KUKA and FANUC are leading industrial robot manufacturers known for precision and reliability in automation. Choosing between KUKA and FANUC depends on your specific application needs, with KUKA excelling in flexible, complex assembly tasks and FANUC offering robust solutions for high-speed, high-volume production.
Table of Comparison
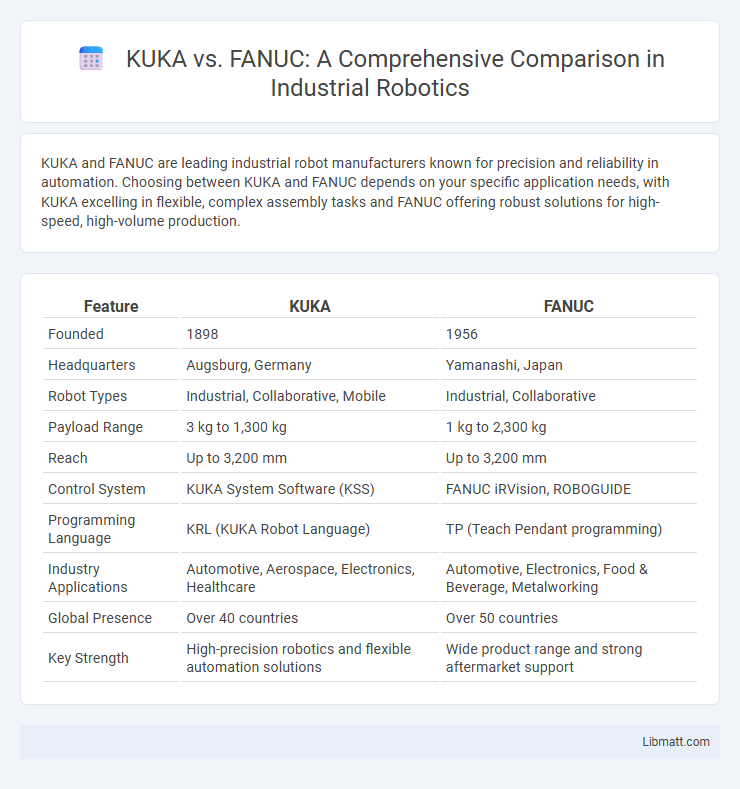
| Feature | KUKA | FANUC |
|---|---|---|
| Founded | 1898 | 1956 |
| Headquarters | Augsburg, Germany | Yamanashi, Japan |
| Robot Types | Industrial, Collaborative, Mobile | Industrial, Collaborative |
| Payload Range | 3 kg to 1,300 kg | 1 kg to 2,300 kg |
| Reach | Up to 3,200 mm | Up to 3,200 mm |
| Control System | KUKA System Software (KSS) | FANUC iRVision, ROBOGUIDE |
| Programming Language | KRL (KUKA Robot Language) | TP (Teach Pendant programming) |
| Industry Applications | Automotive, Aerospace, Electronics, Healthcare | Automotive, Electronics, Food & Beverage, Metalworking |
| Global Presence | Over 40 countries | Over 50 countries |
| Key Strength | High-precision robotics and flexible automation solutions | Wide product range and strong aftermarket support |
Introduction to KUKA and FANUC
KUKA, founded in 1898 in Germany, is a leading manufacturer of industrial robots and automation solutions, renowned for its advanced robotic arms used in automotive and manufacturing sectors. FANUC, established in 1956 in Japan, specializes in factory automation and robotic systems, holding a significant market share with its CNC machines and robotic technology. Both companies drive innovation in robotics, with KUKA emphasizing flexibility and human-robot collaboration, while FANUC focuses on precision and large-scale industrial integration.
Company Backgrounds: KUKA vs FANUC
KUKA, founded in 1898 in Germany, specializes in advanced robotics and automation solutions with a strong presence in automotive manufacturing and Industry 4.0 applications. FANUC, established in 1956 in Japan, is a global leader in CNC systems, robotics, and factory automation, known for its extensive product range and innovation in smart manufacturing. Your choice between KUKA and FANUC depends on specific industrial needs, such as precision automation or scalable factory integration.
Core Technologies and Innovations
KUKA excels in robotics automation through its advanced Sensotec technology and smart factories, integrating AI-driven predictive maintenance and real-time data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes. FANUC leads with its proprietary CNC systems and bundled robotics solutions featuring the ROBOGUIDE offline programming software, enhancing precision and operational efficiency in various industries. Both companies continuously push innovations in collaborative robots (cobots), fostering enhanced human-machine interaction and adaptive automation capabilities.
Robot Product Portfolio Comparison
KUKA offers a diverse robot product portfolio including industrial robots, collaborative robots, and mobile automation solutions tailored for automotive, electronics, and logistics sectors. FANUC's portfolio emphasizes versatility with a wide range of articulated robots, SCARA robots, and collaborative robots designed for precision tasks in automotive, electronics, and packaging industries. Both companies provide advanced control systems and software integration, but KUKA excels in flexible automation systems while FANUC leads in high-speed, high-precision robotic applications.
Control Systems and Software Capabilities
KUKA's control systems primarily utilize the KUKA Robot Language (KRL), offering flexible programming and seamless integration with smart factory environments through its KUKA Sunrise.OS platform. FANUC's control systems are powered by the FANUC Intelligent Platform, featuring the FANUC Robotics System (FANUC R-30iB Plus) that excels in real-time data processing and supports advanced motion control algorithms. Both companies provide robust software capabilities for robotics automation, but FANUC emphasizes AI-driven adaptive controls and extensive compatibility with IoT frameworks, while KUKA focuses on open architecture and seamless connectivity within Industry 4.0 ecosystems.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
KUKA robots excel in automotive manufacturing and logistics automation, offering high precision and flexibility for assembly, material handling, and packaging tasks. FANUC is widely used in electronics, metal fabrication, and aerospace industries, providing reliable robotic arms for welding, painting, and CNC machine tending. Your choice between KUKA and FANUC depends on specific industry applications and operational requirements for scalability and integration.
Performance and Efficiency Analysis
KUKA robots excel in high-precision tasks and complex motion control, leveraging advanced servo technology and real-time adaptive algorithms to enhance operational accuracy and speed. FANUC stands out for its reliability, robust hardware, and extensive automation ecosystem, delivering consistent cycle times and minimal downtime across diverse industrial applications. Performance benchmarks indicate KUKA offers superior flexibility in multi-axis movements, while FANUC optimizes throughput with scalable, user-friendly programming interfaces and integrated AI-driven predictive maintenance.
Ease of Integration and Programming
KUKA robots offer user-friendly integration with flexible KUKA.WorkVisual software, enabling streamlined programming through their intuitive KRL language and comprehensive simulation tools. FANUC provides robust compatibility with a wide range of industry standards and the powerful ROBOGUIDE simulation environment, which simplifies programming and offline development. Understanding your specific application needs will help determine whether KUKA's adaptable control systems or FANUC's established programming ecosystem best enhances your operational efficiency.
Global Reach and Support Services
KUKA and FANUC both maintain extensive global networks, with FANUC operating in over 46 countries and KUKA present in more than 30 nations, ensuring wide accessibility for customers worldwide. FANUC's comprehensive support services include localized technical assistance, training centers, and rapid spare parts delivery, while KUKA emphasizes integrated service solutions and digital tools for proactive maintenance. Your choice between the two may hinge on the specific regional support infrastructure and after-sales service responsiveness tailored to your operational needs.
Cost, ROI, and Final Considerations
KUKA robots typically have higher upfront costs compared to FANUC, but they offer advanced features that can enhance complex automation tasks, potentially improving your operational efficiency and ROI over time. FANUC provides more cost-effective solutions with reliable performance and extensive global support, which can lead to quicker returns on investment for standard manufacturing processes. Evaluating your specific production requirements and total cost of ownership is crucial to determine whether KUKA's innovation or FANUC's affordability aligns better with your automation goals.
KUKA vs FANUC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com