials with high crystallinity and heat resistance. Your choice between polystyrene and polypropylene depends on the specific manufacturing processes that influence factors such as product strength, flexibility, and thermal stability.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polypropylene offers superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to polystyrene, which is more rigid but brittle under stress. Polystyrene exhibits higher tensile strength, making it suitable for applications requiring stiffness, while polypropylene's mechanical strength allows better durability and fatigue resistance. Your choice depends on whether flexibility or rigidity is paramount for the intended use.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Polystyrene exhibits lower thermal resistance, typically with a maximum continuous use temperature around 70degC, making it prone to deformation under heat. Polypropylene offers superior thermal stability with a higher melting point near 160degC, allowing for better performance in high-temperature applications. The enhanced thermal resistance of polypropylene makes it ideal for automotive parts, food containers, and household goods requiring durability under heat stress.
Applications in Various Industries
Polystyrene is widely used in packaging, insulation, and disposable consumer products due to its rigidity and clarity, making it ideal for food containers, CD cases, and protective packaging. Polypropylene finds extensive application in automotive parts, textiles, and medical devices, prized for its chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability, often used in battery cases, ropes, and surgical instruments. Both polymers serve crucial roles across industries, with polystyrene excelling in lightweight protection and polypropylene providing robust performance under mechanical stress.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Polystyrene (PS) poses significant environmental challenges due to its slow biodegradation process and the difficulty of recycling, often ending up in landfills and oceans where it persists for hundreds of years. Polypropylene (PP), on the other hand, offers a more environmentally friendly profile with higher recyclability rates and lower ecological toxicity, making it a preferred choice for sustainable packaging solutions. Advances in recycling technology have improved PP's circular economy potential, reducing landfill waste and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to polystyrene products.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polystyrene generally costs more due to its rigid structure and applications in packaging and insulation, while polypropylene is cheaper, favored for its versatility and durability in automotive and consumer goods. Market availability of polypropylene is higher globally because of its extensive use in various industries, whereas polystyrene supply is more limited and region-specific. Price fluctuations for both polymers are influenced by raw material costs and demand changes in manufacturing sectors.
Pros and Cons of Polystyrene vs Polypropylene
Polystyrene offers excellent rigidity, thermal insulation, and ease of molding but suffers from brittleness and poor chemical resistance compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene provides superior flexibility, high impact resistance, and better resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for durable applications; however, it has lower clarity and can be more difficult to paint or glue. Choosing between polystyrene and polypropylene depends on specific needs such as structural strength versus flexibility and chemical exposure.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors to Consider
Choosing between polystyrene and polypropylene depends on factors such as durability, flexibility, and temperature resistance. Polystyrene offers rigidity and clarity, making it ideal for packaging and disposable items, while polypropylene excels in chemical resistance and flexibility, suitable for reusable containers and automotive parts. Understanding your product's exposure to stress, heat, and chemicals ensures you select the most appropriate material for longevity and performance.
Polystyrene vs Polypropylene Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com