Homing sensors establish a machine's reference position at startup by detecting a specific home point, enabling precise initialization for subsequent operations. Index sensors, on the other hand, provide a periodic reference signal during motion, allowing your system to accurately track rotational positions and synchronize movements.
Table of Comparison
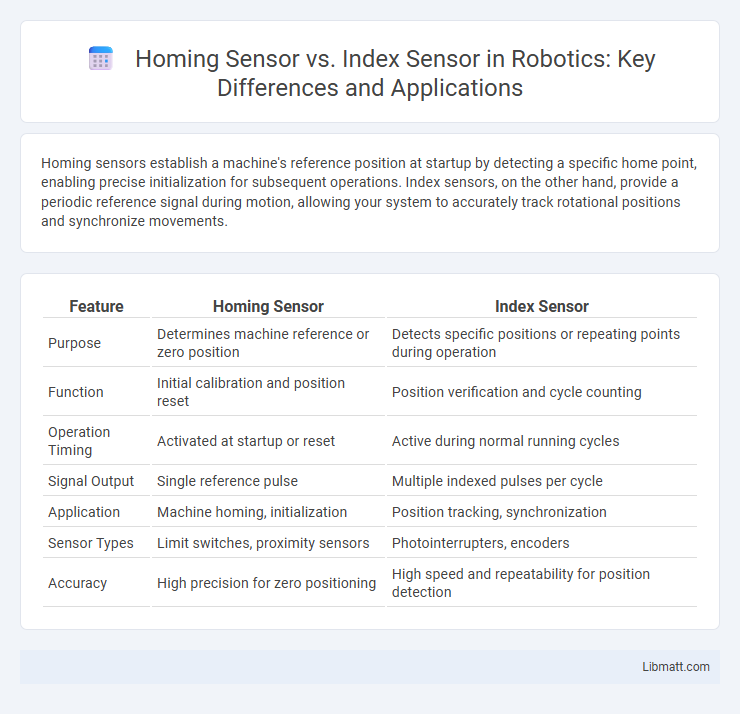
| Feature | Homing Sensor | Index Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Determines machine reference or zero position | Detects specific positions or repeating points during operation |
| Function | Initial calibration and position reset | Position verification and cycle counting |
| Operation Timing | Activated at startup or reset | Active during normal running cycles |
| Signal Output | Single reference pulse | Multiple indexed pulses per cycle |
| Application | Machine homing, initialization | Position tracking, synchronization |
| Sensor Types | Limit switches, proximity sensors | Photointerrupters, encoders |
| Accuracy | High precision for zero positioning | High speed and repeatability for position detection |
Introduction to Homing and Index Sensors
Homing sensors establish a reference position by detecting a specific mechanical or magnetic marker, enabling precise machine zeroing for repeatability in automation systems. Index sensors generate pulses or signals at regular intervals along a rotating shaft or linear path, facilitating accurate position tracking and speed measurement. Both sensor types are integral to motion control applications, ensuring accurate alignment and synchronization in CNC machines, robotics, and conveyor systems.
What is a Homing Sensor?
A homing sensor is a precise positioning device used in automation and robotics to detect a reference or home position for a moving part, ensuring accurate alignment and repeatability. Unlike index sensors that track incremental movement or mark positions along a path, homing sensors provide a fixed point of reference for resetting or initializing a system. Your equipment relies on homing sensors to establish a baseline position essential for calibration and consistent operation.
What is an Index Sensor?
An index sensor is a precise feedback device used in motion control systems to detect a specific reference position within a rotary encoder's full rotation, providing a unique pulse once per revolution for accurate positioning. This sensor enhances machine accuracy by enabling synchronization between the actual shaft position and the control system. Compared to homing sensors, which typically locate a home or start position, index sensors offer continuous rotary position referencing critical for applications requiring exact angular measurement.
Key Differences Between Homing and Index Sensors
Homing sensors are designed to establish a reference position by detecting a specific point during machine initialization, while index sensors provide repetitive signal triggers at regular intervals for position tracking during operation. Homing sensors typically activate once per cycle to set a zero or origin point, whereas index sensors generate continuous pulses to monitor rotational or linear encoder positions. The primary difference lies in their function: homing sensors ensure consistent startup alignment, and index sensors supply ongoing positional feedback for precise motion control.
Working Principles of Homing Sensors
Homing sensors operate by detecting a specific reference point or home position using a physical or optical trigger, enabling precise alignment and positional calibration in automation systems. These sensors commonly use switches, optical sensors, or magnetic sensors to send a signal when the moving part reaches the home position, ensuring accurate repeatability. Your system relies on homing sensors to establish a fixed starting location, essential for maintaining consistent operational accuracy in CNC machines, robotics, and conveyor systems.
Working Principles of Index Sensors
Index sensors detect precise angular positions by generating a single pulse once per revolution, using a physical or magnetic marker on a rotating shaft or disk. This sensor's working principle relies on a reference point that allows your control system to establish an accurate zero or home position for synchronization. Unlike homing sensors, index sensors provide a consistent, repeatable signal essential for applications requiring precise motor or shaft positioning.
Applications of Homing Sensors
Homing sensors are widely used in robotics and automated machinery to establish a reference position for precise movement control and system calibration. These sensors enable machines such as CNC routers, 3D printers, and industrial robots to return to a defined home position after power cycles or interruptions, ensuring accuracy and repeatability. In contrast to index sensors, which detect rotational position for incremental movement, homing sensors provide a fixed absolute reference crucial for the initial setup and ongoing operational reliability.
Applications of Index Sensors
Index sensors are widely used in industrial automation for precise position referencing in rotary encoders, enabling accurate speed and position control of motors and machinery. These sensors provide critical zero-point or reference signals in applications such as CNC machines, robotics, and conveyor systems where exact synchronization is essential. Their ability to generate a unique index pulse once per revolution ensures reliable repeatability and enhances the accuracy of motion control processes.
Choosing Between Homing and Index Sensors
Choosing between homing and index sensors depends on the specific application requirements, such as precision, speed, and operational environment. Homing sensors provide accurate machine position references by detecting a predetermined physical location, essential for initializing or resetting systems. Index sensors excel in identifying specific points within a repetitive cycle, making them ideal for synchronization tasks and high-speed operations.
Conclusion: Which Sensor Fits Your Needs?
Homing sensors provide precise reference points for system initialization, ideal for applications requiring accurate repeatability and positional calibration. Index sensors deliver high-resolution incremental feedback during operation, best suited for continuous motion monitoring and speed control. Choosing between homing and index sensors depends on whether your priority is initial positioning accuracy or ongoing motion tracking performance.
Homing Sensor vs Index Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com