Hot melt adhesive offers strong, immediate bonding through heat activation, making it ideal for applications requiring fast setting and high durability. Your choice of pressure-sensitive adhesive provides flexibility and repositionability, adhering instantly with light pressure and excelling in applications like labels and tapes.
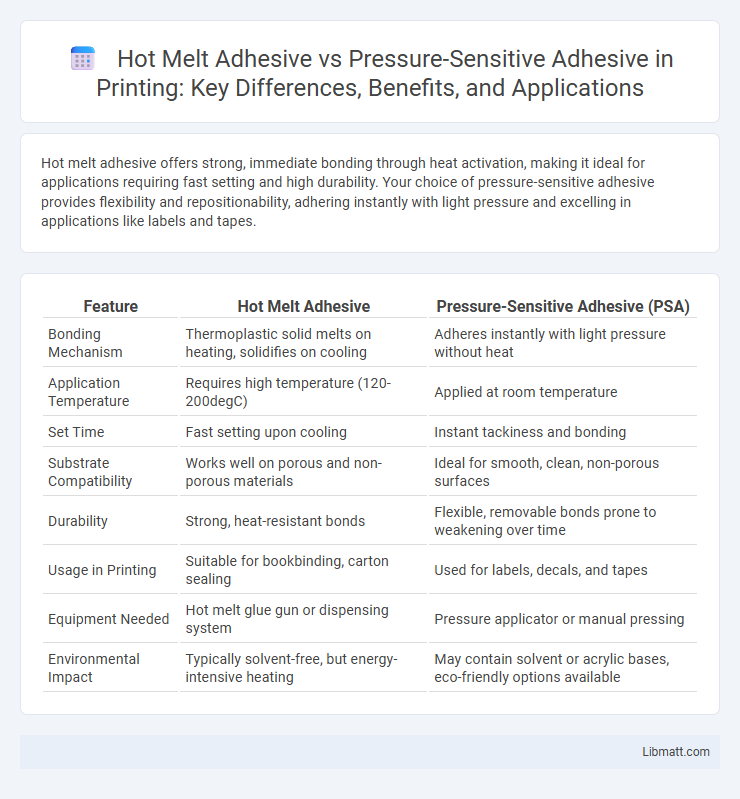
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hot Melt Adhesive | Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding Mechanism | Thermoplastic solid melts on heating, solidifies on cooling | Adheres instantly with light pressure without heat |
| Application Temperature | Requires high temperature (120-200degC) | Applied at room temperature |
| Set Time | Fast setting upon cooling | Instant tackiness and bonding |
| Substrate Compatibility | Works well on porous and non-porous materials | Ideal for smooth, clean, non-porous surfaces |
| Durability | Strong, heat-resistant bonds | Flexible, removable bonds prone to weakening over time |
| Usage in Printing | Suitable for bookbinding, carton sealing | Used for labels, decals, and tapes |
| Equipment Needed | Hot melt glue gun or dispensing system | Pressure applicator or manual pressing |
| Environmental Impact | Typically solvent-free, but energy-intensive heating | May contain solvent or acrylic bases, eco-friendly options available |
Introduction to Adhesive Technologies
Hot melt adhesives (HMAs) are thermoplastic materials that become tacky when heated and solidify upon cooling, offering strong, fast-setting bonds ideal for packaging and product assembly. Pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) maintain a permanent tack at room temperature and bond upon light pressure without the need for heat, widely used in tapes, labels, and medical applications. Both technologies play critical roles in manufacturing, providing tailored bonding solutions based on application requirements such as bonding strength, flexibility, and curing time.
Defining Hot Melt Adhesive
Hot melt adhesive (HMA) is a thermoplastic polymer applied in a molten state that solidifies upon cooling to form a strong bond. Unlike pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSA), which remain tacky and adhere under light pressure, HMAs provide high initial strength and resistance to heat and chemicals. Commonly used in packaging, woodworking, and automotive industries, hot melt adhesives offer fast set times and durable bonding performance.
Understanding Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive
Pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA) is a type of adhesive that forms a bond when pressure is applied to marry the adhesive with the adherend, without requiring solvent, water, or heat activation. PSAs are characterized by their ability to maintain tackiness over time, allowing for repositionability and easy application on various substrates like paper, plastics, and metals. Unlike hot melt adhesives, PSAs offer long-term adhesion with flexibility and resistance to aging and environmental factors, making them ideal for labels, tapes, and flexible packaging.
Composition and Formulation Differences
Hot melt adhesives are primarily composed of thermoplastic polymers such as ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), polyolefins, and styrenic block copolymers, formulated to melt and solidify rapidly upon cooling, providing strong bond strength. Pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) consist of viscoelastic polymers like acrylics, rubber-based compounds, and silicones, designed to remain tacky at room temperature for instant adhesion under light pressure. The key formulation difference lies in hot melt adhesives requiring heat activation, while PSAs rely on inherent tackiness and do not require heat to bond surfaces.
Application Methods and Equipment
Hot melt adhesives require application equipment such as heated glue guns, roller coaters, or spray systems that melt the solid adhesive for precise, fast bonding upon cooling. Pressure-sensitive adhesives are applied using rollers, brushes, or transfer tapes without heat, relying on pressure to activate bonding immediately upon contact. Your choice depends on the production speed, substrate compatibility, and equipment investment suitable for your specific application needs.
Performance in Various Conditions
Hot melt adhesives exhibit superior performance in high-temperature environments due to their thermoplastic nature, providing strong initial tack and fast setting times on diverse substrates. Pressure-sensitive adhesives maintain consistent adhesion across a wide range of temperatures and humidity levels, making them ideal for applications requiring flexibility and removability. Both adhesives offer distinct advantages; hot melts excel in bonding strength and chemical resistance, while pressure-sensitive adhesives deliver reliable performance on low-energy surfaces and in dynamic conditions.
Bonding Strength and Durability
Hot melt adhesives exhibit high bonding strength and excellent durability, making them ideal for applications requiring strong, permanent bonds on materials like plastics, metals, and wood. Pressure-sensitive adhesives provide moderate bonding strength with flexibility, suitable for temporary or repositionable bonds on surfaces such as paper, films, and tapes. Durability of hot melt adhesives generally surpasses pressure-sensitive adhesives, especially under heat and environmental stress conditions.
Common Uses and Industries
Hot melt adhesives are widely used in packaging, woodworking, and automotive industries due to their fast bonding and high heat resistance, ideal for bonding materials like plastics, metals, and paper. Pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) dominate the labeling, medical, and electronics sectors, offering strong adhesion at room temperature without the need for heat or solvents, perfect for tapes, stickers, and flexible films. Your choice depends on application requirements, such as bond strength, curing time, and substrate compatibility.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Hot melt adhesives typically have a lower environmental impact due to their solvent-free formulation, resulting in reduced VOC emissions and less hazardous waste compared to pressure-sensitive adhesives, which often contain solvents or plasticizers. In terms of safety, hot melt adhesives require high temperatures for application, posing burn risks, whereas pressure-sensitive adhesives are safer to handle but may release harmful chemicals during curing or disposal. Your choice should consider not only the adhesive's performance but also the environmental regulations and safety protocols relevant to your application.
Choosing the Right Adhesive for Your Needs
Hot melt adhesives offer strong, fast-setting bonds ideal for packaging and product assembly, while pressure-sensitive adhesives provide flexibility and reusability suitable for labels and tapes. Your choice depends on factors like bonding strength, surface type, and application conditions, ensuring optimal performance and durability. Understanding these key differences helps you select the adhesive that best meets your specific project requirements.
Hot melt adhesive vs pressure-sensitive adhesive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com