Low payload robots offer increased speed and precision for delicate tasks, making them ideal for electronics assembly or small-scale manufacturing. High payload robots handle heavier loads and perform heavy-duty operations such as automotive assembly or material handling, enhancing your production capabilities with strength and durability.
Table of Comparison
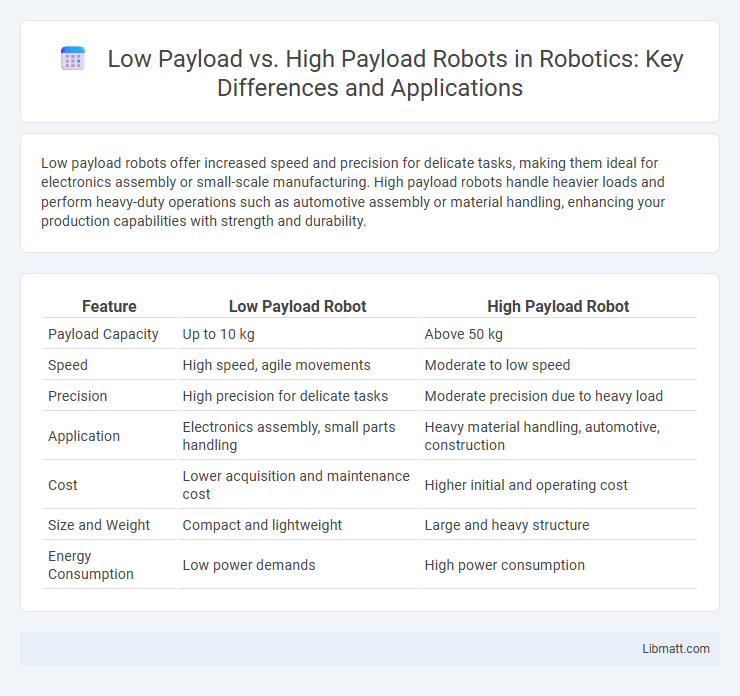
| Feature | Low Payload Robot | High Payload Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Payload Capacity | Up to 10 kg | Above 50 kg |
| Speed | High speed, agile movements | Moderate to low speed |
| Precision | High precision for delicate tasks | Moderate precision due to heavy load |
| Application | Electronics assembly, small parts handling | Heavy material handling, automotive, construction |
| Cost | Lower acquisition and maintenance cost | Higher initial and operating cost |
| Size and Weight | Compact and lightweight | Large and heavy structure |
| Energy Consumption | Low power demands | High power consumption |
Understanding Robot Payload Capacity
Robot payload capacity defines the maximum weight a robot can handle effectively, directly impacting its operational efficiency and application scope. Low payload robots, typically managing under 10 kilograms, excel in precision tasks like electronics assembly, while high payload robots, capable of lifting hundreds of kilograms, are suited for heavy-duty functions such as automotive manufacturing. Understanding your specific task requirements ensures you select a robot with the appropriate payload capacity, optimizing performance and safety.
Defining Low Payload Robots
Low payload robots are designed to handle tasks requiring less lifting capacity, typically under 10 kilograms, making them ideal for precise assembly, small part handling, and delicate operations in electronics manufacturing. These robots excel in scenarios demanding high speed and accuracy without the need for heavy lifting, improving efficiency in production lines with lightweight materials. Compared to high payload robots, low payload models offer greater agility and flexibility for intricate tasks in compact spaces.
Defining High Payload Robots
High payload robots are industrial machines designed to handle heavy loads exceeding 100 kilograms, typically used in automotive assembly, construction, and metal fabrication industries. These robots are equipped with robust actuators and reinforced frames to maintain precision and stability under significant weight. High payload capabilities enable efficient handling of large components, reducing manual labor and increasing productivity in demanding manufacturing environments.
Key Applications of Low Payload Robots
Low payload robots, typically handling weights under 10 kilograms, excel in precision tasks such as electronics assembly, medical device manufacturing, and small parts packaging. Their agility and fine motor control make them ideal for delicate operations including soldering, inspection, and micro-assembly in industries like pharmaceuticals and consumer electronics. Automation with low payload robots enhances efficiency, reduces human error, and supports complex tasks requiring detailed manipulation in tight spaces.
Key Applications of High Payload Robots
High payload robots are essential for industries requiring the handling of heavy materials, such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace assembly, and large-scale construction. They excel in tasks like heavy welding, material transport, and large component assembly, enabling increased efficiency and safety. Your production line benefits from high payload robots through enhanced precision and reduced downtime when managing substantial loads.
Performance Differences: Speed and Precision
Low payload robots offer higher speed and exceptional precision, making them ideal for delicate tasks requiring accuracy and rapid movements. High payload robots typically move slower due to heavier loads but excel in strength and stability for handling bulky or heavy objects. Your choice depends on balancing performance needs between speed, precision, and load capacity within your operations.
Integration in Manufacturing Processes
Low payload robots excel in precision tasks and easily integrate into existing manufacturing lines for assembly, inspection, and small part handling. High payload robots provide robust solutions for heavy lifting, material transfer, and large component assembly, enabling automation of demanding industrial processes. Both robot types enhance operational efficiency, with integration tailored to specific load requirements and workflow optimization.
Cost Considerations and ROI Analysis
Low payload robots typically have lower initial costs and reduced maintenance expenses, making them ideal for small-scale automation projects with minimal investment. High payload robots require significant upfront capital but deliver greater productivity and versatility in heavy-duty applications, often resulting in a faster return on investment (ROI) for large-scale operations. Your choice depends on balancing immediate budget constraints against long-term operational savings and efficiency gains.
Safety and Space Requirements
Low payload robots typically offer enhanced safety features due to their lighter weight and reduced impact force, making them suitable for close human-robot collaboration in confined spaces. High payload robots require more robust safety measures and larger operational zones because of their greater mass and power, which increase risk factors in shared work environments. Space requirements for low payload robots are minimal, allowing installation in tight areas, whereas high payload robots demand significant clearance and reinforced flooring to accommodate their size and load capacity.
Choosing the Right Robot for Your Needs
Choosing the right robot involves evaluating payload capacity against task requirements; low payload robots are ideal for precision tasks and light material handling, offering faster operation and greater energy efficiency. High payload robots support heavy-duty applications such as automotive assembly and large part manipulation, enabling increased productivity in manufacturing environments. Assessing workflow demands, payload weights, and cycle times ensures selecting a robot that balances operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Low payload vs High payload robot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com