Electrostatic printing utilizes static electricity to transfer toner onto paper, making it ideal for high-speed and large-volume printing tasks. Laser printing offers precise image quality and faster output for detailed documents, ensuring your prints are sharp and professional.
Table of Comparison
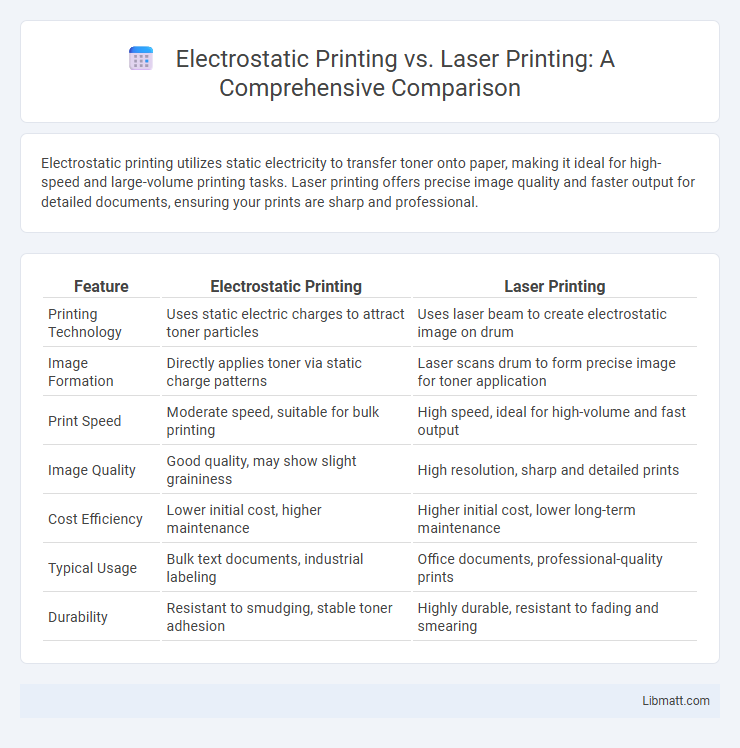
| Feature | Electrostatic Printing | Laser Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Technology | Uses static electric charges to attract toner particles | Uses laser beam to create electrostatic image on drum |
| Image Formation | Directly applies toner via static charge patterns | Laser scans drum to form precise image for toner application |
| Print Speed | Moderate speed, suitable for bulk printing | High speed, ideal for high-volume and fast output |
| Image Quality | Good quality, may show slight graininess | High resolution, sharp and detailed prints |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance | Higher initial cost, lower long-term maintenance |
| Typical Usage | Bulk text documents, industrial labeling | Office documents, professional-quality prints |
| Durability | Resistant to smudging, stable toner adhesion | Highly durable, resistant to fading and smearing |
Introduction to Electrostatic and Laser Printing
Electrostatic printing utilizes charged particles to transfer toner onto paper, producing high-quality images through an electrostatic process. Laser printing employs a focused laser beam to create precise images by altering the electrical charge on a drum, enabling sharp and fast output ideal for both text and graphics. Your choice between electrostatic and laser printing depends on the required print resolution, speed, and application, with laser printers often preferred for their efficiency and accuracy.
How Electrostatic Printing Works
Electrostatic printing operates by using charged particles to transfer toner onto paper, creating images through electrostatic attraction rather than heat. This method involves charging a photoconductor drum, which selectively attracts toner particles that are then pressed onto the paper, forming precise and high-quality prints. Your choice of electrostatic printing ensures efficiency in producing sharp images without the complexity of heat-based processes found in laser printing.
Fundamentals of Laser Printing Technology
Laser printing technology uses a laser beam to create an electrostatic image on a photosensitive drum, which attracts toner particles that are then fused onto paper through heat and pressure. Unlike electrostatic printing, which relies on direct electrostatic charges to transfer ink, laser printing offers higher precision and faster output ideal for high-volume and high-quality document production. Understanding these fundamentals helps you choose printing solutions that best meet your efficiency and print quality requirements.
Print Quality Comparison
Electrostatic printing offers precise toner adhesion resulting in high-definition images and sharp text, especially effective for large-volume productions. Laser printing excels in delivering crisp detail and smooth gradients, making it ideal for professional documents and color printouts. Your choice depends on the balance between print speed, quality consistency, and the specific application needs.
Speed and Productivity Differences
Electrostatic printing typically offers slower print speeds compared to laser printing due to its complex image formation process relying on electrostatic charges. Laser printing achieves higher productivity with speeds often exceeding 30 pages per minute, enabled by rapid laser scanning and toner fixing mechanisms. Industries requiring fast, high-volume output favor laser printing for its efficiency and consistent speed performance.
Cost Efficiency: Electrostatic vs Laser Printing
Electrostatic printing typically offers greater cost efficiency for high-volume printing due to lower per-page expenses and reduced maintenance costs compared to laser printing. Laser printing involves higher upfront investments in toner and drum replacements, making it less economical for bulk printing over time. Your choice depends on balancing initial costs against long-term savings, with electrostatic printing often favored for large-scale, continuous print jobs.
Applications and Use Cases
Electrostatic printing is widely used in industrial applications such as textile printing, packaging, and large-format graphics due to its ability to handle diverse materials and surfaces. Laser printing excels in office environments and professional settings where high-speed, high-resolution document reproduction and precise text output are essential. Your choice between these technologies should consider the printing volume, material type, and quality requirements specific to your task.
Environmental Impact and Energy Consumption
Electrostatic printing generally consumes less energy than laser printing because it uses fewer heat-intensive components, reducing your overall carbon footprint. Laser printers rely on a fuser unit that heats toner to bond it to paper, which increases electricity use and contributes to higher environmental impact. Choosing electrostatic printing can minimize hazardous emissions and lower energy consumption, promoting a more eco-friendly office environment.
Maintenance and Reliability
Electrostatic printing requires less frequent maintenance due to its simpler mechanism, reducing downtime and upkeep costs compared to laser printing. Laser printers have moving parts such as drums and fusers that need regular replacement to maintain print quality and operational reliability. You can achieve higher consistency with electrostatic printing, especially in high-volume environments where durability and minimal maintenance are critical.
Choosing the Right Printing Method
Electrostatic printing offers high-speed, low-cost output ideal for large-volume jobs, while laser printing provides superior image quality and precision for detailed documents. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize affordability and speed or sharp resolution and color accuracy. Evaluating print volume, budget constraints, and specific project requirements ensures you select the most efficient printing method for your needs.
Electrostatic Printing vs Laser Printing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com