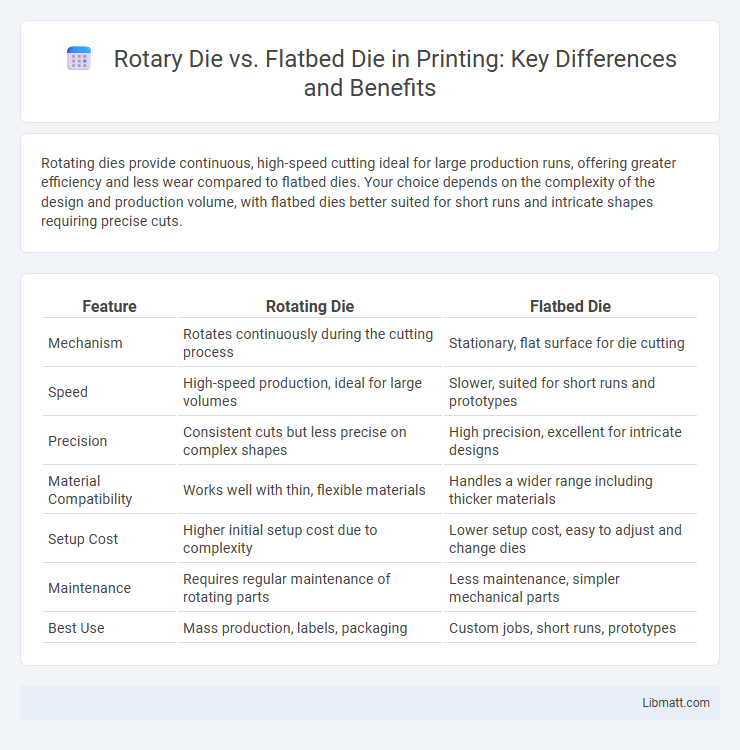
Rotating dies provide continuous, high-speed cutting ideal for large production runs, offering greater efficiency and less wear compared to flatbed dies. Your choice depends on the complexity of the design and production volume, with flatbed dies better suited for short runs and intricate shapes requiring precise cuts.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rotating Die | Flatbed Die |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Rotates continuously during the cutting process | Stationary, flat surface for die cutting |
| Speed | High-speed production, ideal for large volumes | Slower, suited for short runs and prototypes |
| Precision | Consistent cuts but less precise on complex shapes | High precision, excellent for intricate designs |
| Material Compatibility | Works well with thin, flexible materials | Handles a wider range including thicker materials |
| Setup Cost | Higher initial setup cost due to complexity | Lower setup cost, easy to adjust and change dies |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance of rotating parts | Less maintenance, simpler mechanical parts |
| Best Use | Mass production, labels, packaging | Custom jobs, short runs, prototypes |
Introduction to Rotating Die and Flatbed Die
Rotating die and flatbed die represent two common printing methods for die cutting, each with unique operational designs and efficiencies. Rotating die cutting uses a cylindrical tool that continuously spins to cut shapes, making it ideal for high-speed, large-volume production runs. Flatbed die cutting employs a flat surface to press the die onto material, offering precision and versatility for complex or lower-volume projects, ensuring Your specific production needs are met effectively.
Principle of Operation: Rotating Die vs Flatbed Die
Rotating dies operate by continuously spinning cylindrical tools that imprint designs on materials with high-speed precision, ideal for long-run production and consistent output. Flatbed dies use a stationary flat surface pressing down onto the material, offering greater control for intricate cuts and short production runs. Your choice depends on whether rapid, continuous operation or precise, detailed cutting is the priority for your manufacturing process.
Key Structural Differences
Rotating dies feature a cylindrical design that continuously spins, allowing for high-speed, seamless cutting or embossing, while flatbed dies consist of a stationary, flat surface that presses down on materials for precise, static cuts. The rotating die's round structure enables rapid production and is ideal for long runs, whereas flatbed dies excel in detailed, complex designs with thicker substrates. Key structural differences include the rotating die's dynamic, rolling action versus the flatbed's stable, press-type mechanism, influencing their applications in manufacturing and packaging industries.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Rotating die cutting machines offer higher production speeds due to continuous rotary motion, making them ideal for large-volume runs with consistent output. Flatbed die cutting operates at slower speeds because it uses a linear press motion, limiting efficiency in high-demand scenarios. The performance of rotating die cutters excels in speed and throughput, while flatbed dies provide greater precision for smaller batches or complex cuts.
Material Compatibility
Rotating die systems excel in processing flexible materials such as films, foils, and thin plastics due to their continuous motion, enabling high-speed, precise cutting with minimal material waste. Flatbed die cutters are better suited for rigid or thicker materials like cardboard, leather, and thicker paper, providing accurate, deep cuts with consistent pressure distribution. Optimizing your choice of die cutting technology according to material compatibility ensures improved efficiency and product quality in manufacturing operations.
Precision and Accuracy
Rotating die cutters offer higher precision and accuracy due to continuous rotary motion, enabling consistent, sharp cuts ideal for intricate designs and high-volume production. Flatbed die cutters provide precise cuts but may lack uniformity in speed and pressure, affecting accuracy in detailed or repetitive tasks. Industrial processes requiring tight tolerances often favor rotating dies for their superior alignment control and reduced material distortion.
Maintenance and Durability
Rotating dies generally require more frequent maintenance due to their complex moving parts and higher operational speeds, but they offer enhanced durability for high-volume production runs. Flatbed dies, with fewer mechanical components, typically demand less upkeep and are more resistant to wear, making them suitable for lower-volume jobs with less frequent changeovers. Your choice between these options should consider the balance between maintenance schedules and the expected lifespan of the die based on your production needs.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Rotating die systems typically offer higher cost efficiency due to faster production speeds and reduced material waste compared to flatbed dies, which operate with slower indexing and greater setup times. Flatbed dies incur higher operational costs from frequent maintenance and limited automation, making them less suitable for large-scale manufacturing. Your choice between these dies should consider volume demands and long-term savings, as rotating dies deliver more efficient output for high-volume runs.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Rotating die machines excel in high-speed, continuous production environments such as packaging, labels, and flexible materials, making them ideal for industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. Flatbed die machines offer greater precision and versatility for short runs and complex designs, commonly used in automotive, electronics, and aerospace sectors where customized parts and prototypes are essential. Understanding Your specific application requirements helps determine the optimal die cutting solution, balancing speed with accuracy and material compatibility.
Choosing the Right Die-Cutting Method
Choosing the right die-cutting method depends on factors like production volume, material type, and precision requirements. Rotating dies excel in high-speed, continuous operations with flexible materials, while flatbed dies are ideal for precise, intricate cuts on thicker or rigid substrates. Your decision should prioritize efficiency and quality based on specific project demands.
Rotating Die vs Flatbed Die Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com