G Code controls the movement and positioning of CNC machines, guiding tool paths with precise instructions, while M Code manages machine functions like coolant control, spindle speed, and tool changes. Understanding the distinction between G Code and M Code helps you optimize CNC programming for efficient and accurate machining processes.
Table of Comparison
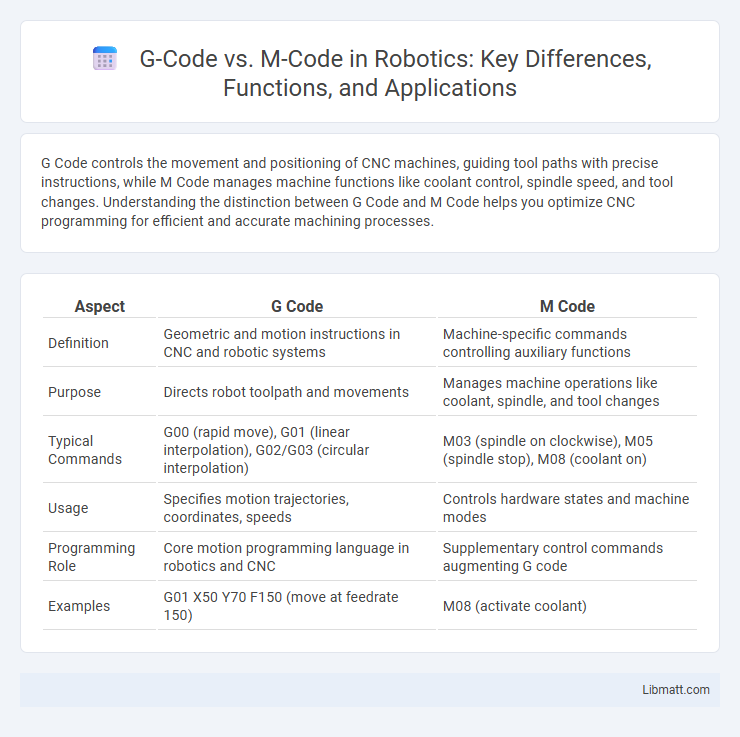
| Aspect | G Code | M Code |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Geometric and motion instructions in CNC and robotic systems | Machine-specific commands controlling auxiliary functions |
| Purpose | Directs robot toolpath and movements | Manages machine operations like coolant, spindle, and tool changes |
| Typical Commands | G00 (rapid move), G01 (linear interpolation), G02/G03 (circular interpolation) | M03 (spindle on clockwise), M05 (spindle stop), M08 (coolant on) |
| Usage | Specifies motion trajectories, coordinates, speeds | Controls hardware states and machine modes |
| Programming Role | Core motion programming language in robotics and CNC | Supplementary control commands augmenting G code |
| Examples | G01 X50 Y70 F150 (move at feedrate 150) | M08 (activate coolant) |
Introduction to G Code and M Code
G Code commands control the movement and operation of CNC machines, directing tool path and positioning with precision. M Code manages auxiliary functions such as coolant activation, spindle control, and other machine-specific actions. Understanding both codes enhances your ability to program CNC machines efficiently, ensuring accurate and smooth manufacturing processes.
What is G Code?
G Code is a fundamental programming language used in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining to control automated machine tools. It directs specific movements like positioning, cutting paths, and feed rates, enabling precise manufacturing processes. Understanding G Code helps you optimize machine operations and improve production efficiency.
What is M Code?
M Code is a set of machine control commands used in CNC programming to manage auxiliary functions such as tool changes, coolant activation, and spindle control. Unlike G Code, which directs the movement of the machine tool, M Code handles non-motion operations that are essential for the machining process. Understanding M Code allows you to effectively coordinate machine actions and optimize manufacturing efficiency.
Key Differences Between G Code and M Code
G Code primarily controls the movement and operation paths of CNC machines, defining tool trajectories and machining functions, while M Code manages machine-specific actions such as starting or stopping the spindle, coolant control, and tool changes. G Code commands are essential for precision in shaping parts through motion control, whereas M Code handles auxiliary functions that support the machining process. Understanding the distinction allows you to program CNC machines effectively, optimizing both tool paths and machine operations for accurate manufacturing results.
Functions and Applications of G Code
G Code primarily controls the movement and positioning of CNC machines, dictating precise tool paths and machining operations such as cutting, drilling, and milling. It is essential for defining coordinates, shapes, and speeds, enabling your CNC equipment to execute complex manufacturing tasks with accuracy. These functions make G Code indispensable for automating production in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Functions and Applications of M Code
M Code primarily controls machine functions such as coolant activation, spindle speed, tool changes, and program stops in CNC operations, ensuring precise machine behavior beyond mere toolpath movements defined by G Code. It governs auxiliary actions essential for operational efficiency and safety, including enabling or disabling clamps, controlling coolant flow, or initiating automatic tool changes. Your effective CNC programming leverages M Code to synchronize machine mechanics with G Code instructions, optimizing both productivity and machining accuracy.
G Code and M Code Syntax Comparison
G Code commands control the movement and positioning of CNC machines using a format like G01 X10 Y20 for linear interpolation. M Code commands manage machine functions and auxiliary operations, typically written as M03 to start the spindle or M05 to stop it. Both G Code and M Code follow a structured syntax with letter prefixes followed by numerical values, enabling precise control of machining processes.
Importance in CNC Machining
G Code and M Code are essential in CNC machining for precise machine control and automation. G Code directs the tool path and movements, ensuring accurate positioning and cutting operations, while M Code manages machine functions such as spindle control, coolant activation, and tool changes. Mastery of both codes is critical for optimizing machining efficiency, reducing errors, and improving production quality.
Common Mistakes with G Code and M Code
Common mistakes with G Code and M Code include incorrect syntax and wrong code usage, which can lead to machine errors or unexpected tool movements. Confusing similar codes, such as G01 (linear interpolation) with G00 (rapid positioning), or misusing M codes like M03 (spindle on clockwise) and M05 (spindle stop), often results in operational delays or safety risks. Ensuring your CNC program accurately sequences and matches these codes with your machine's specifications helps prevent costly errors and improves machining precision.
Choosing the Right Code for Your CNC Project
Selecting the right code for your CNC project hinges on understanding the core functions of G Code and M Code. G Code directs the machine's geometric movements, such as positioning, cutting paths, and feed rates, while M Code manages auxiliary functions like tool changes, coolant control, and spindle operations. Mastering the appropriate use of both ensures precise machining and optimal workflow efficiency tailored to your project's specific requirements.
G Code vs M Code Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com