Hot fill packaging involves filling containers with products at high temperatures to sterilize and seal them, preserving freshness without preservatives. Cold fill packaging, on the other hand, fills containers at lower temperatures, relying on refrigeration and preservatives to maintain product quality and extend shelf life.
Table of Comparison
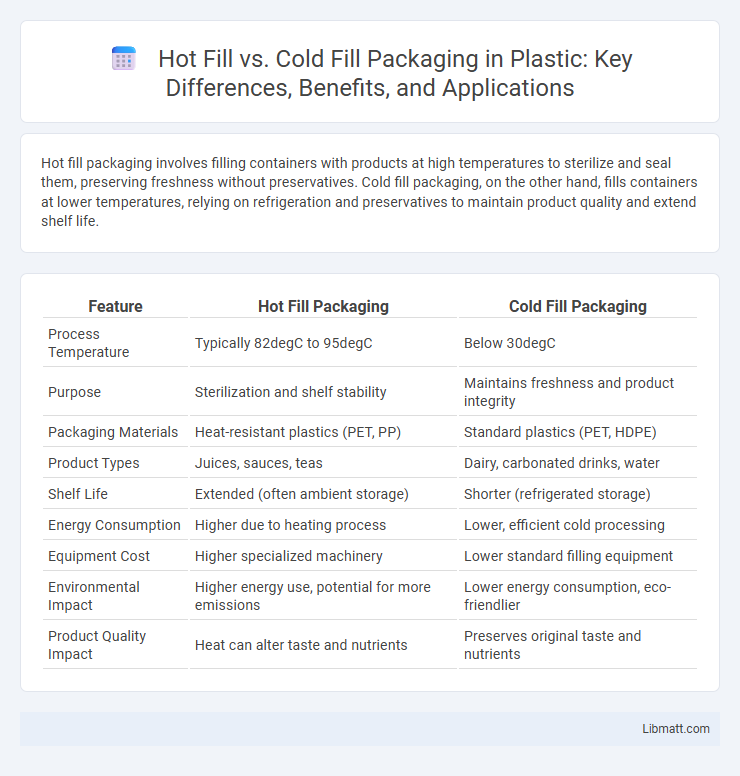
| Feature | Hot Fill Packaging | Cold Fill Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Typically 82degC to 95degC | Below 30degC |
| Purpose | Sterilization and shelf stability | Maintains freshness and product integrity |
| Packaging Materials | Heat-resistant plastics (PET, PP) | Standard plastics (PET, HDPE) |
| Product Types | Juices, sauces, teas | Dairy, carbonated drinks, water |
| Shelf Life | Extended (often ambient storage) | Shorter (refrigerated storage) |
| Energy Consumption | Higher due to heating process | Lower, efficient cold processing |
| Equipment Cost | Higher specialized machinery | Lower standard filling equipment |
| Environmental Impact | Higher energy use, potential for more emissions | Lower energy consumption, eco-friendlier |
| Product Quality Impact | Heat can alter taste and nutrients | Preserves original taste and nutrients |
Introduction to Hot Fill and Cold Fill Packaging
Hot fill packaging involves filling sterilized containers with products heated typically between 180degF to 205degF to eliminate harmful microorganisms, extending shelf life without preservatives. Cold fill packaging, on the other hand, fills products at or near refrigeration temperatures to maintain freshness and nutrient integrity, often requiring preservatives or pasteurization after filling. Understanding these methods helps you select the best packaging process based on your product's stability, safety, and shelf life requirements.
Key Differences Between Hot Fill and Cold Fill
Hot fill packaging involves heating the product to a high temperature before filling, which sterilizes both the product and container, extending shelf life without preservatives. Cold fill packaging requires the product and container to remain at lower temperatures during filling, preserving heat-sensitive ingredients but often necessitating refrigeration or preservatives for safety. Your choice between hot fill and cold fill greatly impacts product stability, packaging material selection, and storage requirements.
How Hot Fill Packaging Works
Hot fill packaging involves heating a liquid product to a temperature typically between 185degF and 205degF to sterilize both the product and the container. The hot liquid is then filled into pre-sterilized, flexible or glass containers, which are immediately sealed to create a vacuum as the content cools, preventing contamination and extending shelf life. Your product benefits from this method by reducing the need for preservatives while ensuring safety and maintaining flavor integrity.
How Cold Fill Packaging Works
Cold fill packaging involves filling products at low temperatures to preserve freshness and extend shelf life by minimizing microbial growth. This method uses sterilized containers and often requires refrigerated storage and transportation to maintain product quality. It is commonly applied in beverages, sauces, and dairy products where heat-sensitive ingredients are present.
Benefits of Hot Fill Packaging
Hot fill packaging offers superior shelf stability by effectively eliminating harmful microorganisms through high-temperature processing, extending your product's freshness without preservatives. This method ensures a strong seal and enhanced package integrity, reducing the risk of contamination and leakage. Hot fill packaging also allows for versatile container materials, supporting eco-friendly options like recyclable PET plastics.
Advantages of Cold Fill Packaging
Cold fill packaging preserves product freshness and extends shelf life by avoiding heat exposure, which maintains the nutritional value and flavor integrity of your beverages or foods. It reduces energy consumption during production, leading to cost savings and a smaller environmental footprint. Your brand can benefit from faster production cycles and enhanced package appearance due to the absence of heat distortion.
Ideal Applications for Hot Fill vs Cold Fill
Hot fill packaging is ideal for acidic products like fruit juices, teas, and sauces that require pasteurization to eliminate pathogens and extend shelf life without preservatives. Cold fill packaging suits beverages such as carbonated drinks, dairy products, and water, where maintaining freshness and carbonation is essential, and heat would degrade quality. Selecting between hot fill and cold fill depends on product acidity, heat sensitivity, and desired shelf stability.
Packaging Material Compatibility
Hot fill packaging requires materials that can withstand high temperatures, such as heat-resistant PET or glass, to prevent deformation and ensure product safety. Cold fill packaging materials like HDPE and certain flexible plastics are designed for room-temperature filling processes, preserving the product's integrity without thermal stress. Selecting compatible packaging materials is essential to maintain product stability, shelf life, and compliance with food safety standards.
Cost Considerations: Hot Fill vs Cold Fill
Hot fill packaging generally incurs higher initial costs due to the need for heat-resistant materials and specialized equipment to withstand elevated temperatures. Cold fill packaging offers lower material costs and simpler processing requirements but may demand additional preservatives or refrigeration solutions, impacting overall expenses. Evaluating production volume, product stability, and shelf-life requirements is crucial for selecting the most cost-efficient packaging method.
Choosing the Right Packaging Method for Your Product
Selecting between hot fill and cold fill packaging depends on factors such as product type, shelf life, and sterilization requirements. Hot fill packaging is ideal for acidic beverages and products needing pasteurization to ensure microbial safety, while cold fill suits products sensitive to heat or requiring preservatives. Evaluating your product's thermal stability and desired shelf conditions ensures you choose the most effective packaging method to maintain quality and safety.
Hot Fill vs Cold Fill Packaging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com