Pick and place focuses on transferring components swiftly and accurately from one location to another, optimizing speed and precision in manufacturing processes. Assembly involves the integration of multiple parts to create a functional product, requiring more complex coordination and quality control to ensure overall system reliability.
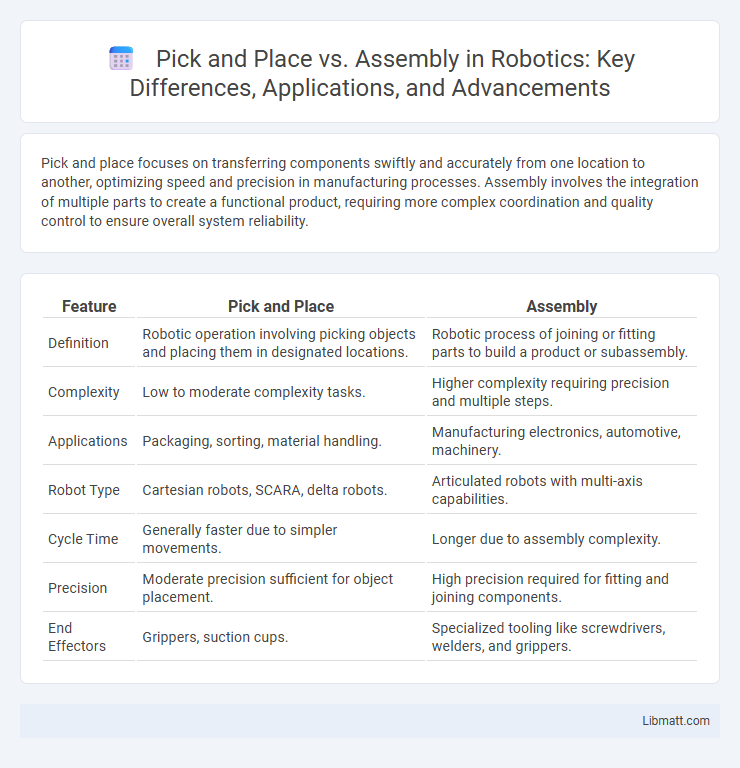
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pick and Place | Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Robotic operation involving picking objects and placing them in designated locations. | Robotic process of joining or fitting parts to build a product or subassembly. |
| Complexity | Low to moderate complexity tasks. | Higher complexity requiring precision and multiple steps. |
| Applications | Packaging, sorting, material handling. | Manufacturing electronics, automotive, machinery. |
| Robot Type | Cartesian robots, SCARA, delta robots. | Articulated robots with multi-axis capabilities. |
| Cycle Time | Generally faster due to simpler movements. | Longer due to assembly complexity. |
| Precision | Moderate precision sufficient for object placement. | High precision required for fitting and joining components. |
| End Effectors | Grippers, suction cups. | Specialized tooling like screwdrivers, welders, and grippers. |
Introduction to Pick and Place and Assembly
Pick and place systems automate the precise movement of components from one location to another, enhancing efficiency in manufacturing and packaging processes. Assembly involves the systematic joining or fitting of parts to create a finished product, often requiring more complex operations than pick and place tasks. Your choice between pick and place or assembly depends on the complexity and specificity of the production requirements.
Key Differences Between Pick and Place and Assembly
Pick and place systems primarily focus on accurately positioning components by picking them up and placing them onto a target surface, emphasizing speed and precision in repetitive tasks. Assembly processes involve multiple intricate steps beyond placement, such as joining, fastening, or combining parts to form a complete product, requiring complex machinery and often human intervention. Understanding these key differences helps optimize Your manufacturing workflow by selecting the right technique for either simple handling or creating fully assembled products.
Core Principles of Pick and Place Systems
Pick and place systems operate on the core principle of quickly and accurately moving objects from one location to another using robotic arms equipped with sensors and grippers designed for precise handling. These systems rely on automation technology such as vision systems and programmable controllers to optimize speed and accuracy in repetitive tasks. Your manufacturing process benefits from reduced labor costs and increased efficiency by employing these precise mechanical movements tailored for sorting, packaging, or component placement.
Fundamental Aspects of Assembly Processes
Pick and place systems focus on transferring components from one location to another with high speed and accuracy, primarily handling positioning tasks without joining parts. Assembly processes involve multiple stages, including aligning, fastening, and integrating components into a final product, emphasizing precision in fitting and securing elements to achieve structural integrity. Fundamental aspects of assembly processes include joint types, force application, tolerance management, and sequence optimization to ensure product functionality and durability.
Advantages of Pick and Place Automation
Pick and place automation enhances manufacturing efficiency by significantly reducing cycle times and minimizing human error during component handling. It improves precision and repeatability, ensuring consistent product quality and lowering defect rates. Automated systems also reduce labor costs and increase workplace safety by handling hazardous or delicate materials that may pose risks to human operators.
Benefits of Automated Assembly Lines
Automated assembly lines enhance production efficiency by significantly reducing manual labor and minimizing human error during the pick and place operations. These systems enable consistent, high-speed placement of components with precise accuracy, increasing overall throughput and product quality. Integration of robotics in automated assembly also lowers operational costs and improves workplace safety by handling repetitive and hazardous tasks.
Typical Applications for Pick and Place
Typical applications for pick and place robots include packaging, sorting, and electronic component handling due to their speed and precision. These systems excel in repetitive tasks like moving items from conveyors to pallets or placing components on circuit boards in manufacturing. Your production line benefits from increased efficiency and accuracy when implementing pick and place technology for these applications.
Common Uses for Assembly Solutions
Assembly solutions are commonly used in electronics manufacturing for integrating components onto circuit boards and in automotive industries for constructing complex parts like engines and transmissions. These solutions streamline production by automating tasks such as fastening, welding, and aligning parts, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. They play a crucial role in medical device fabrication, ensuring precise assembly of small, intricate components for reliable operation.
Choosing Between Pick and Place vs Assembly
Choosing between pick and place and assembly processes depends heavily on the complexity and precision required in manufacturing operations. Pick and place systems excel in rapid, repetitive tasks involving the accurate movement of components, ideal for electronics or packaging industries. Assembly operations are preferred for intricate product construction requiring multiple component integration, often involving custom fixtures and robotic arms to enhance precision and efficiency.
Future Trends in Pick and Place and Assembly Technologies
Future trends in pick and place and assembly technologies emphasize increased automation through artificial intelligence and machine learning, enabling smarter and more adaptive manufacturing processes. Collaborative robots (cobots) are becoming more prevalent, enhancing precision and flexibility while improving safety in human-robot interactions. Your operations can benefit from these advancements by integrating vision systems and IoT connectivity to optimize efficiency and reduce downtime.
Pick and place vs Assembly Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com