Passive compliance involves following rules or instructions without question, relying on external enforcement to maintain adherence. Active compliance requires understanding, internalizing, and willingly applying guidelines, ensuring Your actions align with both the letter and spirit of regulations.
Table of Comparison
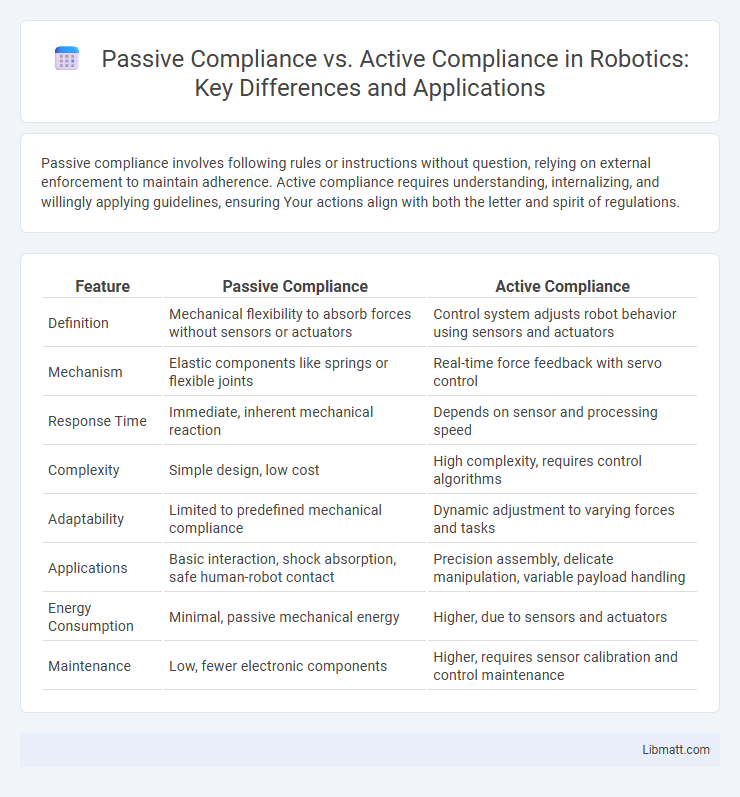
| Feature | Passive Compliance | Active Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mechanical flexibility to absorb forces without sensors or actuators | Control system adjusts robot behavior using sensors and actuators |
| Mechanism | Elastic components like springs or flexible joints | Real-time force feedback with servo control |
| Response Time | Immediate, inherent mechanical reaction | Depends on sensor and processing speed |
| Complexity | Simple design, low cost | High complexity, requires control algorithms |
| Adaptability | Limited to predefined mechanical compliance | Dynamic adjustment to varying forces and tasks |
| Applications | Basic interaction, shock absorption, safe human-robot contact | Precision assembly, delicate manipulation, variable payload handling |
| Energy Consumption | Minimal, passive mechanical energy | Higher, due to sensors and actuators |
| Maintenance | Low, fewer electronic components | Higher, requires sensor calibration and control maintenance |
Introduction to Compliance Strategies
Passive compliance involves following rules or regulations without taking initiative to adapt or improve processes, often driven by external enforcement. Active compliance emphasizes proactive engagement, where organizations anticipate regulatory changes and integrate compliance into their strategic planning and daily operations. This approach enhances risk management, fosters a culture of accountability, and ensures sustained adherence to legal and ethical standards.
Defining Passive Compliance
Passive compliance refers to the process of conforming to regulations or standards through minimal effort, often characterized by adhering strictly to established rules without proactive engagement or improvement initiatives. It involves reactive behavior where organizations or individuals meet requirements only to avoid penalties, lacking dynamic adaptation to evolving standards. This contrasts with active compliance, which emphasizes continual monitoring, risk assessment, and strategic implementation beyond baseline obligations.
What is Active Compliance?
Active compliance involves intentional and conscious adherence to rules or regulations, where individuals or organizations proactively interpret, apply, and sometimes adapt policies to meet legal or ethical standards. This approach requires ongoing monitoring, feedback, and engagement to ensure compliance is maintained effectively and responsively. Your organization benefits from active compliance by reducing risks and fostering a culture of responsibility and transparency.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Compliance
Passive compliance involves automatically adapting to external forces without additional energy input, relying on the inherent flexibility of materials or structures. Active compliance requires sensors and actuators to continuously adjust responses based on real-time feedback, enabling precise control and adaptability. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right compliance method for applications demanding either simplicity and energy efficiency or dynamic responsiveness and accuracy.
Benefits of Passive Compliance
Passive compliance offers benefits such as reduced mechanical complexity, leading to lower maintenance requirements and enhanced reliability in robotic systems. It provides intrinsic safety by absorbing unexpected forces, minimizing damage to both robots and surroundings during interactions. Energy efficiency is improved through compliance elements that store and release energy without active control, optimizing performance in dynamic tasks.
Advantages of Active Compliance
Active compliance offers precise control over system responses by actively adjusting to external disturbances, enhancing stability and performance in dynamic environments. It improves safety by continuously monitoring and adapting to real-time conditions, reducing the risk of mechanical failure or damage. Your equipment benefits from increased efficiency and longevity due to optimized force and motion regulation in active compliance systems.
Risks Associated with Passive Compliance
Passive compliance often results in overlooked regulatory changes, increasing the risk of penalties and legal issues due to inadequate adherence. Organizations relying solely on passive compliance may experience operational inefficiencies and missed opportunities for improvement, compromising overall performance and stakeholder trust. In contrast, active compliance continuously monitors and adapts to evolving standards, significantly reducing potential risks and enhancing regulatory alignment.
Challenges of Implementing Active Compliance
Implementing active compliance presents challenges such as the need for continuous monitoring, real-time data analytics, and dynamic risk assessment tools to ensure timely responses to regulatory changes. Organizations must invest in advanced technologies and skilled personnel to handle complex compliance processes, which can strain resources and increase operational costs. Moreover, maintaining transparency and accountability while adapting rapidly to evolving regulations requires robust governance frameworks and cross-departmental coordination.
Choosing the Right Compliance Approach
Choosing the right compliance approach involves evaluating organizational goals, risk tolerance, and regulatory requirements to determine whether passive or active compliance is more effective. Passive compliance relies on meeting minimum legal standards with limited proactive engagement, suitable for low-risk environments, while active compliance emphasizes continuous monitoring, improvement, and strategic alignment, ideal for high-risk or heavily regulated industries. Implementing an active compliance strategy enhances adaptability and reduces legal penalties, whereas passive compliance may lower operational costs but increase vulnerability to compliance breaches.
Future Trends in Compliance Management
Future trends in compliance management emphasize the transition from passive compliance, characterized by reactive adherence to regulations, to active compliance, which involves proactive risk management and continuous monitoring using AI-driven technologies. Organizations increasingly deploy machine learning algorithms and real-time data analytics to detect anomalies and ensure dynamic regulatory adherence. This shift enhances operational resilience and supports predictive compliance strategies in rapidly evolving regulatory environments.
Passive compliance vs Active compliance Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com