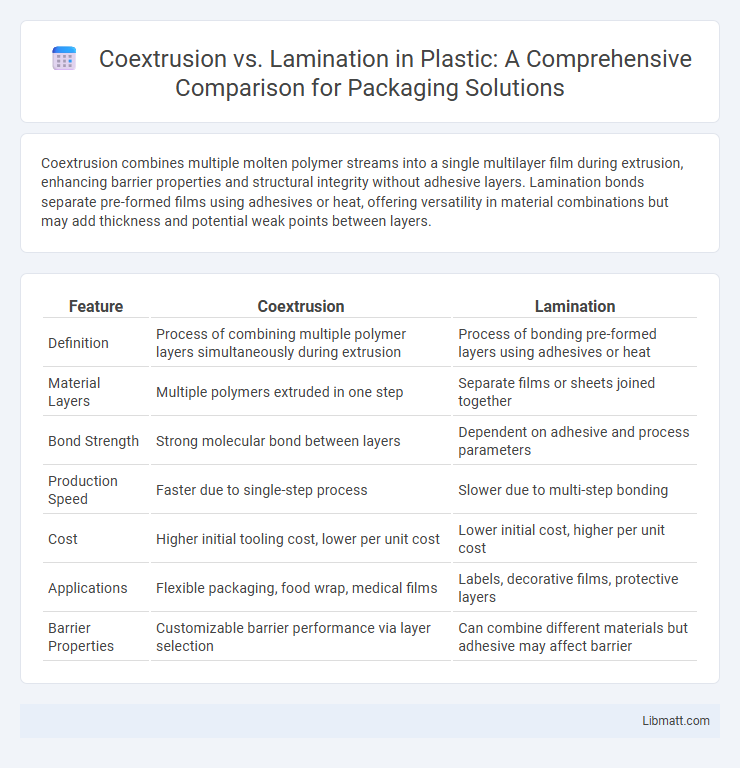
Coextrusion combines multiple molten polymer streams into a single multilayer film during extrusion, enhancing barrier properties and structural integrity without adhesive layers. Lamination bonds separate pre-formed films using adhesives or heat, offering versatility in material combinations but may add thickness and potential weak points between layers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Coextrusion | Lamination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of combining multiple polymer layers simultaneously during extrusion | Process of bonding pre-formed layers using adhesives or heat |
| Material Layers | Multiple polymers extruded in one step | Separate films or sheets joined together |
| Bond Strength | Strong molecular bond between layers | Dependent on adhesive and process parameters |
| Production Speed | Faster due to single-step process | Slower due to multi-step bonding |
| Cost | Higher initial tooling cost, lower per unit cost | Lower initial cost, higher per unit cost |
| Applications | Flexible packaging, food wrap, medical films | Labels, decorative films, protective layers |
| Barrier Properties | Customizable barrier performance via layer selection | Can combine different materials but adhesive may affect barrier |
Understanding Coextrusion: Definition and Process
Coextrusion is a manufacturing process where two or more layers of molten polymers are simultaneously extruded through a single die to form a multi-layered film or sheet with combined properties. This technique enables the creation of customized materials with enhanced mechanical strength, barrier performance, and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for packaging and industrial applications. Understanding your product requirements helps determine whether coextrusion offers better material integration and efficiency compared to lamination.
What Is Lamination? Techniques and Applications
Lamination is a process that bonds multiple layers of materials, such as paper, fabric, or plastic films, to create a composite with enhanced strength, durability, and barrier properties. Common techniques include adhesive lamination, where layers are glued together, and extrusion lamination, which uses a molten polymer to bond surfaces without adhesives. Lamination is widely applied in packaging, printing, automotive interiors, and protective coverings due to its ability to improve resistance to moisture, abrasion, and chemical exposure.
Key Material Differences in Coextrusion and Lamination
Coextrusion involves the simultaneous extrusion of multiple polymer layers to create a unified film with distinct material properties, enabling precise control over barrier, strength, and flexibility. Lamination, on the other hand, combines pre-formed layers of different materials using adhesives or heat to bond substrates, often incorporating paper, aluminum foil, or plastic films. Your choice between these methods depends on desired material characteristics, such as moisture resistance or printability, and the structural integrity required for your application.
Performance Comparison: Strength and Durability
Coextrusion offers superior strength and durability by fusing multiple polymer layers into a single, cohesive structure, enhancing resistance to impact and environmental stress. Lamination relies on bonding separate films or sheets, which can introduce weak points prone to delamination under mechanical or thermal strain. Your choice between coextrusion and lamination should consider the specific application demands for durability, with coextrusion typically providing enhanced long-term performance in high-stress environments.
Cost Analysis: Coextrusion vs Lamination
Coextrusion typically incurs higher initial equipment costs but offers lower operational expenses due to reduced material waste and faster production speeds compared to lamination. Lamination involves additional adhesive layers and curing processes, increasing material and energy costs over time. Your choice depends on balancing upfront investment with long-term efficiency and material savings.
Barrier Properties: Which Method Performs Better?
Coextrusion offers superior barrier properties compared to lamination due to its ability to create a seamless multilayer structure that prevents moisture, oxygen, and other gases from penetrating. In contrast, lamination relies on adhesive layers between films, which may introduce weak points and potential delamination under stress. Therefore, coextrusion is generally preferred in applications requiring enhanced protection and longer shelf life.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Coextrusion offers enhanced sustainability by reducing material usage and energy consumption through simultaneous layering in a single process, minimizing waste generation compared to lamination. Lamination, involving multiple adhesive layers and separate processing steps, often results in higher energy demands and challenges in recycling due to mixed-material structures. Choosing coextrusion can significantly lower environmental impact by improving recyclability and decreasing carbon footprint in packaging applications.
Typical Industry Uses: Coextrusion vs Lamination
Coextrusion dominates in packaging industries such as food and beverage, where multi-layer films are required for enhanced barrier properties, moisture resistance, and cost efficiency. Lamination is prevalent in printed materials, flexible packaging, and labels, offering superior surface finish, printability, and adhesion between diverse substrates. Both methods serve critical roles in automotive, medical device packaging, and electronics sectors, chosen based on performance requirements and material compatibility.
Design Flexibility and Customization Options
Coextrusion offers superior design flexibility by enabling multiple polymer layers to be extruded simultaneously, allowing precise control over layer thickness and material properties for customized barrier, strength, and appearance. Lamination provides versatility through combining different substrates and adhesives, accommodating a wide range of materials like films, foils, and papers for tailored performance and decorative finishes. Both methods support customization, but coextrusion excels in integrating functional layers within a single structure, while lamination facilitates diverse material combinations for complex designs.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Packaging Needs
Coextrusion and lamination are critical packaging technologies, each offering unique benefits depending on your product requirements. Coextrusion creates multi-layer films through simultaneous extrusion of different polymers, providing superior barrier properties and uniformity, ideal for flexible packaging demanding durability and product protection. Lamination bonds multiple pre-made layers or films, offering design versatility and enhanced aesthetics, suitable when combining diverse materials like foil with plastics for specialty packaging solutions.
Coextrusion vs lamination Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com