Offset lithography offers cost-effective, high-speed printing with vibrant color reproduction ideal for large runs, while photogravure excels in producing fine detail and rich tonal depth used for high-quality photographic prints and luxury packaging. Understanding these differences helps you select the printing method that best matches your project's quality and budget requirements.
Table of Comparison
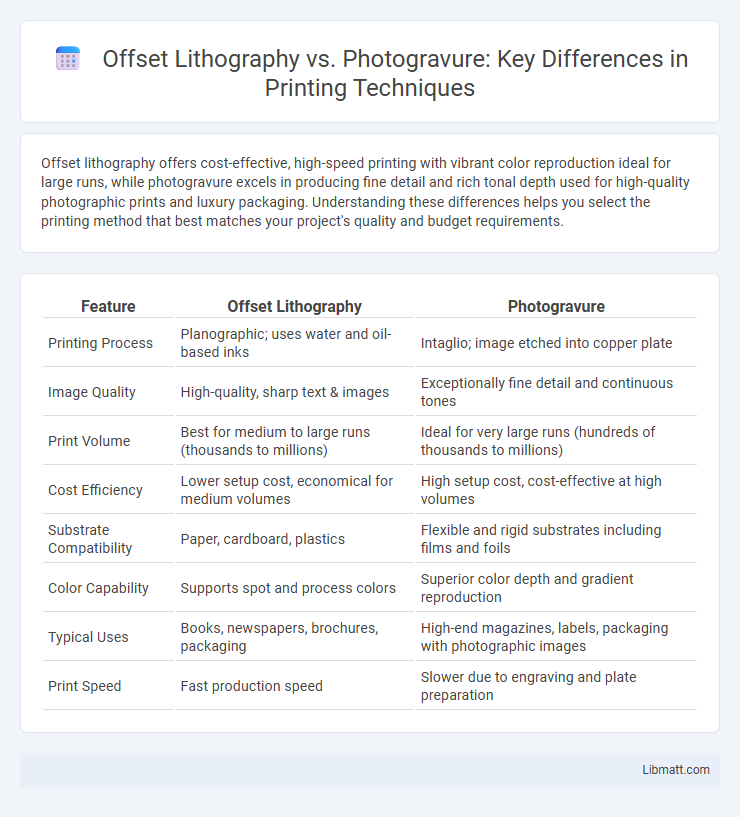
| Feature | Offset Lithography | Photogravure |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Process | Planographic; uses water and oil-based inks | Intaglio; image etched into copper plate |
| Image Quality | High-quality, sharp text & images | Exceptionally fine detail and continuous tones |
| Print Volume | Best for medium to large runs (thousands to millions) | Ideal for very large runs (hundreds of thousands to millions) |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower setup cost, economical for medium volumes | High setup cost, cost-effective at high volumes |
| Substrate Compatibility | Paper, cardboard, plastics | Flexible and rigid substrates including films and foils |
| Color Capability | Supports spot and process colors | Superior color depth and gradient reproduction |
| Typical Uses | Books, newspapers, brochures, packaging | High-end magazines, labels, packaging with photographic images |
| Print Speed | Fast production speed | Slower due to engraving and plate preparation |
Introduction to Printing Technologies
Offset lithography employs a flat image carrier where the image area is chemically treated to attract ink, offering high-speed and cost-effective printing for commercial applications. Photogravure uses engraved cylinders to transfer ink onto paper, enabling superior image quality with continuous-tone reproduction ideal for fine art and high-end magazines. Both technologies differ significantly in mechanism and application scope, with offset lithography favored for versatility and photogravure preferred for detailed, high-fidelity imagery.
What is Offset Lithography?
Offset lithography is a widely used printing technique that transfers ink from a flat, chemically treated plate to a rubber blanket, then onto paper or other substrates, enabling high-quality image reproduction with consistent sharpness and color fidelity. This method relies on the immiscibility of oil and water, where the image areas attract ink while the non-image areas repel it, making it ideal for mass production of books, newspapers, and packaging. Offset lithography offers cost-effective printing with fast turnaround times and excellent detail retention, especially for detailed text and graphics.
What is Photogravure?
Photogravure is a high-quality intaglio printing process that uses photochemical etching to transfer images onto a copper plate, allowing for detailed and continuous-tone reproduction. It excels in producing rich, deep tonal ranges ideal for fine art prints and high-end photographic reproductions. Compared to offset lithography, photogravure offers superior image clarity and depth but is more labor-intensive and costly.
Key Differences Between Offset Lithography and Photogravure
Offset lithography uses a flat plate to transfer ink onto a rubber blanket before printing on paper, enabling quick and cost-effective production for high-volume runs. Photogravure involves etching an image onto a copper plate, producing rich, continuous-tone prints ideal for high-quality photographic reproductions. Your choice depends on the desired print quality and production volume, with offset lithography favored for sharp text and photogravure for depth and tonal variation.
Print Quality Comparison
Offset lithography delivers sharp, consistent prints ideal for high-volume jobs with excellent color fidelity and fine detail reproduction. Photogravure offers superior image quality with rich tonal variations and deep, continuous tones, making it the preferred choice for high-end photo reproduction. Your printing needs will determine the best method, as photogravure excels in exceptional print depth, while offset lithography provides efficiency and versatility.
Cost Efficiency and Production Scale
Offset lithography offers higher cost efficiency for large production scales due to its faster setup times and lower per-unit costs, making it ideal for high-volume printing jobs like newspapers and packaging. Photogravure, while delivering superior image quality and rich tonal range, incurs higher initial setup expenses and longer production times, limiting its cost-effectiveness primarily to high-end, long-run print projects such as luxury magazines and art books. Businesses must evaluate production volume and budget constraints to choose between offset lithography's scalability and photogravure's premium quality.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Offset lithography excels in high-volume print runs like newspapers, brochures, and packaging due to its cost-efficiency and fast setup. Photogravure is ideal for premium-quality reproductions, such as art books, postcards, and high-end magazines, offering superior image depth and continuous-tone printing. When selecting a method, your choice depends on the desired print quality and volume, with offset suited for large runs and photogravure preferred for detailed, high-fidelity imagery.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Offset lithography generates less hazardous waste and uses fewer toxic chemicals compared to photogravure, making it a more environmentally friendly option. Photogravure involves the use of heavy metals and solvents that contribute to higher pollution levels and challenging waste disposal. Your choice of printing method can significantly influence sustainability efforts by minimizing harmful emissions and resource consumption.
Emerging Trends in Printing Technology
Offset lithography continues to dominate commercial printing due to its cost-effectiveness and high-speed production, while photogravure is gaining attention for premium packaging and fine art prints because of its superior image quality and color richness. Emerging trends show a growing integration of digital workflows in offset lithography, enhancing precision and reducing setup times, whereas photogravure is evolving with hybrid techniques that combine traditional engraving with digital plate-making technology. Your choice between these methods should consider advancements in automation, environmental sustainability, and the specific quality demands of your printing projects.
Choosing the Right Printing Method for Your Project
Offset lithography offers high-speed production and cost-efficiency for large print runs with consistent image quality, making it ideal for brochures, newspapers, and packaging. Photogravure delivers superior image fidelity and rich tonal ranges, perfect for fine art prints, high-end magazines, and photo reproductions requiring exceptional detail. Evaluating project volume, image quality requirements, and budget constraints is crucial in selecting the most suitable printing method.
Offset lithography vs photogravure Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com