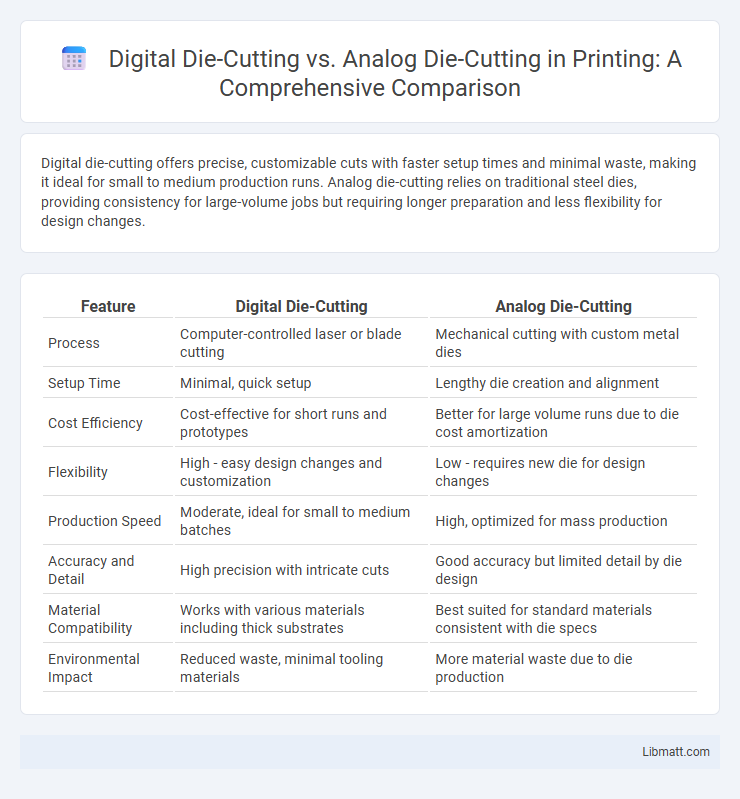
Digital die-cutting offers precise, customizable cuts with faster setup times and minimal waste, making it ideal for small to medium production runs. Analog die-cutting relies on traditional steel dies, providing consistency for large-volume jobs but requiring longer preparation and less flexibility for design changes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Digital Die-Cutting | Analog Die-Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Computer-controlled laser or blade cutting | Mechanical cutting with custom metal dies |
| Setup Time | Minimal, quick setup | Lengthy die creation and alignment |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for short runs and prototypes | Better for large volume runs due to die cost amortization |
| Flexibility | High - easy design changes and customization | Low - requires new die for design changes |
| Production Speed | Moderate, ideal for small to medium batches | High, optimized for mass production |
| Accuracy and Detail | High precision with intricate cuts | Good accuracy but limited detail by die design |
| Material Compatibility | Works with various materials including thick substrates | Best suited for standard materials consistent with die specs |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced waste, minimal tooling materials | More material waste due to die production |
Introduction to Die-Cutting Technologies
Digital die-cutting technology uses computer-controlled lasers or blades to precisely cut materials, enabling faster setup times and intricate designs with minimal waste. Analog die-cutting relies on physical metal dies to stamp shapes, offering durability and cost-efficiency for high-volume production but limited flexibility for design changes. Both methods serve distinct needs in packaging, labeling, and manufacturing industries, with digital die-cutting favored for customization and short runs, while analog excels in mass production.
What is Digital Die-Cutting?
Digital die-cutting uses computer-controlled machines to precisely cut materials based on digital designs, offering fast setup and high customization. Unlike analog die-cutting, which requires physical dies and longer preparation times, digital die-cutting enables on-demand production with minimal waste and greater design flexibility. Your projects benefit from quicker turnaround and the ability to easily modify cuts without investing in new dies.
What is Analog Die-Cutting?
Analog die-cutting is a traditional manufacturing process that uses physical steel dies to cut shapes, patterns, or designs from materials such as paper, cardboard, or fabric. This method relies on creating custom metal dies through machining or engraving, which then apply pressure to the material to achieve precise, repeatable cuts. Analog die-cutting is highly effective for large production runs due to its speed and cost efficiency once the die is fabricated.
Key Differences Between Digital and Analog Die-Cutting
Digital die-cutting uses computer-controlled lasers or blades to create precise, customizable cuts without physical dies, offering faster setup times and flexibility for small runs. Analog die-cutting relies on steel rule or rotary dies to physically cut shapes, providing consistent high-volume output but requiring expensive die fabrication and longer lead times. Digital die-cutting excels in prototyping and short runs, while analog die-cutting suits mass production where repeatability and cost-efficiency are critical.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Digital die-cutting offers significantly faster turnaround times by eliminating the need for custom steel dies and setup, enabling instant changes and on-demand production. Analog die-cutting, reliant on physical dies, involves longer preparation and slower processing speeds, making it less efficient for short runs or prototype projects. High-volume jobs may still benefit from analog methods, but digital die-cutting maximizes efficiency and reduces waste in variable or small-batch runs.
Cost Considerations: Digital vs Analog
Digital die-cutting offers lower initial costs due to the absence of physical tooling, making it ideal for short runs and prototyping, while analog die-cutting incurs higher upfront expenses for custom steel dies. Your cost efficiency improves with digital when producing small to medium volumes, as it eliminates setup fees and reduces material waste. For large-scale or repetitive jobs, analog die-cutting becomes more cost-effective due to faster production speeds and durability of dies over time.
Application Suitability and Flexibility
Digital die-cutting offers superior flexibility and is ideal for short runs, customized designs, and rapid prototyping, making it suitable for businesses seeking agility and varied applications. Analog die-cutting excels in high-volume production with consistent and precise cuts, making it cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing. Your choice depends on the balance between customization needs and production scale for optimal application suitability.
Quality and Precision in Die-Cutting
Digital die-cutting delivers superior quality and precision through computer-controlled accuracy, ensuring consistent cuts with intricate details and minimal material waste. Analog die-cutting relies on physical dies that may wear down over time, leading to less uniformity and potential inaccuracies in complex designs. The scalability and repeatability of digital die-cutting provide enhanced efficiency for high-precision applications in packaging, labeling, and custom manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Waste Reduction
Digital die-cutting significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing material waste through precise cutting and on-demand production, unlike analog die-cutting which generates excess waste due to fixed dies and setup processes. The use of digital technology eliminates the need for physical dies, reducing resource consumption and the disposal of metal tooling. This results in a more sustainable production cycle, lowering the carbon footprint associated with traditional analog die-cutting methods.
Choosing the Right Die-Cutting Method for Your Project
Digital die-cutting offers precise, customizable cuts with faster turnaround times, making it ideal for short runs and intricate designs. Analog die-cutting relies on physical dies, providing consistent results for large production volumes and simpler shapes at lower per-unit costs. Your choice depends on project complexity, quantity, and budget, ensuring the best balance between quality and efficiency.
Digital die-cutting vs analog die-cutting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com