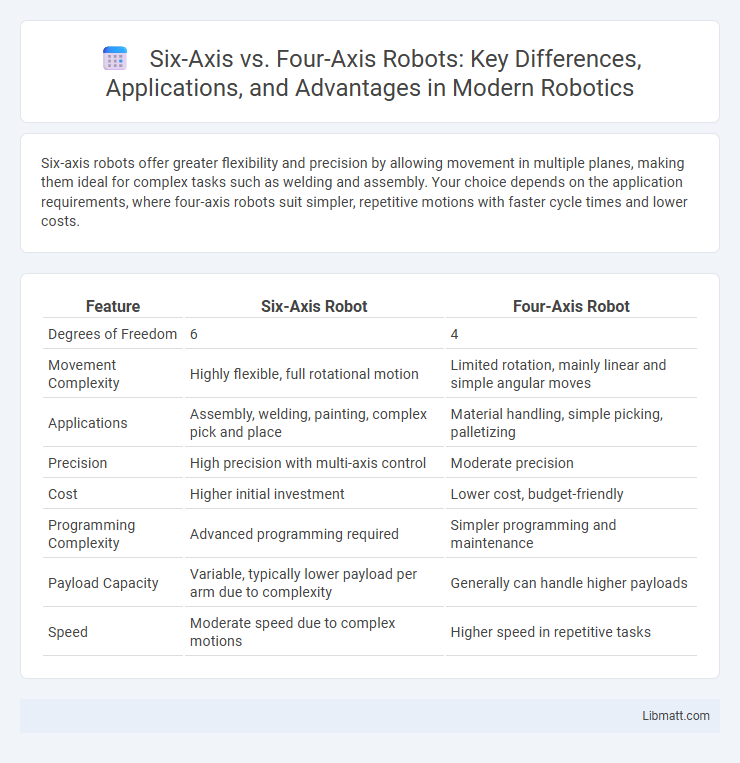
Six-axis robots offer greater flexibility and precision by allowing movement in multiple planes, making them ideal for complex tasks such as welding and assembly. Your choice depends on the application requirements, where four-axis robots suit simpler, repetitive motions with faster cycle times and lower costs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Six-Axis Robot | Four-Axis Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Degrees of Freedom | 6 | 4 |
| Movement Complexity | Highly flexible, full rotational motion | Limited rotation, mainly linear and simple angular moves |
| Applications | Assembly, welding, painting, complex pick and place | Material handling, simple picking, palletizing |
| Precision | High precision with multi-axis control | Moderate precision |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Programming Complexity | Advanced programming required | Simpler programming and maintenance |
| Payload Capacity | Variable, typically lower payload per arm due to complexity | Generally can handle higher payloads |
| Speed | Moderate speed due to complex motions | Higher speed in repetitive tasks |
Introduction to Robotic Axes
Robotic axes define the degrees of freedom a robot has, directly influencing its motion capabilities and precision. A six-axis robot offers enhanced flexibility and range of movement by incorporating additional rotational joints compared to a four-axis robot, which typically has fewer movement options and is suited for simpler tasks. Understanding the difference in axis configurations helps you select the right robot for applications requiring complex maneuvering or basic automated processes.
What is a Four-Axis Robot?
A four-axis robot is an industrial robotic arm designed with four rotational joints, allowing it to perform basic tasks such as pick-and-place, material handling, and simple assembly processes. Its limited degrees of freedom enable efficient movement in predefined planes, making it suitable for repetitive operations in manufacturing environments. Compared to six-axis robots, four-axis models are more cost-effective but offer less flexibility and precision in complex applications.
What is a Six-Axis Robot?
A Six-Axis Robot features six degrees of freedom, allowing it to move with exceptional flexibility across complex three-dimensional paths. Its six rotational joints enable precise articulation, making it suitable for intricate tasks such as welding, assembly, and material handling. You can rely on this type of robot for applications requiring extensive movement range and adaptability compared to Four-Axis robots.
Key Differences Between Four-Axis and Six-Axis Robots
Six-axis robots offer enhanced flexibility with six degrees of freedom, allowing complex, multi-directional movement ideal for intricate tasks such as welding, assembly, and painting. Four-axis robots provide movement primarily along four axes, making them suitable for simpler, linear operations like pick-and-place or palletizing applications. The key difference lies in their range of motion and adaptability, where six-axis robots excel in versatility while four-axis systems are typically more cost-effective and easier to program for basic automation tasks.
Movement Capabilities and Range of Motion
Six-axis robots offer enhanced movement capabilities with six degrees of freedom, allowing them to perform complex and precise tasks involving rotation and articulation in multiple planes. Four-axis robots provide more limited motion, typically restricted to linear and rotational movements around a fixed base, making them suitable for simpler applications. The increased range of motion in six-axis robots enables greater flexibility for intricate assembly, welding, and material handling operations.
Application Areas of Four-Axis Robots
Four-axis robots are primarily utilized in applications requiring simple, repetitive tasks such as material handling, packaging, and palletizing in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. These robots excel in environments where high speed and accuracy for limited degrees of freedom are critical, often performing pick-and-place operations. Their cost-effectiveness and straightforward programming make them ideal for assembly lines and manufacturing processes with standardized movement patterns.
Application Areas of Six-Axis Robots
Six-axis robots dominate in complex applications such as automotive assembly, aerospace manufacturing, and precision welding, where intricate movements and high flexibility are essential. Their ability to maneuver in multiple directions enables them to perform tasks like painting, material handling, and machine tending with exceptional accuracy. Industries requiring versatile automation solutions benefit greatly from six-axis robots due to their adaptability in handling diverse and dynamic environments.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Six-axis robots typically involve higher initial costs due to their advanced flexibility and greater range of motion compared to four-axis robots, which are more affordable and simpler in design. Your return on investment (ROI) depends on application complexity; six-axis robots deliver better ROI in tasks requiring intricate movements and adaptability, while four-axis robots offer faster payback in straightforward, repetitive operations. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and integration, helps determine which robot optimizes your budget and production efficiency.
Selecting the Right Robot for Your Needs
Choosing between a six-axis and four-axis robot depends on the complexity of the task and required degrees of freedom. Six-axis robots offer enhanced flexibility and precision, ideal for intricate assembly, welding, and material handling in industries like automotive and aerospace. Four-axis robots provide cost-effective solutions for simpler, high-speed pick-and-place or loading applications with limited rotational movement.
Future Trends in Robotic Automation
Six-axis robots offer enhanced flexibility and precision, making them ideal for complex automations and multi-dimensional tasks in manufacturing and assembly lines. Four-axis robots, while limited in movement, provide cost-effective solutions for simpler, repetitive tasks with faster cycle times. Future trends emphasize the integration of AI-driven controls and collaborative capabilities, where six-axis robots are expected to dominate sectors requiring adaptive and intricate operations, while four-axis units continue to serve streamlined, high-speed production environments.
Six-Axis vs Four-Axis Robot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com