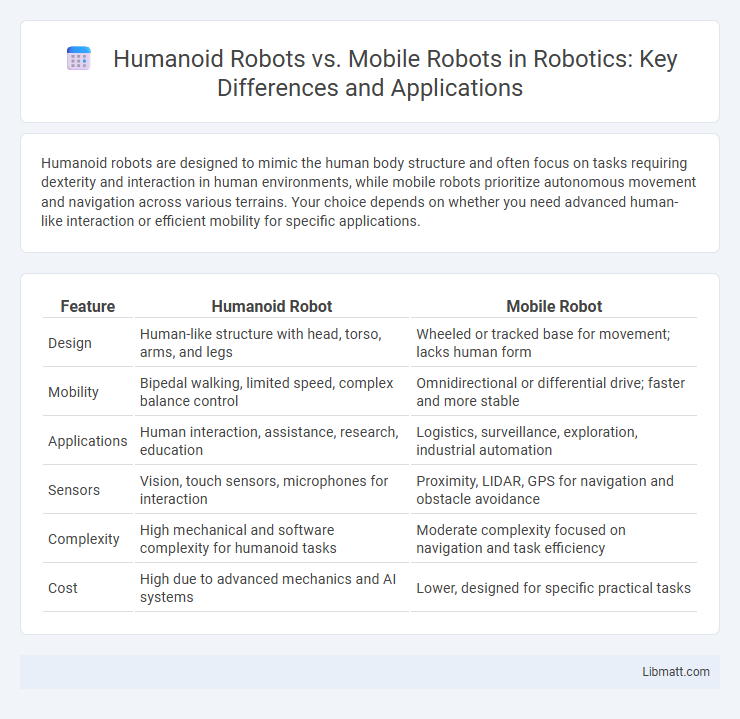
Humanoid robots are designed to mimic the human body structure and often focus on tasks requiring dexterity and interaction in human environments, while mobile robots prioritize autonomous movement and navigation across various terrains. Your choice depends on whether you need advanced human-like interaction or efficient mobility for specific applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Humanoid Robot | Mobile Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Human-like structure with head, torso, arms, and legs | Wheeled or tracked base for movement; lacks human form |
| Mobility | Bipedal walking, limited speed, complex balance control | Omnidirectional or differential drive; faster and more stable |
| Applications | Human interaction, assistance, research, education | Logistics, surveillance, exploration, industrial automation |
| Sensors | Vision, touch sensors, microphones for interaction | Proximity, LIDAR, GPS for navigation and obstacle avoidance |
| Complexity | High mechanical and software complexity for humanoid tasks | Moderate complexity focused on navigation and task efficiency |
| Cost | High due to advanced mechanics and AI systems | Lower, designed for specific practical tasks |
Introduction to Humanoid and Mobile Robots
Humanoid robots are designed to replicate human appearance and movements, featuring limbs, sensors, and advanced AI for tasks requiring human-like interaction and dexterity. Mobile robots, in contrast, emphasize autonomous navigation and mobility across various environments using wheels, tracks, or legs, optimized for exploration, transport, and industrial applications. Both robot types leverage sensors and algorithms but differ fundamentally in design focus: humanoid robots prioritize human-centric functions, while mobile robots prioritize efficient movement and task execution in diverse terrains.
Key Design Differences
Humanoid robots are designed to mimic the human form with features like limbs, sensors, and joints enabling complex interactions in human environments, while mobile robots focus on efficient navigation and mobility using wheels or tracks without humanoid anatomy. You will find that humanoid robots often incorporate advanced balance and dexterity systems, whereas mobile robots emphasize path planning, obstacle detection, and terrain adaptability. These key design differences directly impact their applications, with humanoid robots suited for tasks requiring human-like manipulation and mobile robots optimized for transportation or inspection in varied environments.
Functional Capabilities Comparison
Humanoid robots excel in tasks requiring human-like dexterity, such as manipulating tools and interacting with complex environments due to their anthropomorphic design, enabling them to perform functions in settings designed for humans. Mobile robots prioritize efficient navigation and mobility across various terrains, equipped with sensors and algorithms optimized for mapping, obstacle avoidance, and autonomous movement. While humanoid robots offer versatility in tasks involving fine motor skills and social interaction, mobile robots provide superior agility and endurance for logistics, surveillance, and exploration applications.
Applications in Industry and Daily Life
Humanoid robots excel in complex tasks requiring human-like interaction, such as customer service and healthcare assistance, offering intuitive communication and adaptability. Mobile robots are widely deployed in industries for material handling, automated warehouses, and delivery services, enhancing efficiency through autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance. In daily life, mobile robots perform cleaning and surveillance, while humanoid robots support elderly care and educational activities, bridging robotics with social needs.
Mobility and Maneuverability
Humanoid robots excel in maneuverability with their bipedal structure, allowing them to navigate complex, human-centric environments such as stairs and uneven terrain. Mobile robots, often equipped with wheels or tracks, offer superior speed and stability on flat surfaces but struggle with obstacles and varied terrains. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize adaptable movement in dynamic spaces or efficient travel on smooth surfaces.
Sensor and Perception Technologies
Humanoid robots utilize advanced sensor arrays, including cameras, LiDAR, and tactile sensors, to mimic human perception and interact seamlessly with complex environments. Mobile robots predominantly rely on GPS, ultrasonic sensors, and infrared sensors to navigate and map their surroundings efficiently. Your choice between humanoid and mobile robots should consider the sensor technologies best suited for the specific tasks and environmental challenges you face.
Human-Robot Interaction
Humanoid robots excel in human-robot interaction due to their anthropomorphic design, enabling intuitive communication through gestures, facial expressions, and natural language processing. Mobile robots prioritize navigation and task efficiency in dynamic environments but often lack the expressive interfaces necessary for seamless social engagement. Advances in AI and sensor technology enhance humanoid robots' ability to interpret human emotions and respond contextually, making them ideal for personalized assistance and collaborative tasks.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Humanoid robots typically incur higher costs due to their complex mechanical structures and advanced sensors, requiring specialized maintenance and frequent software updates. Mobile robots often benefit from lower expenses and simpler upkeep, as their designs focus on basic navigation and task execution. Your choice should weigh the initial investment against the long-term maintenance demands to optimize operational efficiency.
Future Trends and Developments
Humanoid robots are advancing with improved AI-driven interaction capabilities and enhanced dexterity for complex tasks, while mobile robots are evolving through autonomous navigation and swarm intelligence for efficient logistics and exploration. Integration of machine learning and sensor fusion is accelerating the development of adaptive behaviors in both robot types. Future trends emphasize collaborative robotics, with humanoid and mobile robots working seamlessly alongside humans in dynamic environments.
Choosing the Right Robot for Your Needs
Choosing the right robot depends on your specific application requirements and environment. Humanoid robots, designed to mimic human movements and interactions, excel in roles requiring social engagement or navigating human-centric spaces, while mobile robots offer versatile navigation and efficiency in industrial or logistical tasks. Your decision should consider factors such as operational complexity, interaction needs, and the workspace to ensure optimal performance and ROI.
Humanoid Robot vs Mobile Robot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com