CNC machining offers high precision and customization by removing material from a solid block, making it ideal for complex prototypes and low-volume production. Plastic casting, on the other hand, is cost-effective for mass production with intricate shapes but may have limitations in detail accuracy compared to CNC machining.
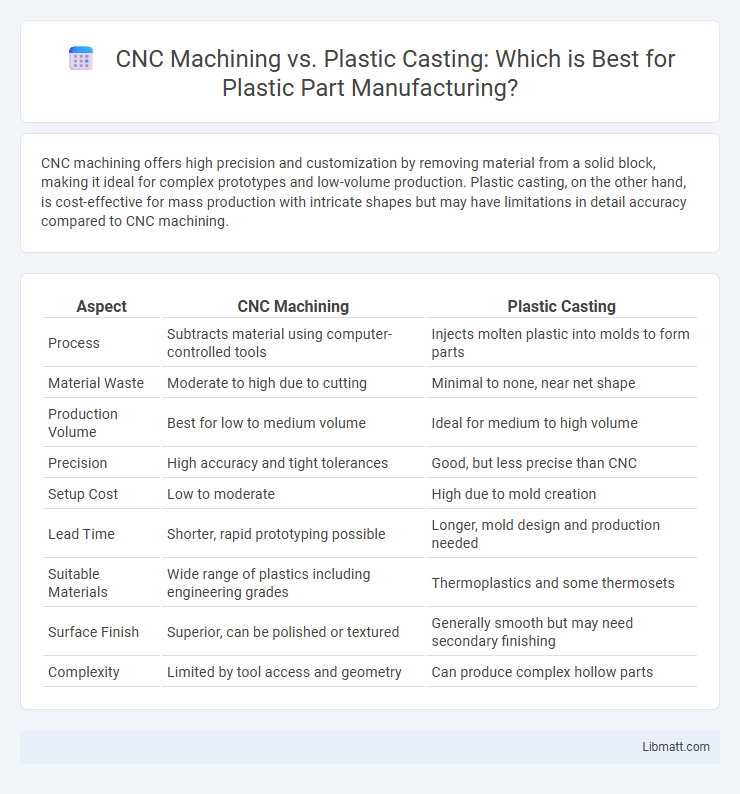
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | CNC Machining | Plastic Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Subtracts material using computer-controlled tools | Injects molten plastic into molds to form parts |
| Material Waste | Moderate to high due to cutting | Minimal to none, near net shape |
| Production Volume | Best for low to medium volume | Ideal for medium to high volume |
| Precision | High accuracy and tight tolerances | Good, but less precise than CNC |
| Setup Cost | Low to moderate | High due to mold creation |
| Lead Time | Shorter, rapid prototyping possible | Longer, mold design and production needed |
| Suitable Materials | Wide range of plastics including engineering grades | Thermoplastics and some thermosets |
| Surface Finish | Superior, can be polished or textured | Generally smooth but may need secondary finishing |
| Complexity | Limited by tool access and geometry | Can produce complex hollow parts |
Overview: CNC Machining vs Plastic Casting
CNC machining offers precise and repeatable fabrication by removing material from solid blocks using computer-controlled tools, ideal for complex geometries and tight tolerances. Plastic casting involves pouring molten plastic into molds, enabling cost-effective mass production with intricate shapes but less dimensional accuracy. Your choice depends on factors like production volume, material properties, and required precision.
Material Compatibility and Selection
CNC machining offers broad material compatibility, enabling precise shaping of metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as various plastics such as ABS and polycarbonate, ideal for prototypes and low to medium volume production. Plastic casting primarily suits thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers, including materials like epoxy, polyurethane, and silicone, which allow for complex geometries and high-volume manufacturing at lower costs. Selection depends on mechanical properties required, production volume, and material behavior under machining or molding processes, influencing final product durability and finish.
Production Speed and Turnaround Time
CNC machining offers faster production speed for low to medium volume runs due to its precision and automation, enabling quick design changes without the need for new tooling. Plastic casting requires longer lead times because it involves creating molds, which is time-consuming but becomes more efficient for high-volume production. Turnaround time for CNC machining is typically shorter, making it ideal for prototyping and small batch manufacturing.
Cost Comparison: Tooling and Manufacturing
CNC machining typically incurs higher initial costs due to complex tooling and setup but offers cost efficiency for low to medium production volumes through precise material usage and reduced waste. Plastic casting features lower initial tooling expenses, making it more economical for high-volume manufacturing, though per-part costs can rise with intricate mold designs. Evaluating production scale and part complexity is crucial to determining the most cost-effective manufacturing process.
Design Complexity and Flexibility
CNC machining excels in handling complex and detailed designs with high precision, allowing for intricate geometries and tight tolerances that are difficult to achieve with plastic casting. Plastic casting offers greater flexibility for producing large volumes of parts with consistent dimensions but is limited in reproducing fine details and rapid design modifications. The choice between CNC machining and plastic casting depends on the complexity of the design and the flexibility required for prototyping or mass production.
Surface Finish and Tolerances
CNC machining delivers superior surface finishes with tight tolerances often within +-0.005 mm, making it ideal for precision parts requiring smooth, detailed surfaces. Plastic casting typically produces rougher surfaces and looser tolerances around +-0.1 mm, suitable for larger, less detailed components where exact dimensions are less critical. The choice between these processes hinges on the desired finish quality and dimensional accuracy for the final product.
Volume Suitability: Prototyping to Mass Production
CNC machining offers exceptional precision and is ideal for low to medium volume production runs, particularly in prototyping where design iterations are frequent. Plastic casting, including injection molding, excels in high-volume manufacturing, delivering consistent part quality and reduced per-unit cost as quantities increase. Selecting the appropriate method depends on production scale, with CNC machining suited for initial prototypes and small batches, while plastic casting supports mass production efficiently.
Environmental Impact and Waste Management
CNC machining generates less plastic waste compared to traditional plastic casting, as it precisely removes material without excess runoff, promoting efficient resource use. Plastic casting often produces higher volumes of scrap and offcuts that require careful disposal or recycling to mitigate environmental harm. Your choice between CNC machining and plastic casting can significantly affect sustainability efforts, with machining offering more control over minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Common Applications in Industry
CNC machining is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries for producing precise metal and plastic components such as engine parts, surgical instruments, and custom prototypes. Plastic casting is commonly applied in consumer goods, electrical enclosures, and toy manufacturing, offering cost-effective production of complex shapes in materials like epoxy, polyurethane, and silicone. Both methods support rapid prototyping and small to medium batch production, with CNC machining excelling in tight tolerances and plastic casting favored for intricate designs and lower tooling costs.
Choosing the Best Solution for Your Project
CNC machining offers high precision and tight tolerances, making it ideal for complex prototypes or low-volume production runs requiring durability and intricate details. Plastic casting suits large-volume manufacturing with cost-effective tooling and rapid production, best for parts with simpler geometries and flexible material options. Evaluating project requirements such as quantity, budget, material properties, and design complexity is crucial to selecting the most efficient and economical manufacturing method.
CNC Machining vs Plastic Casting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com