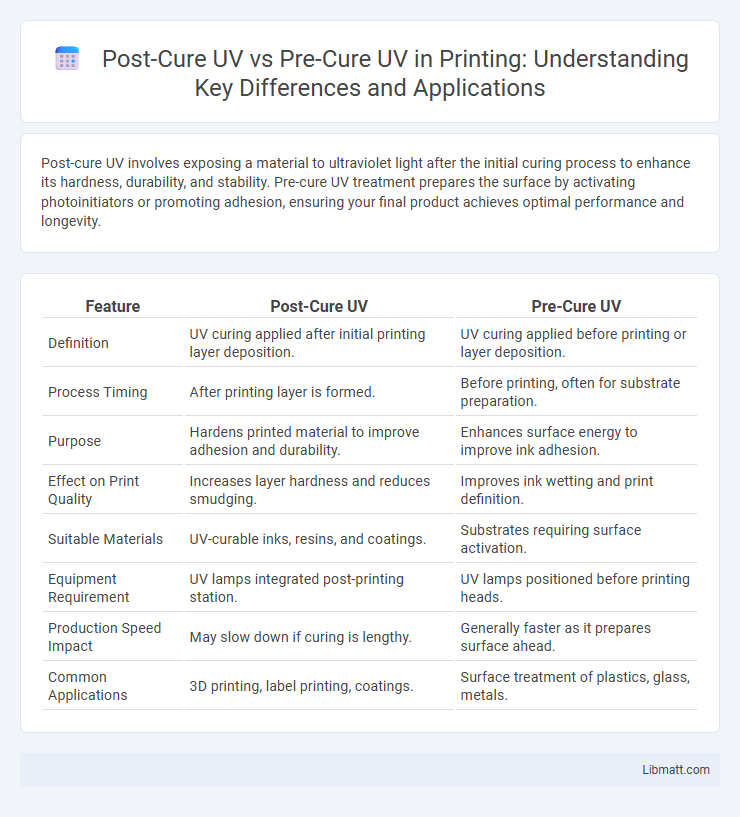
Post-cure UV involves exposing a material to ultraviolet light after the initial curing process to enhance its hardness, durability, and stability. Pre-cure UV treatment prepares the surface by activating photoinitiators or promoting adhesion, ensuring your final product achieves optimal performance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Post-Cure UV | Pre-Cure UV |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | UV curing applied after initial printing layer deposition. | UV curing applied before printing or layer deposition. |
| Process Timing | After printing layer is formed. | Before printing, often for substrate preparation. |
| Purpose | Hardens printed material to improve adhesion and durability. | Enhances surface energy to improve ink adhesion. |
| Effect on Print Quality | Increases layer hardness and reduces smudging. | Improves ink wetting and print definition. |
| Suitable Materials | UV-curable inks, resins, and coatings. | Substrates requiring surface activation. |
| Equipment Requirement | UV lamps integrated post-printing station. | UV lamps positioned before printing heads. |
| Production Speed Impact | May slow down if curing is lengthy. | Generally faster as it prepares surface ahead. |
| Common Applications | 3D printing, label printing, coatings. | Surface treatment of plastics, glass, metals. |
Introduction to UV Curing Technologies
UV curing technologies employ ultraviolet light to rapidly harden or polymerize coatings, adhesives, and inks, enhancing production efficiency across industries. Pre-cure UV initiates surface curing to create a tack-free layer, enabling handling and laminating, while post-cure UV strengthens the entire material, improving durability and chemical resistance. Understanding the distinctions between pre-cure and post-cure UV processes is critical for optimizing manufacturing workflows and product performance in sectors such as electronics, automotive, and printing.
Defining Pre-cure UV and Post-cure UV
Pre-cure UV refers to the ultraviolet light exposure applied before the primary curing process to initiate partial polymerization in UV-sensitive materials, enhancing adhesion and structural stability. Post-cure UV involves the application of ultraviolet light after the initial curing phase to complete polymerization, ensuring maximum hardness, chemical resistance, and durability of the final product. Both pre-cure and post-cure UV techniques are critical in industries such as 3D printing, coatings, and adhesives for optimizing material properties and performance.
Applications of Pre-cure versus Post-cure UV
Pre-cure UV is commonly used in applications requiring rapid surface curing, such as in 3D printing and dental restorations, where immediate handling strength is critical. Post-cure UV enhances material properties like hardness and durability, making it suitable for finalizing parts in electronics manufacturing and medical devices. Your choice between pre-cure and post-cure UV depends on whether initial surface strength or long-term performance is the priority.
Workflow Differences: Pre-cure vs Post-cure UV
Pre-cure UV involves partially curing resin materials before the main processing, allowing for better shape retention and reduced deformation during handling. Post-cure UV occurs after the initial curing stage, enhancing mechanical strength and chemical resistance by completing polymerization. The workflow difference lies in pre-cure enabling intermediate stability for subsequent operations, while post-cure focuses on finalizing material properties to meet performance standards.
Material Compatibility with UV Curing Methods
Post-cure UV processes are highly compatible with materials that require thorough polymerization after initial shaping, ensuring enhanced mechanical properties and chemical resistance, especially in epoxy and acrylic resins. Pre-cure UV methods suit substrates sensitive to heat or solvents, facilitating surface-level curing without compromising material integrity, commonly used in thin films and coatings. Selecting the appropriate UV curing stage depends on the chemical formulation and thermal stability of the material, impacting adhesion, flexibility, and final product performance.
Advantages of Post-cure UV
Post-cure UV enhances the mechanical properties and chemical resistance of 3D printed parts by completing polymerization after the initial print, resulting in improved durability and stability. It reduces residual monomers and enhances surface hardness, providing a finely detailed and smooth finish essential for industrial applications. Post-cure UV also minimizes warping and ensures consistent dimensional accuracy across complex geometries, outperforming pre-cure UV in final part quality.
Benefits of Pre-cure UV
Pre-cure UV treatment enhances the initial adhesion and surface hardness of 3D printed materials, reducing curing time and improving layer bonding. This process minimizes warping and shrinkage, leading to higher dimensional accuracy and smoother finishes. Pre-cure UV also increases resistance to environmental factors, resulting in more durable and stable end products.
Limitations and Challenges of Each UV Method
Post-cure UV processes can struggle with uniform light penetration, leading to incomplete curing in thicker or complex-shaped parts, which limits the mechanical properties and surface finish quality. Pre-cure UV methods often face challenges in adhesion and premature polymerization, causing inconsistencies in layer bonding and dimensional accuracy during 3D printing or coatings. You must consider these limitations when selecting the appropriate UV curing process to optimize product performance and durability.
Choosing Between Post-cure and Pre-cure UV
Choosing between post-cure UV and pre-cure UV depends on the specific application requirements and material properties. Post-cure UV enhances the mechanical strength and chemical resistance of 3D printed parts by completing polymerization after the initial print, while pre-cure UV is used to solidify resin layers during the printing process for precise detail and faster build times. Optimizing cure stages ensures improved durability, surface finish, and overall performance in UV-cured polymer applications.
Future Trends in UV Curing Technology
Future trends in UV curing technology emphasize enhanced efficiency and precision, with post-cure UV processes gaining traction for their ability to achieve deeper, more uniform polymerization in complex coatings and 3D prints. Innovations in LED UV sources enable rapid pre-cure UV steps that reduce energy consumption and increase throughput in high-volume manufacturing. Your production lines can benefit from hybrid curing systems combining pre-cure and post-cure techniques to optimize material properties and minimize defects.
Post-cure UV vs pre-cure UV Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com