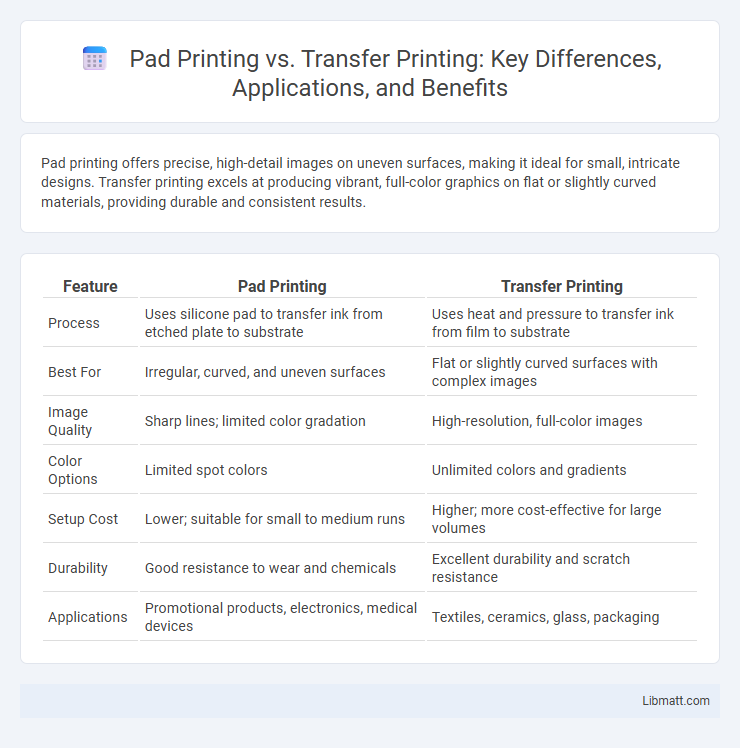
Pad printing offers precise, high-detail images on uneven surfaces, making it ideal for small, intricate designs. Transfer printing excels at producing vibrant, full-color graphics on flat or slightly curved materials, providing durable and consistent results.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pad Printing | Transfer Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses silicone pad to transfer ink from etched plate to substrate | Uses heat and pressure to transfer ink from film to substrate |
| Best For | Irregular, curved, and uneven surfaces | Flat or slightly curved surfaces with complex images |
| Image Quality | Sharp lines; limited color gradation | High-resolution, full-color images |
| Color Options | Limited spot colors | Unlimited colors and gradients |
| Setup Cost | Lower; suitable for small to medium runs | Higher; more cost-effective for large volumes |
| Durability | Good resistance to wear and chemicals | Excellent durability and scratch resistance |
| Applications | Promotional products, electronics, medical devices | Textiles, ceramics, glass, packaging |
Introduction to Pad Printing and Transfer Printing
Pad printing utilizes a silicone pad to transfer ink from an etched plate onto curved or irregular surfaces, making it ideal for detailed, multicolor designs on small objects such as promotional products and electronics. Transfer printing involves applying a printed image onto a substrate through heat and pressure, commonly used for textiles and ceramics to achieve durable and vibrant designs. Both techniques offer distinct advantages in precision and application suitability across various industries.
Key Differences Between Pad Printing and Transfer Printing
Pad printing uses a silicone pad to transfer ink directly onto irregular or curved surfaces, offering high precision and adaptability for complex shapes. Transfer printing involves printing designs onto a special film that is then heat-pressed onto the substrate, providing vibrant colors and detailed graphics on flat or slightly curved surfaces. Key differences include pad printing's suitability for small, intricate designs on varied textures versus transfer printing's advantage in producing large, full-color images with consistent quality.
How Pad Printing Works: An Overview
Pad printing uses a silicone pad to transfer ink from an etched plate onto irregular or curved surfaces, allowing precise and detailed image reproduction. The process involves ink being applied to the etched plate, excess ink being wiped away, and the pad picking up the remaining ink before pressing it onto the substrate. This technique is highly effective for printing on products like promotional items, electronic components, and medical devices due to its versatility and accuracy.
Understanding the Transfer Printing Process
Transfer printing involves creating a design on a special paper or film that is then heat-pressed onto the target surface, allowing for vibrant, detailed images on irregular or curved objects. Unlike pad printing, which uses silicone pads to transfer ink directly, transfer printing separates image creation and application, resulting in higher resolution and color consistency. This process is ideal for complex designs on materials such as ceramics, plastics, and textiles, offering durability and precision in industrial and decorative applications.
Materials Suitable for Pad vs Transfer Printing
Pad printing excels in transferring detailed images onto irregular, curved, or textured surfaces such as plastics, glass, ceramics, and metals, making it ideal for items like promotional products, electronic components, and medical devices. Transfer printing is most effective on flat or slightly curved surfaces made of materials like ceramics, glass, metals, and certain plastics, commonly used for printing on apparel, ceramics, and signage. The choice between pad and transfer printing depends largely on the substrate's shape and material compatibility, with pad printing offering greater versatility for complex shapes and transfer printing ideal for larger, flatter surfaces.
Print Quality Comparison: Pad Printing vs Transfer Printing
Pad printing offers superior print quality on irregular and curved surfaces, delivering sharp details and consistent ink coverage due to its ability to conform to complex shapes. Transfer printing excels in producing vibrant, high-resolution images with smooth gradients on flat or slightly curved items, making it ideal for intricate designs with multiple colors. Your choice depends on the substrate shape and desired color fidelity, with pad printing favored for durability on textured surfaces and transfer printing preferred for detailed, colorful graphics.
Cost Analysis: Pad Printing and Transfer Printing
Pad printing generally incurs lower initial setup costs compared to transfer printing, making it more cost-effective for small to medium production runs. Transfer printing, while requiring higher upfront investment in screens and plates, offers economies of scale and lower per-unit costs for large volume orders. Both methods vary in material and labor expenses, with pad printing typically using less intricate supplies, whereas transfer printing demands more detailed preparation and higher material costs.
Applications and Industries Using Pad and Transfer Printing
Pad printing excels in decorating irregular surfaces found in electronics, medical devices, and promotional products due to its precision and versatility. Transfer printing is widely used in textiles, ceramics, and automotive industries, offering vibrant, durable designs on flat or curved surfaces. Your choice depends on the material type and design complexity required for applications ranging from plastic components to fabric patterns.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Printing Method
Pad printing offers precise, detailed prints on irregular or curved surfaces, making it ideal for small, intricate designs; however, it can be slower and less cost-effective for large production runs. Transfer printing excels in producing vibrant, multi-color images with consistent quality at high speeds, but it may struggle with complex textures or non-flat surfaces. Your choice depends on the design complexity and production volume, balancing pad printing's versatility against transfer printing's efficiency.
Choosing the Right Printing Method for Your Project
Pad printing offers precise, detailed designs ideal for irregular or curved surfaces, while transfer printing excels in producing vibrant, full-color images on flat or slightly curved items. Your choice depends on factors like material type, design complexity, and production volume to ensure optimal print quality and durability. Evaluating these aspects will help you select the printing method that best fits your project's specific requirements.
Pad printing vs transfer printing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com