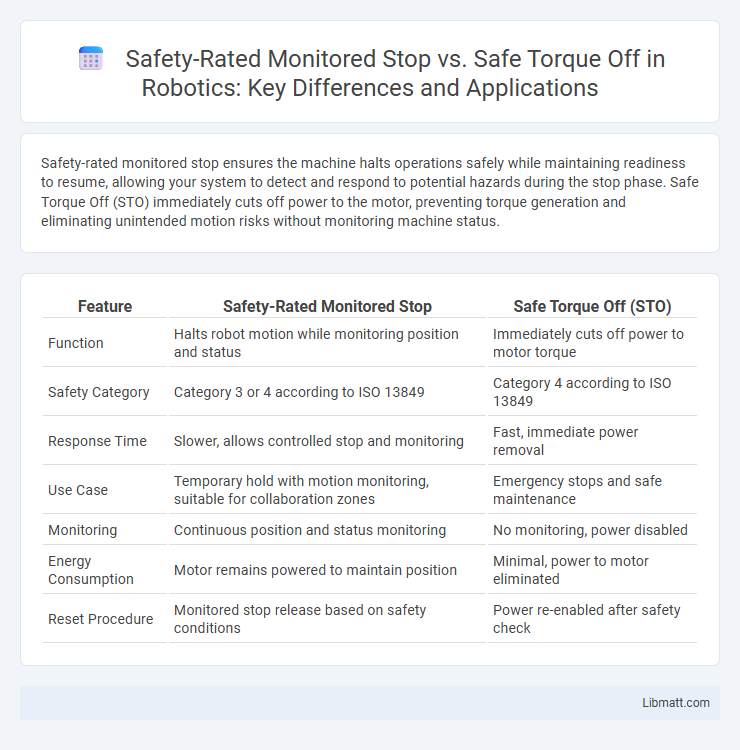
Safety-rated monitored stop ensures the machine halts operations safely while maintaining readiness to resume, allowing your system to detect and respond to potential hazards during the stop phase. Safe Torque Off (STO) immediately cuts off power to the motor, preventing torque generation and eliminating unintended motion risks without monitoring machine status.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Safety-Rated Monitored Stop | Safe Torque Off (STO) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Halts robot motion while monitoring position and status | Immediately cuts off power to motor torque |
| Safety Category | Category 3 or 4 according to ISO 13849 | Category 4 according to ISO 13849 |
| Response Time | Slower, allows controlled stop and monitoring | Fast, immediate power removal |
| Use Case | Temporary hold with motion monitoring, suitable for collaboration zones | Emergency stops and safe maintenance |
| Monitoring | Continuous position and status monitoring | No monitoring, power disabled |
| Energy Consumption | Motor remains powered to maintain position | Minimal, power to motor eliminated |
| Reset Procedure | Monitored stop release based on safety conditions | Power re-enabled after safety check |
Introduction to Functional Safety in Industrial Automation
Functional safety in industrial automation ensures machinery operates without causing harm, with Safety-rated monitored stop and Safe Torque Off (STO) as key safety functions. Safety-rated monitored stop guarantees the machine remains in a safe, halted state during access or maintenance, while STO instantly cuts power to the motor, preventing unintended movement. Understanding these functions helps you implement robust safety systems that comply with international standards like ISO 13849 and IEC 61508, protecting both operators and equipment.
Overview of Safety-Rated Monitored Stop
Safety-Rated Monitored Stop ensures that a machine halts safely while maintaining monitored control over hazardous motion, allowing operators to safely enter or access certain areas. This safety function monitors speed and position, preventing unexpected restarts or movement until conditions are confirmed safe. Your automation system benefits from enhanced protection in collaborative environments, avoiding risks during human-machine interaction.
Understanding Safe Torque Off (STO)
Safe Torque Off (STO) is a critical safety function that immediately disables the power supply to a motor, preventing any torque generation and ensuring the machine cannot start unintentionally. Unlike safety-rated monitored stops that maintain power while monitoring the motor status for safe pauses, STO completely cuts off torque production, providing an extra layer of protection in hazardous situations. STO is widely used in industrial automation to ensure personnel safety during maintenance or emergency stops by eliminating any risk of unexpected motor movement.
Key Differences Between Monitored Stop and STO
A safety-rated monitored stop actively detects and controls machinery during pauses, allowing immediate resumption of operation once safe conditions are met, ensuring real-time monitoring of system status. In contrast, Safe Torque Off (STO) disables power to the motor, preventing torque generation and effectively eliminating hazardous motion without ongoing monitoring during downtime. Monitored stops provide controlled halts with continuous safety feedback, while STO ensures motor inactivation by removing electrical energy, serving as a fundamental safety function for emergency stops and maintenance.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Each Method
Safety-rated monitored stop is ideal for applications requiring controlled halting of machinery to allow safe access for operators during maintenance or material handling, such as robotic cells or conveyor systems. Safe torque off (STO) is suited for emergency shutdowns or scenarios demanding immediate power removal to the motor, effectively preventing unexpected motion in industrial drives or milling machines. Selecting between the two depends on whether the priority is a controlled pause with monitoring or an instantaneous disabling of torque to ensure maximal safety.
Standards and Compliance (ISO 13849, IEC 61800-5-2)
Safety-rated monitored stop and Safe Torque Off (STO) both adhere to strict standards to ensure machinery safety and functionality compliance. ISO 13849 defines safety performance levels, where monitored stop functions typically achieve PL d or e by maintaining controlled stopping and safeguarding, whereas STO complies with IEC 61800-5-2 by immediately disabling power to prevent motor torque, classified as a Category 0 stop. Integrating these standards ensures that automated systems meet global regulatory requirements, minimizing risk during operation and maintenance.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Safety-rated monitored stop requires precise integration of sensor feedback and control logic to ensure reliable detection of stop conditions, posing challenges in configuring accurate timing and fault diagnostics. Safe Torque Off (STO) implementation demands robust hardware and software coordination to immediately cut motor torque, minimizing risk but requiring stringent validation and fail-safe circuit design. To optimize your system safety, regularly update firmware, perform thorough risk assessments, and follow industry standards such as IEC 61508 for both monitored stop and STO functions.
System Integration: Wiring and Control Considerations
Safety-rated monitored stop requires continuous monitoring of the machine's motion and position sensors, integrating complex wiring and control logic to ensure the system halts operations safely during stop phases. Safe Torque Off (STO) simplifies system integration by directly disabling power to the motor drive, reducing wiring complexity and minimizing the need for additional control feedback loops. Your choice between these methods significantly impacts system design, wiring effort, and control architecture, with STO offering streamlined integration suitable for many safety applications.
Safety Performance and Risk Reduction Comparison
Safety-rated monitored stop systems offer continuous verification of machine halts, ensuring that all motion ceases before allowing operator access, which significantly minimizes the risk of unexpected movements. Safe Torque Off (STO) technology instantly removes power to the motor, preventing torque generation and ensuring rapid motor stoppage without mechanical intervention, which reduces the risk of hazardous motion during faults. Your choice between these methods depends on the required safety performance level and risk reduction strategy, with monitored stops providing layered protection through feedback monitoring, while STO offers fail-safe motor shutdown for critical torque-related hazards.
Choosing the Right Safety Function for Your Application
Safety-rated monitored stops provide controlled halting with position monitoring, ideal for applications requiring precise verification before resuming motion. Safe Torque Off (STO) functions by instantly cutting motor torque, ensuring rapid and fail-safe motor shutdown without position feedback, suited for emergency stop scenarios. Selecting between these depends on application demands: choose monitored stops for tasks needing position confirmation and safe restart, while STO fits emergency stops where immediate motor power removal is critical.
Safety-rated monitored stop vs Safe torque off Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com