Copolyester offers enhanced durability and flexibility compared to standard polyester, making it ideal for applications requiring impact resistance and clarity. Choosing copolyester can improve the longevity and performance of your products, especially in packaging and medical industries.
Table of Comparison
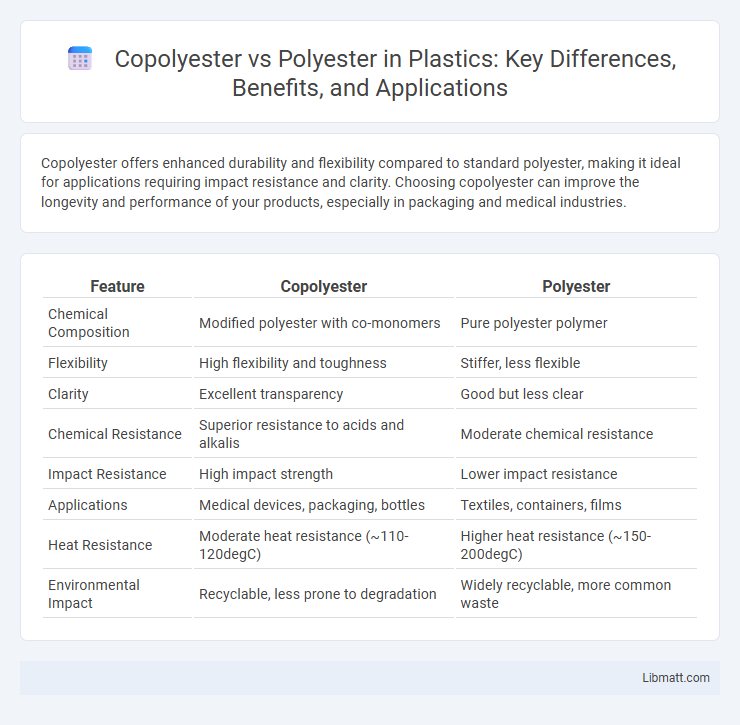
| Feature | Copolyester | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Modified polyester with co-monomers | Pure polyester polymer |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and toughness | Stiffer, less flexible |
| Clarity | Excellent transparency | Good but less clear |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to acids and alkalis | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Impact Resistance | High impact strength | Lower impact resistance |
| Applications | Medical devices, packaging, bottles | Textiles, containers, films |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance (~110-120degC) | Higher heat resistance (~150-200degC) |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, less prone to degradation | Widely recyclable, more common waste |
Introduction to Copolyester and Polyester
Copolyester and polyester are important types of thermoplastic polymers used widely in packaging, textiles, and engineering applications. Copolyester, a modified version of polyester, contains two or more different monomers, which enhance flexibility, impact resistance, and clarity compared to traditional polyester made from a single type of monomer. The molecular structure variations give copolyester distinct physical properties, making it ideal for products requiring durability and chemical resistance, while polyester is favored for strength and cost-effectiveness.
Chemical Structure Differences
Copolyester features a chemical structure composed of multiple monomer types arranged in varying sequences, enhancing flexibility and impact resistance compared to polyester's uniform ester chains derived from a single monomer type. The inclusion of different monomers in copolyesters allows for tailored thermal and mechanical properties, making them suitable for diverse applications where pure polyester might fall short. Your choice between copolyester and polyester should consider these chemical structure differences to meet specific performance requirements.
Manufacturing Processes
Copolyester manufacturing involves the polymerization of multiple monomers, typically combining terephthalic acid, ethylene glycol, and additional monomers like isophthalic acid to enhance flexibility and chemical resistance. Polyester production primarily uses terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol through a polycondensation process, resulting in a more crystalline and rigid polymer structure. The inclusion of different monomers in copolyester alters the polymer chain arrangement, impacting melting temperature and mechanical properties compared to conventional polyester.
Physical Properties Comparison
Copolyester exhibits higher impact resistance and enhanced flexibility compared to traditional polyester, which tends to be more rigid and brittle. Its superior chemical resistance and clarity make copolyester ideal for applications requiring durability and aesthetic appeal. Polyester typically offers better thermal stability and tensile strength but lacks the elasticity and toughness found in copolyesters.
Durability and Performance
Copolyester offers superior durability compared to polyester due to its enhanced chemical resistance and impact strength, making it ideal for applications requiring toughness and flexibility. Polyester excels in thermal stability and UV resistance but tends to be more brittle under stress, limiting its performance in high-impact or variable environments. For demanding uses such as packaging, medical devices, and automotive parts, copolyester provides a balanced combination of strength, clarity, and dimensional stability.
Environmental Impact
Copolyester typically offers a lower environmental impact compared to traditional polyester due to its enhanced recyclability and reduced energy consumption during manufacturing. The production of copolyester generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions and allows for easier recycling processes, contributing to less landfill waste. Polyester, while durable and widely used, often involves higher carbon footprints and challenges in biodegradability, making copolyester a more sustainable alternative in textile and packaging industries.
Applications and Uses
Copolyester offers enhanced chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for medical devices, food packaging, and consumer electronics where durability and clarity are essential. Polyester is widely used in textiles, automotive parts, and plastic bottles due to its strength, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Both materials serve packaging applications, but copolyester's toughness and clarity provide advantages in specialty wraps and reusable containers.
Cost Analysis
Copolyester generally incurs higher production costs than traditional polyester due to its more complex chemical structure and enhanced performance properties. Your decision between copolyester and polyester should consider the balance between budget constraints and the need for durability, as copolyester offers superior impact resistance and clarity, which can justify its premium price. In mass production scenarios, polyester remains cost-effective, while copolyester suits applications requiring long-term reliability despite increased initial expenses.
Pros and Cons of Each Material
Copolyester offers superior clarity, impact resistance, and chemical durability compared to traditional polyester, making it ideal for packaging and medical applications, but it is generally more expensive. Polyester boasts excellent strength, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, but it lacks the toughness and clarity that copolyester provides. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize durability and visual appeal or affordability and general-purpose use.
Choosing the Right Material: Copolyester or Polyester
Copolyester offers superior clarity, flexibility, and chemical resistance compared to traditional polyester, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability and visual appeal. Polyester excels in strength and abrasion resistance, suitable for textile and industrial uses where rigidity and toughness are prioritized. Selecting between copolyester and polyester depends on specific performance needs such as impact resistance, clarity, and environmental stress factors.
Copolyester vs polyester Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com