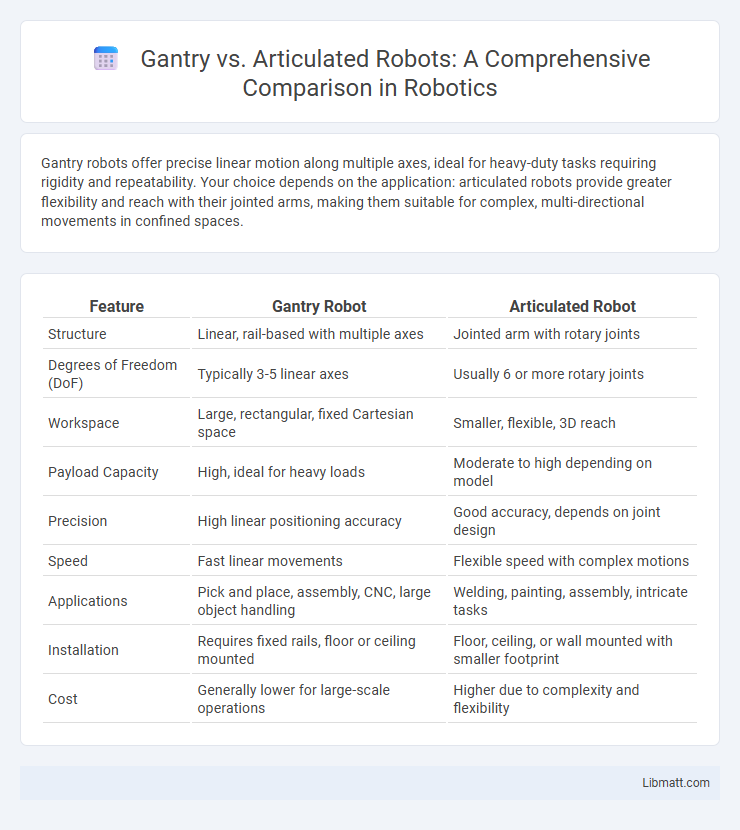
Gantry robots offer precise linear motion along multiple axes, ideal for heavy-duty tasks requiring rigidity and repeatability. Your choice depends on the application: articulated robots provide greater flexibility and reach with their jointed arms, making them suitable for complex, multi-directional movements in confined spaces.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gantry Robot | Articulated Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Linear, rail-based with multiple axes | Jointed arm with rotary joints |
| Degrees of Freedom (DoF) | Typically 3-5 linear axes | Usually 6 or more rotary joints |
| Workspace | Large, rectangular, fixed Cartesian space | Smaller, flexible, 3D reach |
| Payload Capacity | High, ideal for heavy loads | Moderate to high depending on model |
| Precision | High linear positioning accuracy | Good accuracy, depends on joint design |
| Speed | Fast linear movements | Flexible speed with complex motions |
| Applications | Pick and place, assembly, CNC, large object handling | Welding, painting, assembly, intricate tasks |
| Installation | Requires fixed rails, floor or ceiling mounted | Floor, ceiling, or wall mounted with smaller footprint |
| Cost | Generally lower for large-scale operations | Higher due to complexity and flexibility |
Introduction to Gantry and Articulated Robots
Gantry robots are characterized by their linear motion system, moving along fixed rails to provide precise, large-scale automation ideal for material handling and assembly tasks. Articulated robots feature rotary joints, enabling multi-axis movement that mimics a human arm, suited for complex and flexible operations like welding and painting. Understanding these differences helps you select the right robotic solution for your industrial automation needs.
Key Design Differences
Gantry robots feature a fixed, bridge-like structure that moves along three linear axes, providing high precision and repeatability ideal for large-scale manufacturing. Articulated robots utilize rotary joints with multiple degrees of freedom, resembling a human arm, allowing for versatile and complex movements within confined spaces. Your choice depends on whether you need extensive linear reach and stability or flexible, multi-directional articulation for intricate tasks.
Applications of Gantry Robots
Gantry robots excel in applications requiring large workspace coverage and high payload capacity, such as automotive assembly, packaging, and material handling in warehouses. Their precise linear motion makes them ideal for pick-and-place operations, CNC machining, and 3D printing on a large scale. Industries benefit from gantry robots' ability to automate heavy-duty tasks with consistent accuracy and scalability.
Applications of Articulated Robots
Articulated robots excel in applications requiring high flexibility and complex movements, such as automotive assembly, welding, and material handling in dynamic environments. Their multi-jointed arms enable precise tasks like painting, packaging, and machine tending with enhanced reach and dexterity compared to gantry robots. You can leverage articulated robots for operations demanding adaptability and intricate maneuvering beyond the fixed linear paths of gantry systems.
Workspace and Reach Capabilities
Gantry robots offer extensive workspace coverage due to their multi-axis linear movement over large, predetermined areas, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks requiring long reach and high load capacity. Articulated robots feature multiple rotary joints that provide versatile reach and flexible movement within a more confined workspace, excelling in precision tasks and complex maneuvers. The choice between gantry and articulated robots depends on the required operational range and spatial constraints of the application.
Precision and Speed Comparison
Gantry robots offer high precision and speed due to their rigid, linear motion systems, making them ideal for tasks requiring exact positioning over large areas. Articulated robots, while slightly less precise because of their complex jointed arms, excel in speed and flexibility for intricate, multi-axis movements in confined spaces. The choice between the two depends on the application's demand for either superior repeatability or dynamic maneuverability.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Gantry robots provide high precision and load capacity within a defined linear workspace, making them ideal for repetitive tasks requiring stability. Articulated robots offer superior flexibility and adaptability with multiple joints, allowing your automation system to handle complex, multi-axis movements across varied tasks. Choosing between the two depends on the specific spatial constraints and operational versatility your application demands.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Gantry robots typically have higher upfront costs due to their complex rail systems but benefit from lower maintenance expenses because of their simpler mechanical design and fewer moving joints. Articulated robots often incur lower initial investment but require more frequent maintenance and higher repair costs due to their intricate joint assemblies and greater wear on motors and encoders. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing the gantry robot's durability and long-term reliability against the articulated robot's flexibility and potentially higher upkeep.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Gantry robots excel in industries requiring high-precision, large-scale material handling such as automotive manufacturing and electronics assembly, where their linear motion and stability enhance efficiency. Articulated robots are widely used in welding, painting, and complex assembly tasks within automotive and aerospace sectors due to their flexible joints and wide range of motion. Your selection should align with specific industry demands, prioritizing the gantry's rigid structure for heavy loads or the articulated robot's versatility for intricate operations.
Choosing the Right Robot for Your Application
Selecting between a gantry robot and an articulated robot depends on the specific needs of your application, including workspace size and loading requirements. Gantry robots excel in handling heavy loads and offer high precision over large, linear work areas, making them ideal for pick-and-place operations and material handling on factory floors. Articulated robots provide greater flexibility with multiple degrees of freedom, suited for complex tasks like welding, assembly, and painting where intricate movements are essential.
Gantry vs Articulated Robot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com