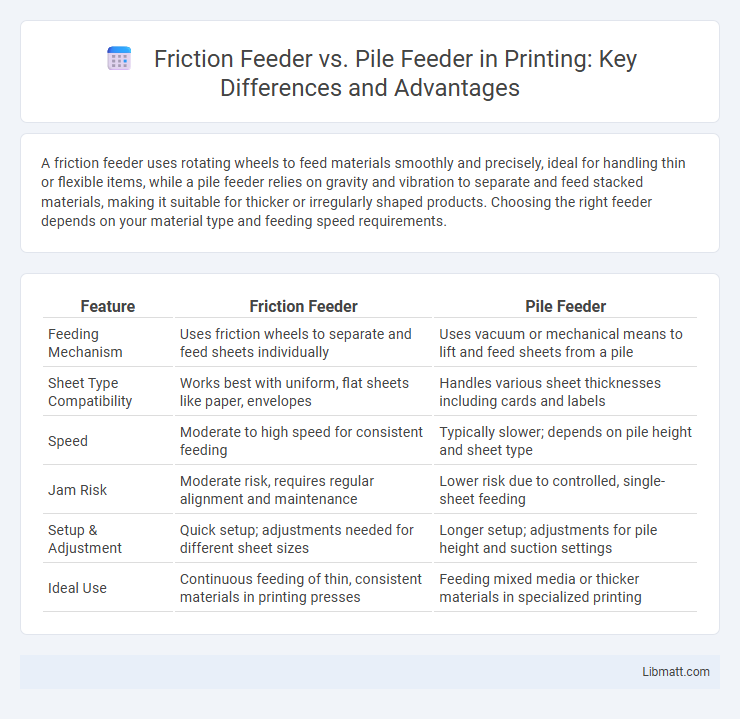
A friction feeder uses rotating wheels to feed materials smoothly and precisely, ideal for handling thin or flexible items, while a pile feeder relies on gravity and vibration to separate and feed stacked materials, making it suitable for thicker or irregularly shaped products. Choosing the right feeder depends on your material type and feeding speed requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Friction Feeder | Pile Feeder |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding Mechanism | Uses friction wheels to separate and feed sheets individually | Uses vacuum or mechanical means to lift and feed sheets from a pile |
| Sheet Type Compatibility | Works best with uniform, flat sheets like paper, envelopes | Handles various sheet thicknesses including cards and labels |
| Speed | Moderate to high speed for consistent feeding | Typically slower; depends on pile height and sheet type |
| Jam Risk | Moderate risk, requires regular alignment and maintenance | Lower risk due to controlled, single-sheet feeding |
| Setup & Adjustment | Quick setup; adjustments needed for different sheet sizes | Longer setup; adjustments for pile height and suction settings |
| Ideal Use | Continuous feeding of thin, consistent materials in printing presses | Feeding mixed media or thicker materials in specialized printing |
Introduction to Friction Feeders and Pile Feeders
Friction feeders use rotating wheels to separate and move individual sheets or items from a continuous stack, ensuring precise and controlled feeding in packaging and printing industries. Pile feeders rely on vacuum or mechanical methods to pick sheets from the top of a pile, ideal for processing large volumes of paper or thin materials with minimal marking. Both technologies optimize production efficiency by addressing different material handling challenges based on thickness, texture, and stacking method.
How Friction Feeders Work
Friction feeders operate by using rotating rubber wheels that create friction to pull individual sheets or flexible materials from a stack, ensuring precise and consistent feed rates. These feeders are ideal for handling lightweight or delicate substrates such as paper, plastic films, and labels, where controlled feeding without damage is essential. Your production line benefits from the friction feeder's ability to accommodate varying thicknesses and sizes with minimal jams or misfeeds.
How Pile Feeders Operate
Pile feeders operate by stacking materials in a loose pile and using a vacuum or separator to lift sheets or items individually from the top of the pile, ensuring consistent feeding without damage. This mechanism efficiently handles irregular or varying sheet sizes, making it ideal for applications with non-uniform stock. Unlike friction feeders that rely on continuous rollers, pile feeders excel in delicate or mixed-media processing by maintaining careful sheet separation during high-speed operations.
Key Differences Between Friction and Pile Feeders
Friction feeders use rotating wheels to advance sheets individually, delivering consistent speed and precise control suitable for lightweight or thin materials. Pile feeders rely on gravity and mechanical pressure to separate and feed stacked items, ideal for handling thicker, bulky, or uneven materials. The key differences lie in feed mechanism, material compatibility, and speed accuracy, with friction feeders excelling in high-speed, delicate applications while pile feeders offer versatility for diverse media.
Advantages of Friction Feeders
Friction feeders offer precise feeding control and can handle a wide variety of materials, including different thicknesses and textures, which ensures consistent product flow in your production line. They provide faster setup times and reduced downtime compared to pile feeders, improving overall efficiency and productivity. Their compact design and versatility make them ideal for applications requiring high-speed feeding with minimal maintenance.
Advantages of Pile Feeders
Pile feeders offer superior versatility for handling a wide range of materials, including mixed sizes and shapes, making them ideal for irregular or delicate items. They provide consistent, high-speed feeding with minimal jams, enhancing overall productivity in automated packaging or processing lines. Your operations benefit from easier setup and maintenance compared to friction feeders, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
Common Applications for Friction Feeders
Friction feeders are widely used in packaging and mailing industries for precise, high-speed feeding of materials such as envelopes, labels, brochures, and flexible films. Their ability to handle uneven or delicate materials without damage makes them ideal for pharmaceutical blister packs, promotional inserts, and product sampling. Common applications include feeding sheets into printers or inserters, handling greeting cards, and automating the sorting and collating of printed media.
Typical Uses for Pile Feeders
Pile feeders are primarily used for handling large stacks of flat, flexible materials such as sheets of paper, envelopes, cardboard, or plastic films in high-volume production environments. They excel in applications requiring the reliable separation and feeding of individual items from thick, uneven piles, commonly found in printing, packaging, and converting industries. Their ability to manage varying material thicknesses and sizes makes them ideal for automated processes that demand consistent, high-speed feeding accuracy.
Choosing the Right Feeder for Your Production Needs
Friction feeders excel in precise, continuous feeding of diverse materials such as envelopes, labels, or flexible sheets, making them ideal for high-speed, low-thickness applications. Pile feeders handle thicker, rigid stacks like brochures or booklets, offering reliable separation without damage, suited for bulk feeding and heavy-duty production. Your choice depends on material type and production speed, with friction feeders favoring versatility and pile feeders prioritizing robustness.
Cost Considerations and Maintenance Comparison
Friction feeders generally have lower upfront costs but may require more frequent maintenance due to wear on rubber rollers, impacting long-term expenses. Pile feeders, although typically more expensive initially, offer greater durability and reduced maintenance needs, making them cost-effective for high-volume operations. You should evaluate your production scale and budget to determine which feeder type aligns best with your operational cost and maintenance preferences.
Friction Feeder vs Pile Feeder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com