Variable data printing allows for customization of each individual printed piece by changing text, images, or graphics, making it ideal for personalized marketing campaigns. Static printing produces identical copies with fixed content, suitable for bulk printing where uniformity and consistency are essential.
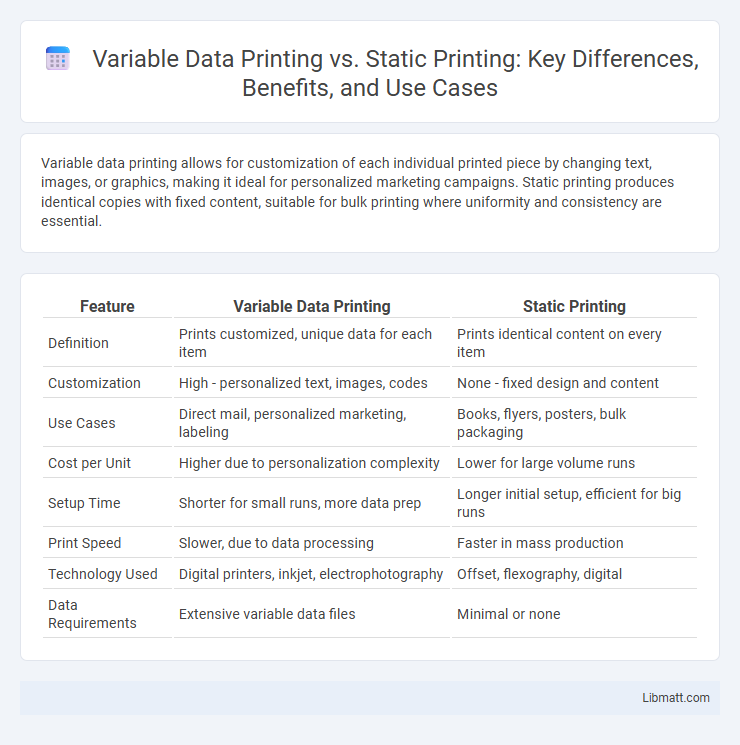
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Variable Data Printing | Static Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prints customized, unique data for each item | Prints identical content on every item |
| Customization | High - personalized text, images, codes | None - fixed design and content |
| Use Cases | Direct mail, personalized marketing, labeling | Books, flyers, posters, bulk packaging |
| Cost per Unit | Higher due to personalization complexity | Lower for large volume runs |
| Setup Time | Shorter for small runs, more data prep | Longer initial setup, efficient for big runs |
| Print Speed | Slower, due to data processing | Faster in mass production |
| Technology Used | Digital printers, inkjet, electrophotography | Offset, flexography, digital |
| Data Requirements | Extensive variable data files | Minimal or none |
Introduction to Variable Data Printing and Static Printing
Variable data printing enables customization of individual print pieces by altering text, images, or graphics with unique information, enhancing personalization and targeted marketing. Static printing produces uniform copies with identical content, ideal for mass distribution where consistency is crucial. The choice between variable data printing and static printing depends on the need for customization versus volume and cost-efficiency.
Key Differences Between Variable and Static Printing
Variable data printing customizes each printed piece with unique information such as names, codes, or graphics, enabling personalized marketing materials and targeted communication. Static printing produces uniform copies where every item is identical, ideal for mass production of brochures, flyers, and labels. The flexibility and cost efficiency in short runs distinguish variable printing from the fixed, high-volume output of static printing.
How Variable Data Printing Works
Variable Data Printing (VDP) works by integrating digital printing technology with database records to customize each printed piece individually. By linking text, images, and graphics to unique data inputs, VDP enables personalized marketing materials, such as direct mail or brochures, that target specific audiences effectively. Your marketing campaigns achieve higher engagement and response rates through tailored content that adjusts dynamically based on recipient details.
Benefits of Variable Data Printing
Variable data printing (VDP) offers significant advantages over static printing by enabling personalized content on each printed piece, increasing customer engagement and response rates. This technology reduces waste and cost by eliminating the need for separate printing plates, making it ideal for targeted marketing campaigns, direct mail, and customized packaging. VDP enhances brand loyalty through tailored messaging and improves tracking and analytics capabilities by integrating unique codes or personalized data into each print.
Advantages of Static Printing
Static printing offers consistent, high-quality output ideal for mass production of identical materials such as brochures, flyers, and packaging. It benefits from lower production costs due to streamlined processes, making it cost-effective for large print runs. The reliability and efficiency of static printing ensure faster turnaround times and minimal setup complexity compared to variable data printing.
Use Cases: When to Choose Variable Data Printing
Variable data printing is ideal for personalized marketing materials, direct mail campaigns, and customized product labels where unique information such as names, addresses, or codes need to change with each printed piece. Choosing variable data printing enhances customer engagement by delivering tailored messages and improves efficiency for businesses requiring high-volume, individualized output. Your business benefits most from variable data printing when mass production meets customization demands, unlike static printing which is better suited for uniform and repetitive print jobs.
Use Cases: When to Choose Static Printing
Static printing is ideal for mass production of identical items such as business cards, brochures, and flyers where consistent quality and cost efficiency are paramount. It excels in scenarios requiring large volumes of uniform print runs without personalization, ensuring faster turnaround and lower unit costs. Selecting static printing is beneficial when customization is unnecessary and standardization guarantees brand consistency across all materials.
Cost Comparison: Variable Data vs. Static Printing
Variable data printing often incurs higher costs than static printing due to the need for specialized digital printers and software to customize each printed piece. Static printing benefits from economies of scale, making it more cost-effective for large runs of identical copies by utilizing traditional offset printing methods. Your decision should weigh the benefits of personalized content against the potential increase in per-unit cost when choosing between variable data and static printing.
Impact on Personalization and Customer Engagement
Variable data printing enables highly personalized marketing materials by tailoring text, images, and offers to individual recipients, significantly enhancing customer engagement. Static printing produces identical copies, limiting customization and reducing the potential to connect with your audience on a personal level. Choosing variable data printing empowers your brand to deliver targeted messages that increase response rates and customer loyalty.
Future Trends in Printing Technology
Variable data printing (VDP) is rapidly advancing with the integration of AI-driven personalization and real-time data processing, enabling highly customized print runs that enhance customer engagement. Static printing, while efficient for mass production, is gradually being supplemented by hybrid technologies that blend static elements with variable content to optimize flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Future trends indicate a growing emphasis on sustainability, faster print speeds, and enhanced digital workflows, positioning VDP as a critical component in the evolution of printing technology.
Variable data printing vs static printing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com