Pad printing offers precise image transfer on irregular or curved surfaces, making it ideal for detailed logos and small objects. Screen printing excels in producing vibrant, durable designs on flat or slightly textured materials, perfect for high-volume production and larger graphics.
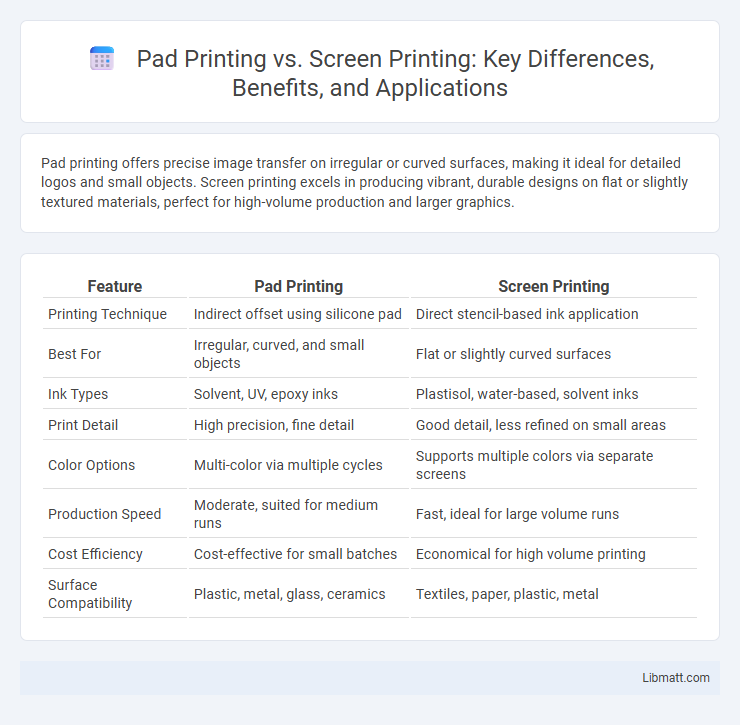
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pad Printing | Screen Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Technique | Indirect offset using silicone pad | Direct stencil-based ink application |
| Best For | Irregular, curved, and small objects | Flat or slightly curved surfaces |
| Ink Types | Solvent, UV, epoxy inks | Plastisol, water-based, solvent inks |
| Print Detail | High precision, fine detail | Good detail, less refined on small areas |
| Color Options | Multi-color via multiple cycles | Supports multiple colors via separate screens |
| Production Speed | Moderate, suited for medium runs | Fast, ideal for large volume runs |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for small batches | Economical for high volume printing |
| Surface Compatibility | Plastic, metal, glass, ceramics | Textiles, paper, plastic, metal |
Introduction to Pad Printing and Screen Printing
Pad printing uses a silicone pad to transfer ink onto irregular or curved surfaces, making it ideal for detailed images on items like promotional products and electronics. Screen printing involves pressing ink through a mesh screen stencil to produce vibrant, durable designs on flat or slightly textured surfaces such as textiles and posters. Both techniques offer unique advantages depending on the substrate complexity and design requirements.
How Pad Printing Works
Pad printing operates through a silicone pad that transfers ink from an etched plate onto three-dimensional objects, allowing precise application on irregular surfaces. The process begins with ink being spread over the etched plate, where the silicone pad picks up the inked image before pressing it onto the target material. This technique is highly effective for detailed graphics on items such as promotional products, electronics, and medical devices, ensuring consistent, high-quality results on complex shapes.
How Screen Printing Works
Screen printing uses a mesh stencil to transfer ink onto a substrate by pressing it through the screen with a squeegee, allowing for precise and vibrant designs on various materials like fabric, plastic, and metal. Each color in the design requires a separate screen, making the process ideal for high-volume production with consistent quality. The technique's durability and ink opacity make it a preferred choice for creating bold, long-lasting prints on promotional products and apparel.
Key Differences Between Pad Printing and Screen Printing
Pad printing excels in transferring detailed, multi-colored images onto irregular, curved, or small surfaces, using a silicone pad for precision. Screen printing operates best on flat or mildly contoured surfaces, offering vibrant, thick layers of ink ideal for large, bold designs with high durability. Key differences include pad printing's versatility on complex shapes and screen printing's superior ink opacity and speed on flat substrates.
Advantages of Pad Printing
Pad printing excels in transferring intricate designs onto irregular or textured surfaces, offering exceptional precision and detail that screen printing may struggle to achieve. This method accommodates a wide variety of materials, including plastics, metals, glass, and ceramics, making it highly versatile for different industries. Your branding or artwork benefits from pad printing's ability to reach tight spaces and complex shapes with consistent ink application.
Advantages of Screen Printing
Screen printing offers superior durability and vibrant color output, making it ideal for long-lasting designs on various surfaces such as textiles, plastics, and metals. Its ability to produce high ink coverage ensures strong opacity and vivid visuals even on dark materials. Cost-effective for large production runs, screen printing delivers consistent quality with faster turnaround times compared to pad printing.
Best Applications for Pad Printing
Pad printing excels in transferring detailed images onto irregular, curved, or textured surfaces, making it ideal for printing on promotional products, electronic components, and medical devices. Its precision and ability to print on small or hard-to-reach areas outperform screen printing in applications requiring intricate designs on varied substrates such as plastics, metals, and glass. Industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods benefit from pad printing's versatility for marking parts and branding with high-quality, durable inks.
Best Applications for Screen Printing
Screen printing excels in producing vibrant, durable designs on flat or slightly curved surfaces, making it ideal for textiles, posters, and promotional materials. This method offers superior ink opacity and thickness, perfect for bold graphics on t-shirts, banners, and signage. Its efficiency in large-volume runs reduces cost per unit, benefiting commercial clothing brands and advertising campaigns.
Cost Considerations: Pad Printing vs Screen Printing
Pad printing generally offers lower setup costs for small to medium production runs due to its minimal stencil and equipment requirements, making it ideal for detailed, multi-surface printing. Screen printing involves higher initial expenses, including screen preparation and setup, which are more cost-effective for large volume jobs offering economies of scale. Businesses should evaluate batch size and print complexity when comparing pad printing's cost-efficiency against screen printing's scalability benefits.
Choosing the Right Printing Method for Your Project
Pad printing excels in transferring intricate, detailed images onto uneven or curved surfaces, making it ideal for small promotional items, electronics, and medical devices. Screen printing is better suited for larger, flat surfaces with vibrant, durable colors, commonly used for apparel, posters, and packaging. When choosing the right printing method for your project, consider the material type, surface shape, image complexity, and desired print durability to ensure optimal results.
Pad Printing vs Screen Printing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com