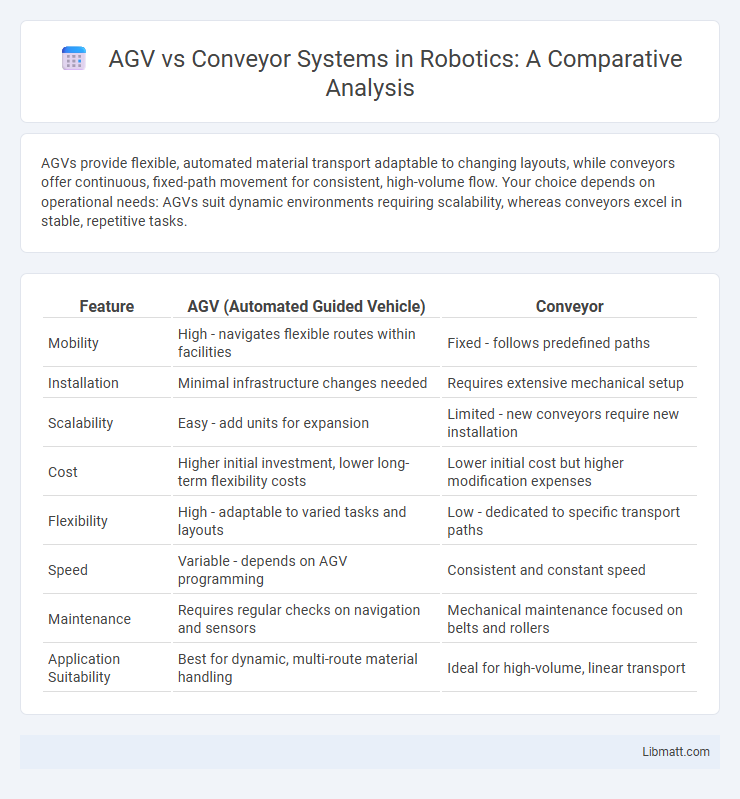
AGVs provide flexible, automated material transport adaptable to changing layouts, while conveyors offer continuous, fixed-path movement for consistent, high-volume flow. Your choice depends on operational needs: AGVs suit dynamic environments requiring scalability, whereas conveyors excel in stable, repetitive tasks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) | Conveyor |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | High - navigates flexible routes within facilities | Fixed - follows predefined paths |
| Installation | Minimal infrastructure changes needed | Requires extensive mechanical setup |
| Scalability | Easy - add units for expansion | Limited - new conveyors require new installation |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower long-term flexibility costs | Lower initial cost but higher modification expenses |
| Flexibility | High - adaptable to varied tasks and layouts | Low - dedicated to specific transport paths |
| Speed | Variable - depends on AGV programming | Consistent and constant speed |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks on navigation and sensors | Mechanical maintenance focused on belts and rollers |
| Application Suitability | Best for dynamic, multi-route material handling | Ideal for high-volume, linear transport |
Introduction to AGV and Conveyor Systems
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and conveyor systems are essential components in modern material handling and logistics operations, designed to improve efficiency and reduce manual labor. AGVs are mobile robots that navigate factory floors or warehouses using sensors and pre-defined paths, offering flexibility in transporting goods. Conveyors provide a fixed pathway for continuous movement of products, ideal for repetitive, high-volume tasks requiring consistent speed and positioning.
Key Differences Between AGVs and Conveyors
AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) offer flexible, automated material transport with programmable routes and real-time adaptability, while conveyors provide fixed, continuous movement along predetermined paths. AGVs are ideal for dynamic environments requiring variable routing and integration with warehouse management systems, whereas conveyors excel in high-volume, repetitive tasks with minimal manual intervention. Your choice depends on operational needs for scalability, layout flexibility, and automation sophistication.
Cost Comparison: AGV vs Conveyor
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) typically involve higher initial investment costs compared to conveyors due to advanced navigation technology and software integration. Conveyors offer lower upfront expenses and maintenance costs but can require extensive facility modifications and are less flexible in dynamic environments. Over time, AGVs may provide greater cost efficiency through reduced labor expenses and enhanced adaptability in complex material handling operations.
Flexibility and Scalability
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) offer superior flexibility compared to conveyors, as they can easily navigate changing layouts and expand routes without significant infrastructure modifications. Conveyors require fixed installations that limit scalability and adaptability, making them less ideal for dynamic environments where production demands fluctuate. Choosing AGVs can enhance your operational agility and support scalable growth with minimal downtime.
Installation and Integration Process
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) require flexible installation with minimal infrastructure changes, allowing easy integration into existing warehouse layouts through wireless communication and software interfacing. Conveyor systems demand extensive upfront installation, including fixed pathways, mechanical setup, and electrical wiring, making integration into current facilities more rigid and time-consuming. AGVs offer scalable deployment with software-driven route adjustments, whereas conveyors necessitate physical modifications for layout changes, impacting overall installation and integration efficiency.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) typically require lower upfront infrastructure investments but can incur higher maintenance costs due to complex navigation and battery management systems. Conveyors involve substantial initial installation and fixed pathway expenses, yet their maintenance tends to be more predictable and less labor-intensive, focusing mainly on mechanical wear and motor servicing. Your choice should consider operational scale and flexibility needs, as AGVs offer adaptable routing options while conveyors provide consistent, low-maintenance material flow.
Safety Considerations
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and conveyors have distinct safety considerations in industrial environments. AGVs require advanced sensor systems and real-time obstacle detection to prevent collisions and ensure safe navigation around personnel. Conveyors necessitate guarding, emergency stop mechanisms, and regular maintenance to mitigate risks such as entanglement, pinch points, and material spillage.
Suitable Applications for AGVs
Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs) excel in flexible material handling environments such as warehouses, manufacturing plants, and distribution centers where dynamic routing and adaptability are essential. AGVs are suitable for applications requiring automated transport of goods over varying distances, especially in facilities with changing layouts or seasonal fluctuations. Unlike conveyors, AGVs can navigate complex pathways, handle diverse payloads, and easily integrate with warehouse management systems for real-time tracking and efficiency.
Suitable Applications for Conveyors
Conveyors are ideal for transporting heavy or bulky materials over fixed, repetitive routes within manufacturing or distribution facilities, offering high throughput and continuous operation. They excel in environments where tasks require consistent speed and minimal variation, such as assembly lines, packaging, and bulk material handling. Your choice of conveyors ensures reliability and efficiency in large-scale, stationary processes where flexibility is less critical than volume and predictability.
Future Trends in Material Handling Systems
Automation technologies like AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) are increasingly favored over traditional conveyor systems due to their flexibility, scalability, and ability to integrate with AI-driven warehouse management systems. Future trends emphasize the use of AGVs equipped with advanced sensors and real-time data analytics to optimize route efficiency and reduce operational costs. Your choice between AGVs and conveyors should consider the growing demand for adaptable, intelligent material handling solutions that support Industry 4.0 standards.
AGV vs Conveyor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com