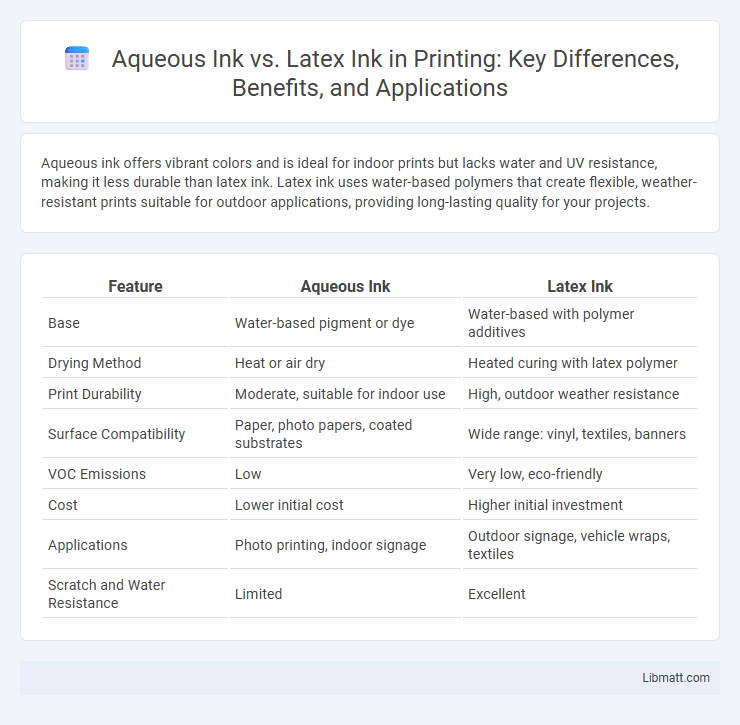
Aqueous ink offers vibrant colors and is ideal for indoor prints but lacks water and UV resistance, making it less durable than latex ink. Latex ink uses water-based polymers that create flexible, weather-resistant prints suitable for outdoor applications, providing long-lasting quality for your projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aqueous Ink | Latex Ink |
|---|---|---|
| Base | Water-based pigment or dye | Water-based with polymer additives |
| Drying Method | Heat or air dry | Heated curing with latex polymer |
| Print Durability | Moderate, suitable for indoor use | High, outdoor weather resistance |
| Surface Compatibility | Paper, photo papers, coated substrates | Wide range: vinyl, textiles, banners |
| VOC Emissions | Low | Very low, eco-friendly |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial investment |
| Applications | Photo printing, indoor signage | Outdoor signage, vehicle wraps, textiles |
| Scratch and Water Resistance | Limited | Excellent |
Introduction to Aqueous and Latex Inks
Aqueous ink, a water-based printing medium, is known for its vibrant color output and eco-friendly properties, making it ideal for high-quality photographic and fine art prints. Latex ink, combining water-based polymer and latex, offers enhanced durability and flexibility, suitable for outdoor signage and heavy-duty applications due to its resistance to water, abrasion, and UV light. Both inks serve distinct industrial and commercial purposes, with aqueous inks prioritized for indoor use and latex inks favored for versatile, long-lasting prints across various substrates.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Aqueous ink primarily consists of water-based solvents, colorants, and various additives, providing excellent environmental safety and easy cleanup due to its non-toxic, non-flammable properties. Latex ink combines water-based polymers with specialized latex particles, allowing it to form a flexible, durable film upon curing that enhances abrasion and chemical resistance. The chemical stability of aqueous ink limits its use to porous substrates, whereas latex ink's polymeric composition enables adhesion to a wider range of materials, including non-porous surfaces.
Printing Process Overview
Aqueous ink printing utilizes water-based solvents that penetrate coated paper fibers, resulting in vibrant colors and fast drying times ideal for indoor prints. Latex ink employs water-based polymer dispersion heated during printing, allowing durable, flexible prints suitable for outdoor use and various media types. Your choice between aqueous and latex inks will impact print longevity, substrate compatibility, and application environment.
Substrate Compatibility
Aqueous ink demonstrates excellent substrate compatibility with coated papers, photo papers, and vinyl materials, providing vibrant colors and sharp details primarily on porous surfaces. Latex ink excels across a broader range of substrates, including uncoated papers, textiles, and rigid materials like metal and glass, due to its flexible polymer base that adheres well without requiring extensive pre-treatment. Your choice between aqueous and latex ink should consider the specific substrate demands of your printing project to ensure optimal adhesion and durability.
Color Vibrancy and Print Quality
Aqueous ink delivers high color vibrancy with sharp detail on coated papers, producing bright, crisp images ideal for indoor prints. Latex ink offers superior print quality on a wider range of substrates, including flexible and outdoor materials, maintaining vibrant colors and durability with scratch and water resistance. Both inks excel in color rendering, but latex ink's versatility and resilience provide enhanced longevity in print applications.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Aqueous ink is water-based, making it non-toxic and environmentally friendly due to its low VOC emissions and easy biodegradability, which reduces air and water pollution. Latex ink also offers environmental benefits, as it contains fewer harmful solvents and produces durable prints without harsh chemicals, but it may require energy-intensive curing processes that impact its overall carbon footprint. Understanding the safety and eco-friendliness of these inks helps you make sustainable choices for your printing needs.
Durability and Longevity
Aqueous ink offers vibrant color output but typically has lower durability, making it prone to fading and water damage over time. Latex ink provides superior longevity with enhanced resistance to UV exposure, scratching, and moisture, ensuring prints remain vivid for extended outdoor and indoor use. The durability of latex ink makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring long-lasting, high-quality prints.
Application Industries
Aqueous ink is predominantly used in industries requiring high-quality photographic prints and fine art reproductions, such as photo labs and graphic design studios, due to its vibrant color range and archival properties. Latex ink finds widespread application in outdoor signage, vehicle wraps, and textile printing industries because of its water resistance, durability, and fast drying on diverse substrates. Both inks serve specialized markets, with aqueous ink excelling in indoor, detailed graphical applications and latex ink thriving in versatile, weather-resistant productions.
Cost Comparison
Aqueous ink generally offers a lower initial cost compared to latex ink, making it a cost-effective choice for short-term or low-volume printing projects. Latex ink, while more expensive upfront, provides greater durability and flexibility, reducing long-term expenses related to maintenance and replacement. Businesses must weigh the immediate savings of aqueous ink against the extended value and resilience provided by latex ink when considering overall cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Ink for Your Needs
Aqueous ink offers vibrant color reproduction and is ideal for indoor prints on coated paper, while latex ink provides durability, water resistance, and faster drying times suited for outdoor applications and flexible materials. Your choice should depend on the substrate, exposure conditions, and desired longevity of the print. Understanding these key differences ensures you select the right ink to meet your specific project requirements.
Aqueous Ink vs Latex Ink Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com