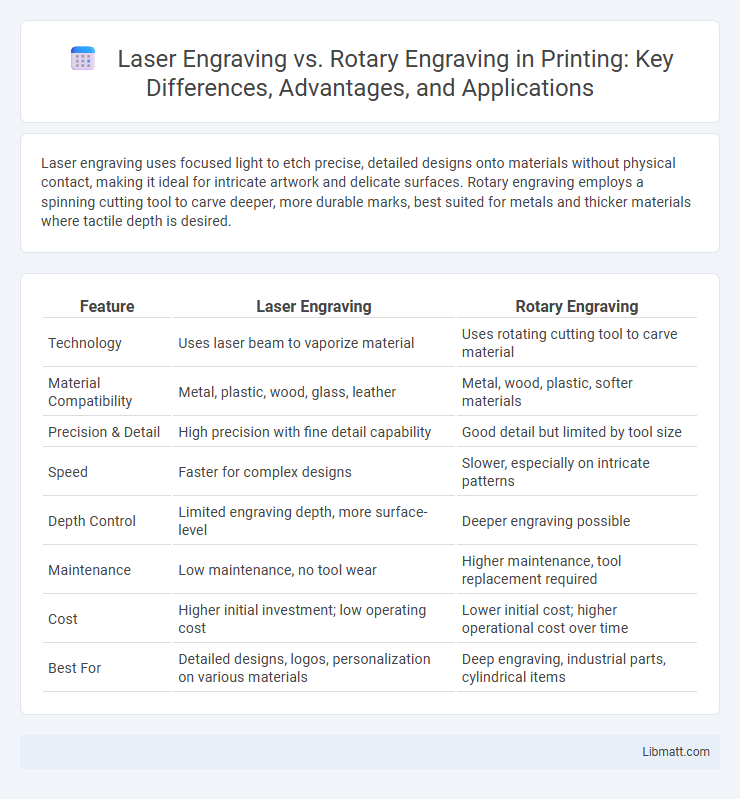
Laser engraving uses focused light to etch precise, detailed designs onto materials without physical contact, making it ideal for intricate artwork and delicate surfaces. Rotary engraving employs a spinning cutting tool to carve deeper, more durable marks, best suited for metals and thicker materials where tactile depth is desired.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laser Engraving | Rotary Engraving |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Uses laser beam to vaporize material | Uses rotating cutting tool to carve material |
| Material Compatibility | Metal, plastic, wood, glass, leather | Metal, wood, plastic, softer materials |
| Precision & Detail | High precision with fine detail capability | Good detail but limited by tool size |
| Speed | Faster for complex designs | Slower, especially on intricate patterns |
| Depth Control | Limited engraving depth, more surface-level | Deeper engraving possible |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, no tool wear | Higher maintenance, tool replacement required |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; low operating cost | Lower initial cost; higher operational cost over time |
| Best For | Detailed designs, logos, personalization on various materials | Deep engraving, industrial parts, cylindrical items |
Introduction to Laser and Rotary Engraving
Laser engraving uses a focused laser beam to vaporize material and create precise, detailed designs on various surfaces like wood, metal, and glass. Rotary engraving employs a spinning cutting tool to physically carve into the material, making it ideal for deeper, tactile engravings on metals and plastics. Understanding these fundamental differences helps you choose the right method based on material type, design complexity, and desired engraving depth.
How Laser Engraving Works
Laser engraving works by directing a high-powered laser beam onto the surface of a material, rapidly heating and vaporizing the targeted area to create precise, detailed designs. The laser's intensity and focus can be adjusted for different depths and textures, making it ideal for intricate patterns on wood, acrylic, glass, and metals. Unlike rotary engraving, which physically cuts into the material with a spinning tool, laser engraving is a non-contact process that produces clean, sharp marks without causing mechanical wear.
How Rotary Engraving Works
Rotary engraving works by using a rotating cutting tool to physically carve or etch the surface of a material, creating detailed designs or text with precision. The cutting bit moves along the X, Y, and sometimes Z axes to achieve depth variation, allowing for three-dimensional effects on materials like metal, wood, and plastic. This method is ideal for deep engraving and producing durable, tactile marks on various substrates.
Key Differences Between Laser and Rotary Engraving
Laser engraving uses focused light beams to etch precise, detailed designs onto materials such as wood, metal, and plastic, offering high versatility and speed. Rotary engraving relies on a spinning cutting tool to physically carve into surfaces, making it ideal for deeper cuts on harder materials like metals and plastics. Your choice between laser and rotary engraving depends on the material type, desired detail level, and cutting depth required for your project.
Material Compatibility: Laser vs Rotary
Laser engraving excels in versatility, effectively marking materials like wood, acrylic, glass, leather, and certain metals with high precision and minimal wear. Rotary engraving performs best on harder materials such as metals, plastics, and wood, relying on physical cutting to create deeper, tactile engravings. Choosing between laser and rotary methods depends largely on the material type and desired engraving depth, with lasers suitable for delicate surfaces and rotary engravers preferred for robust, three-dimensional designs.
Precision and Detail Comparison
Laser engraving provides superior precision and intricate detail by using focused light beams to vaporize material with micron-level accuracy, ideal for complex designs and fine text. Rotary engraving, which relies on mechanical cutting tools, offers durable and deep engravings but lacks the ultra-fine detail achievable with lasers, especially on softer or thin materials. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize high-detail, delicate finishes (laser) or deeper, tactile engravings (rotary) for your project.
Speed and Efficiency: Which is Faster?
Laser engraving typically outpaces rotary engraving in speed and efficiency due to its non-contact process and ability to quickly vaporize materials with high precision. Rotary engraving requires physical contact with the material, often resulting in slower operation times, especially on harder surfaces. Industries prioritizing rapid production and intricate detailing frequently choose laser engraving for its superior throughput and reduced setup time.
Cost Analysis: Laser vs Rotary Engraving
Laser engraving typically involves higher initial equipment costs but offers lower ongoing expenses due to minimal tool wear and faster processing times. Rotary engraving requires less upfront investment but incurs higher maintenance costs from blade replacements and slower production speeds. Your choice depends on long-term project volume and material types, with laser engraving proving more cost-effective for detailed or high-volume work.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Laser engraving excels in detailed, intricate designs on materials like wood, acrylic, glass, and metals, making it ideal for personalized gifts, awards, and electronic device customization. Rotary engraving is best suited for deeper, more durable markings on cylindrical objects such as jewelry, metal pipes, and industrial parts, offering robust results for heavy-duty applications. Choosing between laser and rotary engraving depends on your material type and desired precision or durability level.
Choosing the Right Engraving Method for Your Needs
Laser engraving offers high precision and fine detail, making it ideal for intricate designs on materials like wood, acrylic, and glass. Rotary engraving excels in deeper cuts on metals and plastics, providing durability and lasting impressions suitable for industrial applications. Selecting the right method depends on material type, design complexity, and desired depth, ensuring optimal results for your engraving project.
laser engraving vs rotary engraving Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com